Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Seven
Get insights from 30 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Seven, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Seven
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The moment of inertia of the object I = r2 [sum of moment of inertia of each constituents particles]
All the mass in a cylinder lies at a distance R from the axis of symmetry but most of the mass of a solid sphere lies at a smaller distance than R.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When the vertical height of the objects is very small as compared to the earth's radius we call the objects small, otherwise it is extended. Building and ponds are small objects and deep lake and ocean are examples of extended objects.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
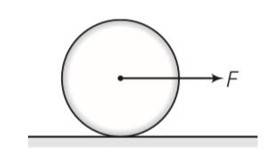
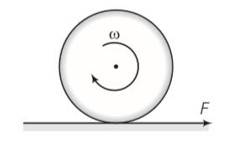
Frictional force f is acting in the opposite direction of F . let the acceleration of centre of mass of disc be a then
F-f=Ma where M is the mass of the disc
fR= (1/2 MR2)
so fR= (1/2MR2) (a/R)
Ma=2f
From the above equation
F = F/3
F< =
f/3 <
F=3
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
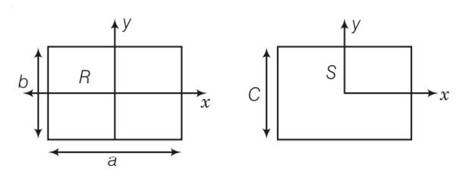
area of square = area of rectangular plate
C2=a b
(a)
here bxR
(b) here a>c so IyR>IyS
(c) IzR-IzS +2ab= (a-b)2
(IzR-IzS)>0
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Situation as given below
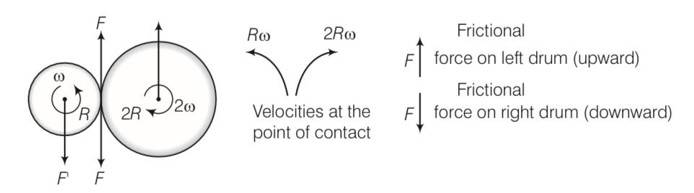
(b) F' =F=F'' where F' and F'' are external forces through support.
So Fnet=O
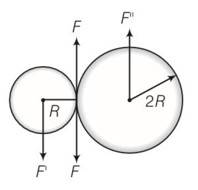
External torque = F (anticlockwise)
(c) Let w1 and w2 be the final angular velocities of smaller and bigger drum in both clockwise and anticlockwise . finally there will be no friction
hence Rw1=2Rw2
so
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Before being bought in contact with the table the disc was in pure rotational motion. Hence Vcm=0
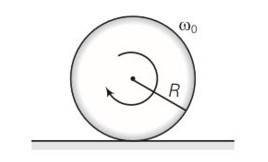
(b) when the disc is placed in contact with table due to friction centre of mass acquires some linear velocity.
(c) when the rotating disc is placed in contact with the table due to friction centre of mass acquires some linear velocity.
(d) friction is responsible for the effects ib b and c
(e) when rolling starts Vcm=wR
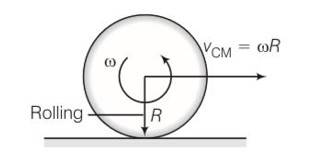
(f) time period for rolling to begin is t=
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) yes the law of conservation of angular momentum can be applied because there is no net external torque on the system of the two discs.
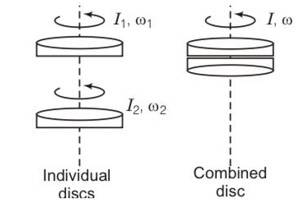
External forces gravitation and normal reaction act through the axis of rotation, hence produce no torque.
(b) by conservation of angular momentum
Lf= Li
Iw=I1w1+I2w2
So w=
(c) Kf=
Kf= ½ (I1w12+I2w22)
Kf-Ki =- 2<0
(d) hence there is loss of KE of the system. The loss of kinetic energy is mainly due to work against the friction.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
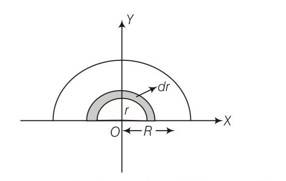
let M and R be mass and radius of half disc , mass per unit area of half disc
So m =
(a) the half disc be supposed to be consist of a large number of semicircular ring of mass dm and thickness dr and radii ranging from r=0 to r=R.
surface area of semicircular ring of radius r and thickness dr =
so mass of the elementary ring dm =
dm=
if x,y are coordinates of centre of mass of this element,
then (x,y)=(0,2r/ )
so x=0 and y =2r/
let xcm and ycm be the coordinates of the centre of mass of the semicircular disc
so xcm=
Ycm=
= 0R
= 4R/3
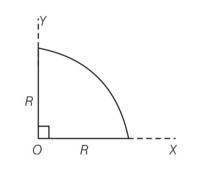
Centre of mass of a uniform quar
New question posted
7 months agoTaking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers