What is Data Driven Testing: Types, Advantages, and More.
Testing applications with numerous input fields and scenarios can be quite challenging. Manually entering data for each test case is slow and prone to errors. Overlooking even one test case can result in bugs slipping through, and this can negatively impact user's experience and trust. So, is there a way to create tests where test data, input, and output values are read from external files? Yes, there is. You can use the Data Driven Testing.
Data driven testing lets testers use external data sources to test an application with multiple data sets. This type of software testing provides better test coverage and helps identify hidden issues.
Before diving further into the topic, let's go through the list of topics that we will cover in this piece.
Table of Content (TOC)
What is Data Driven Testing?
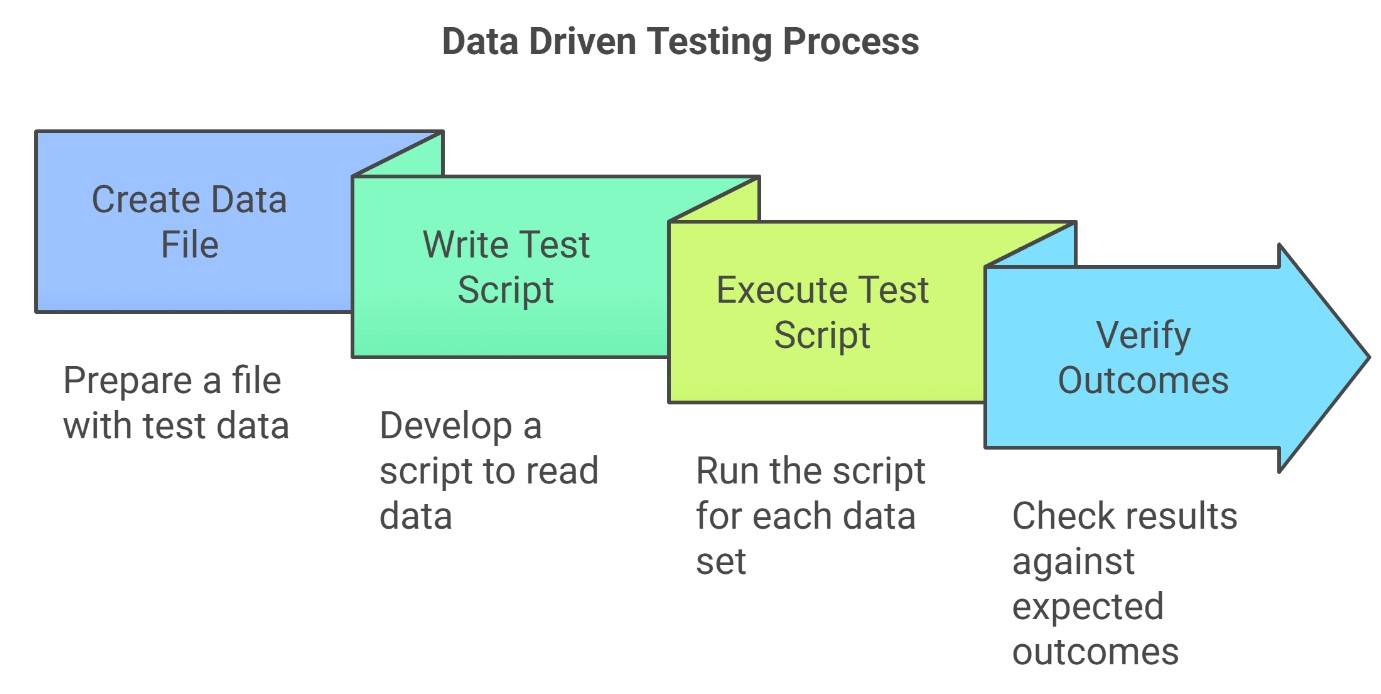
Data driven testing is a type of software testing technique where the same test script is run multiple times using different sets of input data stored in external files like - Excel, Text, CSV, or databases.
The process involves reading input data, running tests, comparing the actual results with expected outcomes, and repeating this for all data sets. This testing method ensures better test coverage, saves time, and allows for consistent and efficient testing. Data-driven testing works well with manual testing types like exploratory and functional testing. It helps automate repetitive tasks.
