Difference Between C and C++
The most important point of difference between C and C++ language is that C is procedural-oriented programming, and C++ is based on object-oriented programming methods.
Table of Content
- Key Difference Between C and C++
- Similarities Between C and C++
- What is C Programming Language?
- Features of C Programming
- Applications of C Programming
- Disadvantages of C Programming
- What is C++ Programming Language?
- Features of C++
- Applications of C++
- Disadvantages of C++
- Latest Development in C and C++ [updated Dec, 2023]
- C vs C++ which one should you learn first in 2024 and Why?
- C++ supports classes, which are a type of object that can be used to group data and methods. C does not support classes.
- C++ supports inheritance, which allows one class to inherit the properties of another class. C does not support inheritance.
- C++ supports polymorphism, which allows objects of different types to be treated similarly. C does not support polymorphism.
- C and C++, the code written by the programmer is transformed into machine code through a process called compilation. This process is handled by a program known as a compiler. The compiler takes the source code, analyses it, and then converts it into a machine-readable format, typically an executable file. This file can then be run directly on a computer's hardware.
- C++ is a more complex language than C. This is because C++ has more features, such as classes, inheritance, and polymorphism.
Let’s understand this in simple words:
| Feature | C | C++ |
|---|---|---|
| Development | Developed in 1972 by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Laboratories. | Developed by Bjarne Stroustrup at Bell Laboratories in the early 1980s. |
| Paradigm | Primarily procedural. Not object-oriented. | Supports both procedural and object-oriented programming. |
| Object-Oriented Programming | Does not support OOP features like polymorphism, encapsulation, and inheritance. | Supports OOP features like polymorphism, encapsulation, and inheritance. |
| Relationship | C++ is often considered a superset of C, but this is not strictly true due to some incompatible features. | Can use most of C's features but has additional features that are not compatible with C. |
| Keywords | Has a smaller set of keywords (around 32). | Has more keywords (63 in standard C++), including OOP-related ones. |
| Data Types | Supports basic built-in data types. | Supports both built-in and user-defined data types. |
| File Extension | Usually uses .c for source files. | Typically uses .cpp for source files. |
| Access Modifiers | Does not have access modifiers like public, private, protected | Has access modifiers: public, private, protected |
| Standard I/O Header | Uses <stdio.h> for standard I/O operations. | Uses <iostream> (without .h) for standard I/O operations. |
| Information Hiding | No inherent support for information hiding. | Supports information hiding through encapsulation. |
| Focus | More process or method-focused. | More data-focused, but also supports process-focused programming. |
| Exception Handling | Lacks direct support for exception handling. | Supports exception handling. |
| Standard I/O Operations | Uses scanf() and printf() for standard I/O. | Uses cin and cout for standard I/O, alongside C-style I/O. |
| Function & Operator Overloading | Does not support function or operator overloading. | Supports both function and operator overloading. |
| Main Function | The main() function cannot be called from other functions. | Similar to C, main() cannot be called from other functions. |
| Reference Variables | Does not support reference variables. | Supports reference variables. |
Best-suited C / C++ courses for you
Learn C / C++ with these high-rated online courses
When to use What - C vs C++
This table shows clear, beginner-friendly scenarios for choosing between C and C++, to illustrate the differences.
| Scenario | When to Use C | When to Use C++ |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Programming Basics | Use C to focus on basic concepts like variables, loops, and direct memory management in a simple way. | Use C++ if you also want to explore object-oriented ideas (classes, inheritance) while learning fundamentals. |
| Simple Command-Line Tools | Choose C for small tools that process text or numbers with straightforward, step-by-step code. | Choose C++ when you want to organize your code better using reusable components and libraries. |
| Basic Game Development | Use C if you want to understand low-level programming and optimise every bit of performance. | Use C++ to take advantage of libraries (like SDL or SFML) and classes for managing game objects easily. |
| Embedded Systems/IoT Projects | Use C on microcontrollers with very limited memory, where every byte counts. | Use C++ when the hardware supports it so you can benefit from cleaner code organisation with classes. |
| Desktop or GUI Applications | Use C when working with older, legacy code or when you need extremely optimised routines. | Use C++ to build modern desktop applications with graphical interfaces using rich libraries. |

Similarities Between C & C++
Some of the similarities in C and C++ programming languages are:
- Syntax: C++ is an extended version of C, therefore both have similar syntax, compilation and code structure.
- Keywords: Most of C’s keywords and operators are used in C++ and perform the same function.
- Execution: C and C++ both follow top-down execution of the code.
- Comment: Inline Comment in both C and C++ is marked by //.
- Multi-Dimensional Array: Both C and C++ support multi-dimensional arrays.
- Dynamic size Array: None of them support dynamic sized arrays.
- Statement Terminator: Both C and C++ uses semi-colon (;) for terminating a statement.
- Preprocessor Directive: #include is used in both C and C++ to include/import a header file.
Preparing for a C++ interview? Check out the Top C++ Interview Questions and Answers
What is C Programming Language?
For Dummies:
C Programming is a way to tell a computer what to do, step by step (procedural language). It was created in 1972 by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Laboratories to make writing computer programs—like the UNIX operating system—easier than writing in complex assembly language. Think of C as a recipe where each step is clearly laid out, making it easier to manage even when things get a bit tricky.
For Professionals:
C is a procedural programming language developed by Dennis Ritchie in 1972 at Bell Laboratories. It was created to rewrite the UNIX kernel in a higher-level language, reducing complexity while maintaining efficiency. Its simple yet powerful design makes it ideal for systems programming and performance-critical tasks.
Check out the best C Programming Courses
Also Read – Understanding Operators in C++
Features of C Programming
Listed below are some of the key features of C programming –
| Feature | Description/Example |
|---|---|
| Procedural Programming | C is designed to be easy to read and follow a logical sequence, which makes writing and debugging code straightforward. |
| Structured Language | It uses a clear, concise syntax with curly braces {} for code blocks and semicolons ; to end statements. |
| Portability | C programs can be easily adapted to run on different platforms like Windows, Linux, and macOS. |
| Low-Level Access | Provides direct access to hardware and the operating system—ideal for writing device drivers or system utilities. |
| Efficiency and Speed | As a compiled language, C converts code into machine language before execution, making it fast and efficient. |
| ANSI Standard | C is standardized by ANSI, ensuring that code remains consistent and portable across different systems. |
| Active Community | A large, active community offers abundant resources such as forums, tutorials, and documentation to help both beginners and professionals. |
| Dynamic Memory Allocation | Supports allocating memory during runtime, making it easier to manage memory usage in larger programs. |
| Pointer Support | Uses pointers to store memory addresses, allowing direct interaction with memory and enabling optimization and low-level hardware access. |
Applications of C Programming
- Operating System like UNIX, Microsoft Windows, are created in C.
- Mac OS X kernel was originally written in C.
- Majority of Adobe software like Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator, Adobe Premier are built using C, C++.
- Build code compilers such as MinGW, Dev-C, Clang C.
- Web Browsers like Mozilla, and Chrome, is designed using C programming.
- Games like Tic-Tac-Toe, Snake, Half-Life, Starcraft in built using C programming. In 2004, a high graphics FPS game Doom 3 was built using C for Windows.
- Apple’s Xcode IDE is written in C, C++, Objective-C and Objective-C++.
- The assembly language code of UNIX operating system’s was rewritten in C in 1972.
- Oracle database rewrote their assembly codes to C in 1983.
- In 1985, when Windows 1.0 was released, its kernel was primarily written in C and assembly.
- Several embedded systems like alarm clock, microwave, tv, remote controlled devices, etc are mostly built using C, embedded C.
Disadvantages of C Programming
- Does not support Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) features such as Polymorphism, Inheritance, and Encapsulation.
- The bugs are not detected after each line of code, instead it is detected after writing the entire program. This makes debugging in C difficult for complex programs.
- C does not support the concept of namespace, due to which two variables cannot be declared with same name.
- C does not Exception Handling which in other languages are used to detect the bugs and generate appropriate responses.
- C language has low level of abstraction. Due to this C has minimum data hiding and this affects the overall security of the language.
Learn more: Basics of C Programming Language
What is C++ Programming Language?
For Dummies
C++ is a computer language created in the early 1980s by Bjarne Stroustrup. It builds on the C language by adding features that let you organize code into “objects” (bundles of data and functions). This makes it easier to manage bigger projects. C++ lets you control how memory is used, so it runs very fast—perfect for creating high-performance programs. Plus, since it’s similar to languages like C# and Java, learning C++ can make it easier to pick up those languages later.
For Professionals
C++ is a high-level programming language developed in the early 1980s by Bjarne Stroustrup at Bell Laboratories. It extends the traditional C language with object-oriented programming capabilities and other enhancements, striking a balance between high-level abstractions and low-level control. This dual nature provides complete control over memory allocation and management, contributing to its reputation as one of the fastest programming languages available. Its similarities with C# and Java also facilitate a smoother transition for developers working across these languages.
Related Read – Binary Search in C++
Features of C++
Let's explore and understand different features of C++
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Object-oriented programming | Lets you organize code into "objects" using concepts like inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation to manage complex systems. |
| Templates | Provides reusable code blocks that let you create generic functions and data types, reducing code duplication. |
| Exception handling | Offers built-in mechanisms to catch and manage errors during program execution, improving reliability. |
| Function overloading | Allows multiple functions to have the same name with different parameters, making your code more intuitive. |
| Operator overloading | Lets you define how standard operators (like +, -, *) behave for custom data types. |
| Namespaces | Helps organize code into separate sections to avoid naming conflicts, especially useful in large projects. |
| Standard Template Library (STL) | A collection of pre-built templates and algorithms for common data structures and operations, speeding up development. |
| Compatibility with C | Fully supports C code and libraries, making it easy to integrate existing C projects into your C++ programs. |
Also Explore: C++ Online Courses & Certifications
Applications of C++
- Google used C++ to create several products like Google Earth, and the Google Chrome browser.
- Spotify one of the most popular audio streaming apps has its back end written in C++.
- Operating Systems like Windows, Mac, and Linux are built using C++.
- Mozilla Firefox used a subset of C++ (C++14) to build Mozilla 59.
- Microsoft products such as Word, Excel, and PowerPoint are written in both C and C++.
- One of the most powerful databases MySQL is written in both C and C++.
- At Microsoft code written for the – DirectX, Windows API, and .NET are all based on C++.
- Very popular games like Witcher 3, Counter-Strike, Doom III Engine, World of Warcraft, King Quest, Football Pro and Invictus are all written in C++ .
- A popular media player Winamp is developed using C++.
- MongoDB a popular open-source NoSQL database is written using C++.
- Unreal Engine for most graphic-intensive 2D, 3D, VR, AR, cross-platform, single-player, or multiplayer games primarily uses C++.
Disadvantages of C++
- For a beginner, C++ might be a relatively difficult language to learn and start with.
- Manual memory management in C++ is a hassle, as there is no garbage collection to automatically remove unwanted data.
- If you’re used to automated memory management, managing memory allocation manually can be a challenge.
- Not very secure because of pointers, global variables, etc.
- C++ does not support built-in code threads due to which the process is slower and complicated.
- The pointers in C++ take up more than the required memory which might not be suitable for some devices.
Understanding C vs C++ with Example
Simple Hello World in C
#include <stdio.h>
int main() { printf("Hello, world!"); return 0;}
Explanation: This C program demonstrates the basic structure of a C program, including the inclusion of a header file (stdio.h for standard input and output functions) and the main function, which is the entry point for C programs. It uses the printf function to print "Hello, world!" to the console.
C++ Program
#include <iostream>
int main() { std::cout << "Hello, world!" << std::endl; return 0;}
Explanation: This C++ program introduces the iostream library, which is used for input and output operations in C++. Instead of the printf function, it uses std::cout along with the insertion operator (<<) to output "Hello, world!" to the console. This example highlights the use of the C++ Standard Library and the shift towards using object-oriented syntax.
Example 2: Class and Object
C++ supports object-oriented programming (OOP), which allows for classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, encapsulation, and abstraction. C, being a procedural language, does not support these features directly. Below is an example to illustrate how C++ can utilise classes and objects, a feature not present in C.
C++ Version
#include <iostream>
class Greeter {public: void sayHello() const { std::cout << "Hello, world!" << std::endl; }};
int main() { Greeter greeter; greeter.sayHello(); return 0;}
Explanation: This C++ program defines a Greeter class with a public method sayHello() that prints "Hello, world!" to the console. An object of the Greeter class is created in the main function, and its sayHello method is called. This example demonstrates how C++ supports classes and objects, enabling the encapsulation of data and methods within an object.
Note for C:
Since C does not support classes and objects natively, achieving similar functionality would require the use of structures (struct) and function pointers to simulate object-oriented programming. However, this would be more complex and not as straightforward as in C++.
Example 3: Function Overloading
Function overloading, a feature of C++ that allows multiple functions to have the same name with different parameters, is another aspect that distinguishes C++ from C.
C++ Version
#include <iostream>
void print(int i) { std::cout << "Printing int: " << i << std::endl;}
void print(double f) { std::cout << "Printing double: " << f << std::endl;}
int main() { print(5); print(3.14159); return 0;}
Explanation: This C++ program showcases function overloading by defining two print functions, one taking an int parameter and the other a double. Depending on the argument type, the appropriate print function is called in the main function. This feature enhances flexibility and readability in C++ programs.
Note for C:
C does not support function overloading. Each function in a C program must have a unique name. To achieve similar functionality, you would need to define functions with different names (e.g., printInt, printDouble).
These examples should provide a clear contrast between C and C++, showcasing the simplicity and procedural nature of C against the more complex, object-oriented, and feature-rich capabilities of C++.
Latest Update from C and C++ [updated March,25]
As of March 25, 2025, the C programming language continues to be a significant force in the world of programming. According to the latest TIOBE Index, C is ranked as the second most popular programming language with a rating of approximately 11.50%. This slight change from previous months highlights the enduring relevance of C in various fields, particularly in systems programming and embedded systems.
Below is a concise, forward‐looking comparison table outlining the latest updates in C (via the upcoming C23) and C++ (with the major leaps in C++20 and emerging refinements in C++23). This table highlights the core aspects that both beginners and seasoned professionals should know. Note that while beginners can get started with the improved, clearer syntax and more consistent libraries, professionals can leverage advanced compile‐time features, modules, and parallelism to build high-performance systems. Check it out:
| Aspect/Feature | C Updates (C23) | C++ Updates (C++20/23) | For Beginners | For Professionals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Release | C23 brings a cleaner syntax, enhanced standard library functions, and better Unicode support. | C++20 has revolutionized modern C++, with C++23 offering incremental improvements and critical fixes. | Learn which standard to target and enjoy more consistent language behavior. | Plan migration strategies and exploit modern features to future-proof large codebases. |
| Library Improvements | New utility functions, improved string/mathematical operations, and better time libraries. | Introduction of ranges, calendars, coroutines, and an overall more powerful STL. | Benefit from simpler APIs and consistent library functions. | Use higher-level abstractions to optimize performance and improve reliability in production. |
| Language Features | Minor enhancements like improved macro handling and better error reporting are on the horizon. | Major features: modules for better code organization, concepts for template constraints, and coroutines. | Get acquainted with modern syntax and better error messages. | Utilize advanced metaprogramming and robust compile-time checks to write safer, more efficient code. |
| Compile-Time Evaluations | Enhanced macro capabilities pave the way for more robust static analysis. | Expanded constexpr use lets you perform complex computations at compile time for safer, faster code. | Start exploring compile-time evaluations early—it’s like debugging the future! | Leverage compile-time computations to optimize critical paths and catch issues before runtime. |
| Concurrency & Parallelism | Incremental improvements in multithreading support and atomic operations. | Native support for parallel algorithms and a more robust concurrency model streamline high-performance code. | Gain a basic understanding of concurrent programming with clearer, standardized constructs. | Fine-tune high-performance applications with better thread support and parallelism capabilities. |
While these updates aren’t exactly “overnight miracles,” they represent a significant step toward more maintainable, efficient, and modern coding practices. In short, beginners get a smoother ride into the world of C and C++, and professionals are armed with the tools to push the limits of performance and reliability.
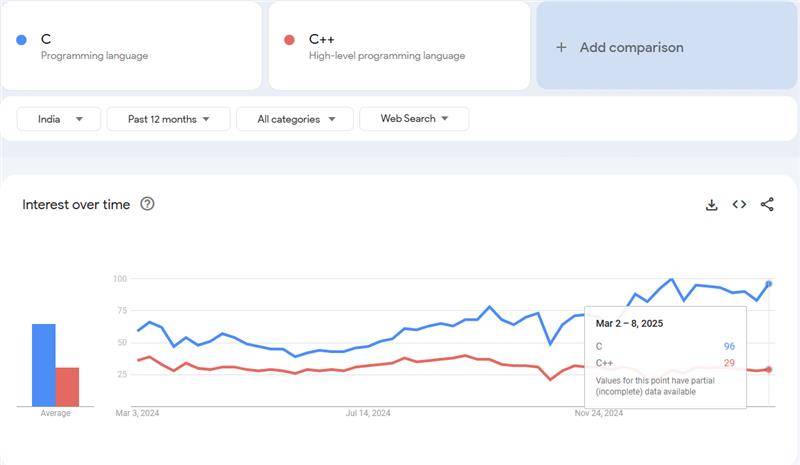
Google Trends Comparison - C vs C++
Over the past year in India, “C” consistently ranks higher in search volume than “C++,” often by a ratio of about 2–3 to 1. This gap is fairly stable, possibly because “C” is commonly taught first in schools and the single-letter term captures broader searches. Meanwhile, “C++” maintains steady interest, especially for competitive programming, game development, and advanced systems, even though it trails “C” in overall search frequency.
C vs C++ which one should I learn first in 2025 and Why?
If you’re completely new to programming, starting with C can be a smart move because it teaches the fundamentals—like memory management, pointers, and low-level operations—in a straightforward way that builds a solid foundation. However, if you’re aiming for modern software development (think game development, high-performance applications, or embedded systems), learning modern C++ first might be more beneficial since it combines C’s power with advanced features like object-oriented programming, templates, and a rich standard library. In 2025, your choice should align with your career goals, but many experts suggest beginning with C to grasp the basics and then transitioning to C++ to leverage its modern, safer, and more expressive capabilities.
- Start with C if you’re completely new to programming to build a strong foundation, then transition to C++ for modern development. C's simpler syntax and procedural nature make it easier to grasp foundational programming concepts.
- If you already have programming experience or aim for modern application development, starting with C++ might be more beneficial.
Recommended Online C Programming and C++ Course for you:
C Programming For Beginners - Master the C Language
- Rating: 4.4 out of 5 (33,049 ratings) 150,317 students - Bestseller on Udemy
- Created by: Tim Buchalka's Learn Programming Academy, Jason Fedin.
Beginning C++ Programming - From Beginner to Beyond
- Rating: 4.6 out of 5 (65,711 ratings) 283,072 students
- Created by: Tim Buchalka's Learn Programming Academy, Dr. Frank Mitropoulos
Conclusion
In conclusion, C and C++ are two very different programming languages that have their own unique features and characteristics. The main difference between C and C++ is that C is function-driven procedural language with no support for objects and classes, whereas C++ is a combination of procedural and object-oriented programming languages. Ultimately, the choice between C and C++ depends on the specific needs and goals of your project, and it is important to carefully consider the trade-offs between the two languages before making a decision. We hope this blog helped you understand the features, applications, disadvantages, and differences between C and C++ to decide which language is more suitable for your projects.
Recommended Reads:
- Difference between Python and Java
- Difference between JavaScript and Java
- Difference between Jupyter Notebook and Python IDLE
- Difference between C and Java
- Difference between C and Python
- Difference between C++ and Java
- Difference between HTML and CSS
- Difference between Float and Double
FAQs
What is the difference between C and C++?
The main difference between C and C++ is that C is a procedural programming language that does not support classes and objects. On the other hand, C++ is an extension of C programming with object-oriented programming (OOP) support.
Is C and C++ a compiled or interpreted language?
