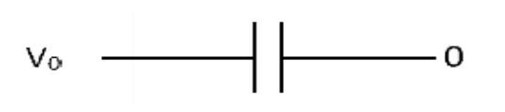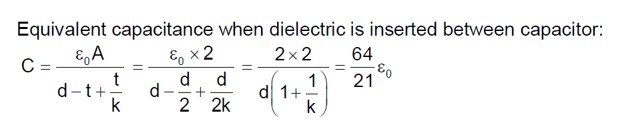Electrostatics
Get insights from 79 questions on Electrostatics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Electrostatics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Heat loss; ΔH = U? - U? = 1/2 (C? / (C? +C? ) (V? -V? )²
= 1/2 * (5*2.5)/ (5+2.5) (220-0)²µJ
= 5/ (2*3) * 22*22*100*10? J
= 5*11*22/3 * 10? J = 1210/3 * 10? J = 1210/3 * 10? ³ J * 4 * 10? ²
According to questions
x/100 = 4*10? ²
So, x=4
Note: But given answer by JEE Main x=36
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
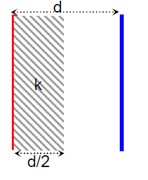
Before inserting slab
C_i = ε? A/d
After inserting dielectric slab
C_i = ε? lw/d
C_f = C? + C?
C_f = (Kε? A? /d) + (ε? A? /d)
C_f = 2C_i ⇒ (Kε? wx/d) + (ε? w (l-x)/d) = 2ε? lw/d
4x + l - x = 2l
x = l/3
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
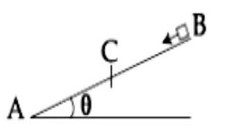
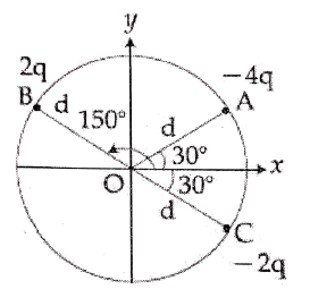
Potential of centre, = V =
Vc = K (Σq)/R
Vc = K (0)/R = 0
Electric field at centre E_B = E_B = ΣE
Let E be electric field produced by each
charge at the centre, then resultant electric field will be
Ec = 0, since equal electric field vectors are acting at equal angle so their resultant is equal to zero.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Enet = Eo/k
Enet = E_free - E_bound = qf/Aε? - qb/Aε?
Eo = qf/Aε?
So, (qf-qb)/Aε? = qf/ (kAε? )
qf - qb = qf/k
qb = qf (1 - 1/k)
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
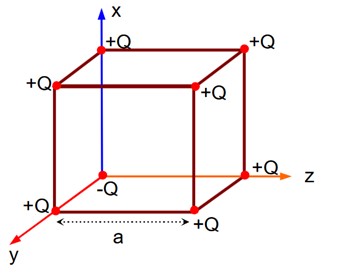
If charge (-Q) at origin is replaced by (+Q), then electric field at the centre of the cube is zero. Thus, electric field at the centre of the cube is as if only (-2Q) charge is present at the origin.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
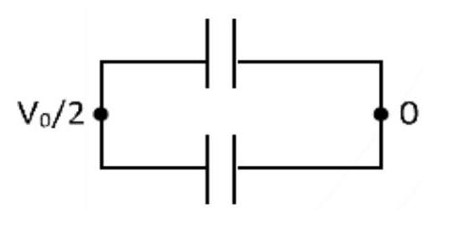
When connected in series, equivalent capacitance,
When connected in parallel, equivalent capacitance
C2 = C + C = 2C
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
(A) If is the velocity of light
so, (Energy of photon)
(B) Velocity of photon is equal to velocity of light i.e. c.
(C)
(D) In photon-electron collision both total energy and total momentum are conserved.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers