Physics Electromagnetic Waves
Get insights from 81 questions on Physics Electromagnetic Waves, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Electromagnetic Waves
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
The EM waves originate from an accelerating charge. The charge moving with uniform velocity produces steady state magnetic field.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
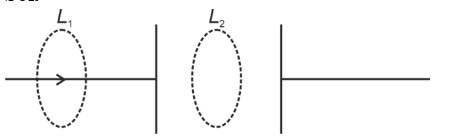
According to modified Ampere's law
For Loop and
For Loop and
Due to
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
So, E0 = B0 C
= 2 * 10-8 * 3 * 108
= 6v/m
Direction will be along z – axis
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Work done is equal to change in K.E.
W1 -> work done by mg
W2 -> work done by air friction
W2 = -0.68 mgh
New answer posted
5 months agoNew answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
E = (50 N/s) sin
Energy 5.5 * 10-12 J., vol v =?
energy density
=
= 497
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