C and C++ are both compiled languages. This means that code written in C or C++ is transformed by a compiler into machine code that can be executed directly by a computer's hardware, rather than being interpreted at runtime. In contrast, interpreted languages are executed by an interpreter, which reads and executes the source code directly, translating it into machine code on the fly. Compiled languages typically offer faster execution times compared to interpreted languages because the compilation step is done beforehand, optimizing the code for execution.
C and C++ are considered compiled languages due to their language design and the process used to convert code written in these languages into executable programs. Here's a detailed explanation:
-
Compilation Process: In compiled languages like C and C++, the code written by the programmer is transformed into machine code through a process called compilation. This process is handled by a program known as a compiler. The compiler takes the source code, analyses it, and then converts it into a machine-readable format, typically an executable file. This file can then be run directly on a computer's hardware.
-
Direct Execution: The executable file generated by the compiler contains machine code that is specific to the target platform's hardware architecture. This allows the program to be executed directly by the computer's CPU. This direct execution by the hardware makes programs written in compiled languages like C and C++ generally faster and more efficient compared to those that are interpreted at runtime.
-
No Intermediate: Unlike interpreted languages, where code is executed on the fly via an interpreter, compiled languages do not require an intermediary at runtime. Once the compilation is complete, the source code is no longer needed for execution. This direct translation to machine code and the absence of an interpreter at runtime contribute to the efficiency and speed of compiled languages.
-
Optimization Opportunities: During the compilation process, the compiler can also perform various optimizations to improve the performance and efficiency of the generated machine code. These optimizations can include removing unnecessary code, optimizing loops, and other improvements that can make the final executable program run faster and use resources more effectively.
-
Static Typing: Both C and C++ are statically typed languages, which means the types of variables are known at compile time. This allows for type checking and other analysis to be done during the compilation process, further contributing to the efficiency and correctness of the final executable.
Which programming language to learn first C or C++?
C is a good option for those who want to learn systems-level programming. After gaining familiarity with procedural programming in the C language, you can move on to learning C++. If you are already familiar with OOP concepts or have some knowledge of Java, it will be better to learn C++ first.
Is C still used in 2023?
C is one of the oldest programming languages and is still used by many developers and companies today. It is majorly used for low-level developments such as operating systems and hardware.
Where are C and C++ used?
C is used in the areas where low-level programming languages are required. C programming is used in operating systems, embedded devices, OS kernels, drivers, IoT applications, and more. C++ is widely used for creating graphics-heavy software, game engines, VR applications, and web browsers.
Should I learn Python or C?
In terms of syntax, Python is easier to learn as it has more English-like syntax and a few keywords compared to C programming. Python programs are easy to understand, read, and write. In terms of performance or speed, C programming is more suitable as Python is slower than C.
Can C code be used in C++?
Yes, C code can be used in C++. C++ is designed to be backward-compatible with C, so you can use most C code in a C++ program. However, there are some differences in syntax and semantics, so you may need to make some changes to the code in order to use it in a C++ program.
Can I learn C++ without C? Is C++ hard to learn?
Yes, we can easily learn C++ without understanding C. C is a subset of C++, even if you skip learning C, you will anyways come across the C language while learning C++.
Which is faster C or C++?
Actually, this is dependent on the feature. For example, if we used object-oriented programming features like virtual functions in our C++ program, this program is sure to be slower since there are always extra efforts necessary to maintain virtual tables and other virtual function details. However, if we use standard C++ capabilities, this C++ program and any other C program will run at the same pace. As a result, it is dependent on elements such as the application we are producing, the features we are using, and so on.
What are the advantages of C over C++?
C is a simpler language than C++, which makes it faster and more efficient. C also has a smaller runtime library and produces smaller executables. In addition, C code is more portable than C++ code, since it is less likely to depend on specific features of a particular compiler or operating system.
What are the advantages of C++ over C?
C++ includes features for object-oriented programming that are not available in C, which makes it more flexible and powerful for certain types of applications. C++ also includes features for exception handling, templates, and namespaces, which can make code more modular and easier to maintain.
Comments
(2)

 Call 8585951111
Call 8585951111