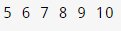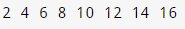How to use For Loop in C++
Loops are used to repeat the same, or similar code number of times. In this article we will discuss how to implement for loops in c++.
In the world of programming, loops are used to achieve efficient and sophisticated programs. In this article, we will discuss the For loop in C++. This loop repeatedly executes a block of statements in the code.
We will be covering the following sections today:
So, without further ado, let’s get started!
C++ For Loop
The C++ for loop is a repetition control structure that helps us create a loop that executes a piece of code repeatedly, as specified by the loop.
For Loop Syntax
Following is the syntax for a for loop in C++:
for (variable: collection) { body of the loop }
Here,
- Initialization – this expression initializes variable(s) and is executed only once.
- Condition – if the specified test condition is True, the body of the for loop is executed. In case the test condition returns False, the for loop is terminated.
- Update – this expression updates the value of initialized variables and then the condition is evaluated again.
Let’s look at the following illustration of the for loop flowchart –
Must Read: What is C++?
Must Check: C++ Online Courses &Certification
C++ For Loop Implementation Examples
Example 1:
#include \n \n <iostream>\n \n \n \n using namespace std;\n \n \n \n int main() {\n \n for (int i = 5; i <= 10; i++) {\n \n cout << i << " ";\n \n }\n \n return 0;\n \n }\n \n \n \n \n \n </iostream>
Output 1:

In the above example, we first initialize a variable i = 5. Then, we specify the condition i <= 10. The loop will run until the test condition holds True.
At last, we specify the update expression i++, which will increment the variable i by 1 during each iteration as long as the condition is True.
Let’s look at the following table to grasp how the loop works:
| Iteration | Initialization | Condition | Action and Update |
| 1st | i = 5 | True | 5 is printed. i incremented to 6. |
| 2nd | i = 6 | True | 6 is printed. i incremented to 7. |
| 3rd | i = 7 | True | 7 is printed. i incremented to 8. |
| 4th | i = 8 | True | 8 is printed. i incremented to 9. |
| 5th | i = 9 | True | 9 is printed. i incremented to 10. |
| 6th | i = 10 | True | 10 is printed. i incremented to 11. |
| 7th | i = 11 | False | The loop is terminated. |
Example 2:
Find the sum of n-natural numbers using for loop –
#include \n \n <iostream>\n \n \n \n using namespace std;\n \n \n \n int main() {\n \n int num, sum;\n \n sum = 0;\n \n \n \n cout << "Enter a positive integer: ";\n \n cin >> num;\n \n \n \n for (int i = 1; i <= num; ++i) {\n \n sum += i;\n \n }\n \n \n \n cout << "Sum: " << sum << endl;\n \n \n \n return 0;\n \n }\n \n \n \n \n \n </iostream>
Output 2:
In the above code, we have declared two variables num and sum = 0. The variable num takes a value from the user. This value will be the number up to which we want to find the sum of natural numbers.
- Then, we initialize the variable i = 1.
- Specify the test condition i <= num so the loop will run from 1 to num.
- Update expression is also specified as i++ so the value of i increments by 1 in each iteration
When i = 11, the condition returns False, the sum is printed: 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 = 21
And, the for loop terminates.
Must Read: Insertion in C++
Best-suited C++ courses for you
Learn C++ with these high-rated online courses
Range-Based For Loops
From C++ 11 onwards, a new range-based for loop has been introduced that works with collections such as arrays and vectors.
Its syntax is given below:
for (variable: collection) { body of the loop }
Here, for every element in the collection, the for loop is executed, and the element is assigned to the variable.
Let’s understand how this works through an example:
#include \n \n <iostream>\n \n \n \n using namespace std;\n \n \n \n int main() {\n \n int num_arr[] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16};\n \n \n \n for (int n : num_arr) {\n \n cout << n << " ";\n \n }\n \n \n \n return 0;\n \n }\n \n \n \n \n \n </iostream>
Output:
Here, we have used a range-based for loop to access all the elements in the array.
Must Read: Quicksort Algorithm in C++
Infinite For Loop
If the test condition in the for loop is always true, it will keep running infinitely until no memory is left. Look at the following example:
// infinite for loop
#include \n \n <iostream>\n \n \n \n using namespace std;\n \n \n \n int main() {\n \n \n \n for(int i = 1; i > 0; i++) {\n \n cout << i << " ";\n \n }\n \n \n \n return 0;\n \n }\n \n \n \n \n \n </iostream>
Output:
Must Read: if-else statement in C++
Conclusion
I hope this article was helpful for you in understanding how the for loop is implemented in C++. We also learned about range-based and infinite for loops in C++.

 Call 8585951111
Call 8585951111