What is Footprinting in Ethical Hacking?
Footprinting in ethical hacking is the process of gathering information about a target system. It helps hackers understand the system's structure and identify potential vulnerabilities. This phase is crucial as it lays the groundwork for further penetration testing. Techniques include using search engines, social media, and network scanning tools.
We will go over footprinting in detail in this article, but first, let’s go over the topics we will be focusing on:
What is footprinting?
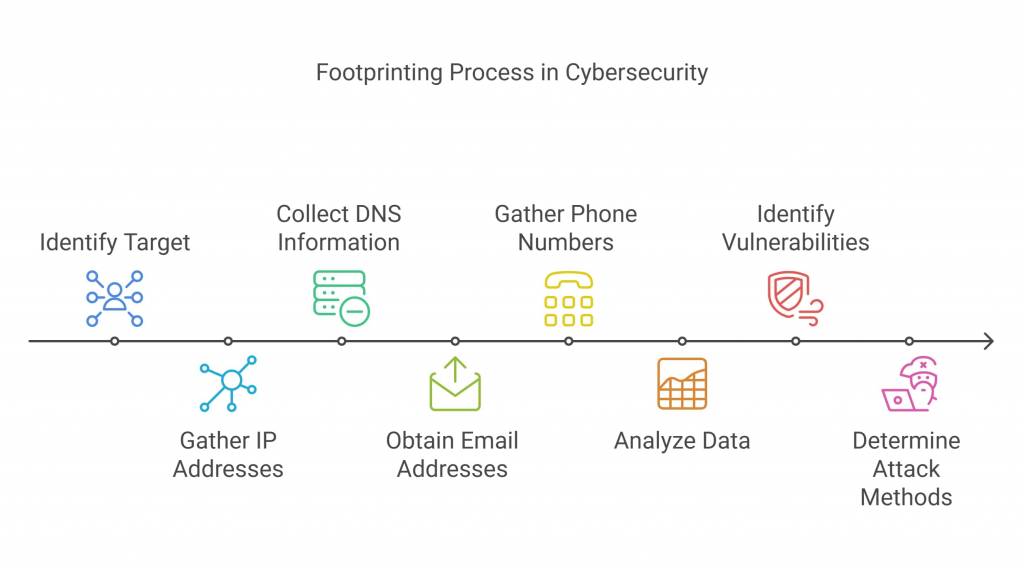
Footprinting is a technique for gathering as much information as possible about a targeted computer system, infrastructure, and network to identify opportunities to penetrate them. It is one of the most effective methods for identifying vulnerabilities.
When a hacker/ethical hacker uses the footprinting technique, he aims to collect data such as IP addresses, DNS information, email addresses, phone numbers, etc. Footprinting is the first step in which a hacker gathers as much information as possible to find ways to infiltrate a target system or, at the very least, determine which types of attacks are more appropriate for the target.

You can also explore- Who is an Ethical hacker?
Best-suited Ethical Hacking courses for you
Learn Ethical Hacking with these high-rated online courses
Types of footprinting
In ethical hacking, two main types of footprinting are:
Active: If you choose to perform active footprinting on a target system, you must be in direct contact with the target machine. However, it frequently triggers the target’s intrusion detection system (IDS), and successfully evading detection requires stealth and creativity. Overall, this type is quite risky.
Passive: You are not in direct contact with the target machine when using passive footprinting, as you are gathering information about a target far from you. It is a more stealthy approach because it does not trigger the target’s IDS and thus is less risky than active footprinting.
Let’s try to understand it using an example:
Passive information gathering includes reviewing a company’s website, whereas active information gathering includes trying to obtain access to classified data through social engineering.
What is the source of information gathered through footprinting?
There are many sources of information gathered during footprinting, such as:
- Social media: Most people release the majority of their information online. Hackers may create a fake account to appear natural to be added as friends or to follow someone’s account to steal their information.
- Using the “Who is” site: This website provides information about the domain name, email address, domain owner, and so on, but hackers use this information for personal gain.
- Social engineering: A vast range of malicious activities carried out through human interactions is collectively termed “social engineering.” It employs psychological manipulation to dupe users into making security errors or disclosing sensitive information.
- Job sites/advertisements: Many JOB websites, such as Naukri.com, for instance, this company might advertise: “Job Opening for Lighttpd 2.0 Server Administrator.” This information indicates that an organization is using the Lighttpd web server version 2.0, and hackers can use this information to their advantage.
- Neo Trace: This is a handy tool for obtaining path information. The graphical representation shows the path between you and the remote site, along with all intermediate nodes and their details, such as IP address, contact information, and location.
You can also explore- What is cybersecurity?
What kind of information can be gathered from footprinting?
A hacker can gather various types of information using this technique, such as:
- URLs
- VPN
- Firewall
- Email id
- Password
- IP address
- Network map
- Server configurations
- knowledge about the operating system of the target machine
- Knowledge about the security configurations of the target machine
Tools for footprinting
Here are some of the well-known tools:
- Harvester: It is an information-gathering tool that allows you to extract a specific target’s email address and subdomains. Harvester is written in Python and searches information from significant search engines such as Google, Yahoo, Bing, and others.
- Metagoofil: A hacker uses this tool to extract information or publicly available data on the internet.
- Sam Spade: It is compatible with all versions of Windows, beginning with Windows 95. This tool can perform extensive investigation and analysis in a short period. For example, it can determine who owns a specific IP address block to inspect the contents of a web page.
- Netifera: It is a powerful tool that provides a comprehensive platform for gathering information about the targeted website you wish to attack. It is a free tool included with the Backtrack Linux operating system.
- SuperScan: It allows you to scan a wide range of information processing addresses and TCP ports. It will check all ports or the ones you specify.
Advantages of footprinting
Some of the advantages are:
- Provides security framework knowledge: The data gathered will assist us in gaining an overview of the company’s security posture. For example, details about the presence of a firewall, application security configurations, and so on.
- Predictics the attack type: Footprinting assists in analyzing the vulnerabilities of the specific locations of the security framework. This helps analyze the types of attacks the system may be vulnerable to.
- Reduces the attack area: Helps to identify a specific range of systems and focus only on specific targets. This will significantly reduce the number of systems on which we will concentrate our efforts.
- Helps to draw network map: Assists in drawing a network map of the target organization’s networks. It also includes other information, such as the topology in use, trusted routers, server presence, and other information.
Preparing for an interview? Check out our top interview question and answer articles: Top Ethical Hacking Interview Questions and Answers
FAQs
What role does footprinting play in ethical hacking?
Footprinting is an ethical hacking technique that collects as much information as possible about a targeted computer system, infrastructure, and networks to identify opportunities to penetrate them.
What are the different types of footprinting?
There are two kinds of footprinting: active and passive.
What is the significance of footprinting?
The primary goals of footprinting are to learn, analyze, and identify security gaps.
What is the distinction between fingerprinting and footprinting?
Footprinting seeks a more comprehensive view of a system or network, whereas fingerprinting focuses more on a specific application or OS.
What is the purpose of footprinting in ethical hacking?
The purpose of footprinting in ethical hacking is to gather detailed information about a target system or organization. It includes identifying IP addresses, domain names, and network infrastructure. Knowing this information helps ethical hackers assess vulnerabilities and plan their testing strategies effectively, ultimately strengthening the target's security.
What tools are commonly used for footprinting?
Some of the common tools used for footprinting are:
- Nmap: A powerful network scanning tool that can discover hosts and services on a network.
- Maltego: A data mining tool that allows users to visualize relationships between data.
- Recon-ng: A web reconnaissance framework that provides various modules for gathering information.
- WHOIS Lookup: A tool for finding domain registration details and ownership information.
- Google Dorking: Using specific search queries on Google to extract sensitive information.
How does footprinting differ from other hacking techniques?
Footprinting differs from other hacking techniques as it focuses on information gathering rather than exploiting systems. In the initial phase, hackers collect data such as IP addresses, domain details, and network structures. Unlike active attacks, footprinting is a passive approach aimed at understanding a target without engaging directly.
What are the ethical considerations in footprinting?
Ethical considerations in footprinting include obtaining permission before probing a target system and ensuring that the data collected is used responsibly. Ethical hackers must respect privacy laws and regulations, avoiding any actions that could harm systems or data integrity. Transparency in intentions and confidentiality are also essential ethical practices.