Best-suited Quality Assurance & Testing courses for you
Learn Quality Assurance & Testing with these high-rated online courses
How Does Data Driven Testing Work?
Let's understand how data-driven testing works using an example.
Data Driven Testing Example
Suppose you have to test a login feature of a website. The test checks if the system accepts valid credentials and rejects invalid ones. So, instead of writing separate test cases for each username and password combination, you decide to use data-driven testing.
Step 1: Create a file (Excel, CSV, etc.) with the following data:
| Username |
Password |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|
| Atul_001@gmail.com |
Password123 |
Success |
| Rashmi_002@gmail.com |
WrongPass |
Failure |
| Aquib_003@gmail.com |
|
Failure |
Step 2: Write a single test script that:
- Reads the data (username, password, and expected result) row by row from the file.
- Inputs the username and password into the login fields on the website.
- Submit the login form.
- Compares the actual result with the expected outcome (checking for a success message or error alert).
Step 3: Execute the test script
The test script will be executed multiple times, once for each row of data, and the application's behaviour will be verified.
Outcome
Using data driven testing, you tested all scenarios efficiently without manually rewriting or running tests for each data set. By doing so, you were able to save a lot of time and effort and reduce the chance of missing any scenario that can result in a bug.
What are the Different Types of Data Driven Testing?
There are mainly four types of data driven testing. Here are the details:
| Data Driven Testing Type |
Description |
|---|---|
| Keyword-Driven Testing |
Test scripts use keywords, and the data table specifies inputs and expected outcomes for each keyword. The test logic is separate from the data, enabling flexibility. |
| Excel-Driven Testing |
Test data is stored in Excel spreadsheets. Scripts read this data to run tests with different input sets. This method is easy to use and maintain. |
| Negative Testing |
Verifies how the application handles unexpected or invalid inputs. Test data includes incorrect values to ensure robust error handling. |
| XML-Driven Testing |
Test data is stored in XML files. Scripts read these files to execute tests with structured and complex data formats. Works well with hierarchical data. |
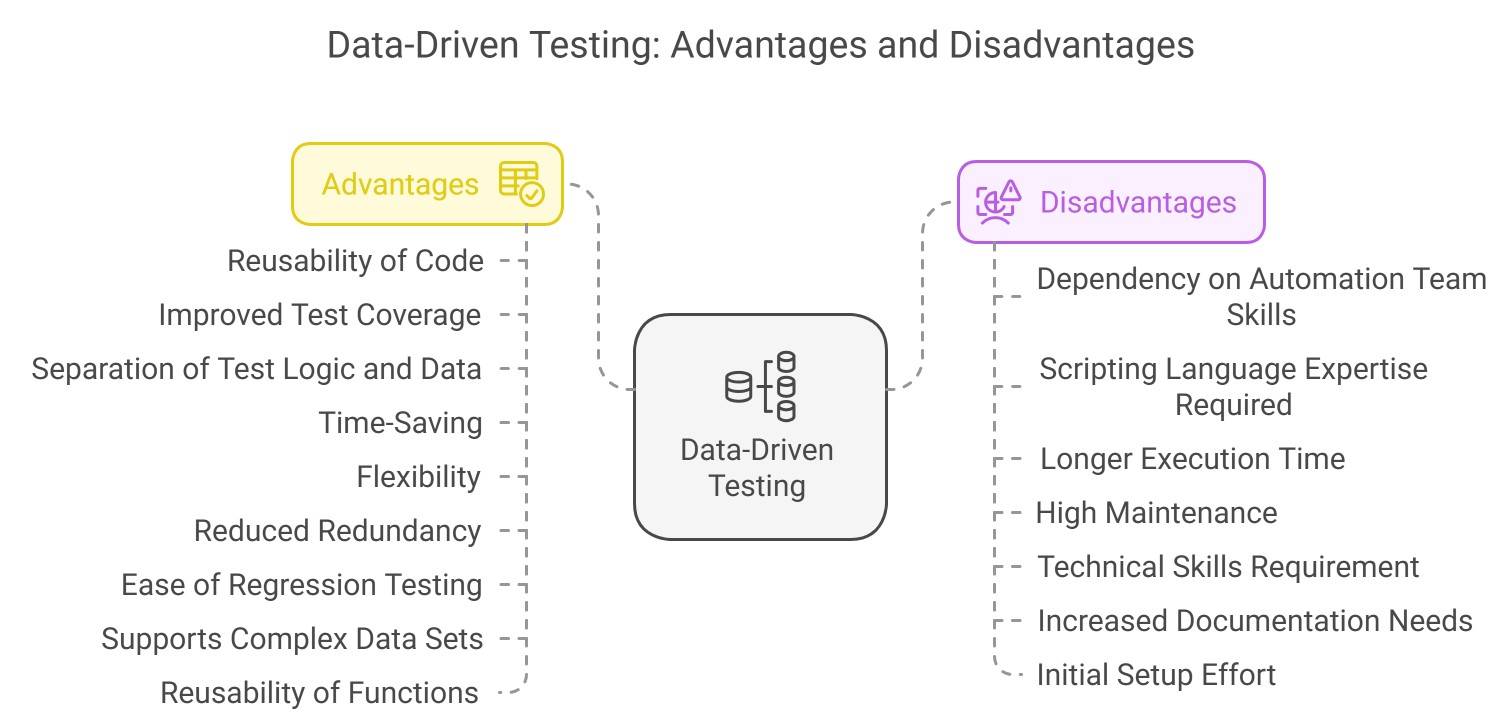
Advantages of Data Driven Testing
Here are data-driven testing advantages:
- Reusability of Code: Test scripts can be reused for multiple data sets, improving efficiency.
- Improved Test Coverage: Different data sets allow comprehensive testing of various scenarios.
- Separation of Test Logic and Data: Test logic is kept separate from test data, making it easier to manage and update.
- Time-Saving: Automated tools handle large volumes of test data, reducing manual effort.
- Flexibility: Requires less maintenance, ensuring easy adaptability for changes in applications.
- Reduced Redundancy: Eliminates duplication of test scripts, simplifying test management.
- Ease of Regression Testing: Simplifies retesting by using predefined data sets for validation.
- Supports Complex Data Sets: Can handle data from multiple sources like Excel, XML, or databases.
- Reusability of Functions: Common functions or actions can be reused in multiple test cases.
Disadvantages of Data Driven Testing
Here are data-driven testing disadvantages:
- Dependency on Automation Team Skills: Test quality relies heavily on the expertise of the automation team.
- Scripting Language Expertise Required: Testers need a strong knowledge of scripting languages.
- Longer Execution Time: Large data sets can lead to increased execution time.
- High Maintenance: Complex test scripts require regular maintenance and can be challenging to understand.
- Technical Skills Requirement: Testers must possess advanced technical skills and knowledge of automation tools.
- Increased Documentation Needs: Extensive documentation is required to manage test scripts and data.
- Initial Setup Effort: Significant effort is required to set up the framework and data files before testing.
Conclusion
Data driven testing is a powerful approach that enhances software testing efficiency by utilizing external data sources for a range of test cases. It offers significant advantages such as improved test coverage, reusability, and time savings. However, it also presents challenges, including dependencies on automation skills and potential maintenance complexities.
By understanding both its strengths and limitations, testing teams can leverage data-driven testing effectively to deliver more reliable software and enhance user experience.
FAQs Related to Data Driven Testing
What is Data driven testing in Selenium?
Data driven testing in Selenium is a technique where the same test script is executed multiple times with different sets of input data. In Selenium, this is typically done by reading test data from external sources like Excel, CSV, or databases.
The process involves:
- Reading input data (such as test cases and expected results).
- Running the same Selenium test with different data sets.
- Comparing the actual results with expected outcomes for each input set.
- Repeating the process for all data in the source file
What is data driven testing?
Data-driven testing, or DDT, is a software testing approach that utilizes external data sources such as databases, spreadsheets, or CSV files to store test data. This method avoids hardcoding data into the test cases, enabling the same test logic to run repeatedly with various data sets.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of data driven testing?
Data-driven testing (DDT) offers several advantages, such as the reusability of test scripts, efficiency in executing tests with various data sets, and improved test coverage. It simplifies maintenance by separating test data from the scripts, allowing for easy updates.
However, DDT also has its drawbacks. The initial setup can be complex and time-consuming, and managing external data sources may introduce additional overhead. It may not effectively handle complex logic testing, and the quality of test results heavily depends on the accuracy of the data used.