physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
x (t)=A+B
Let A>B and
Now velocity is equal to x (t)=dx/dt=-B
So a (t)= dv/dt= B
Above condition are satisfied by the equation.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) The equation we use here is x= 1-sint
So velocity = dx/dt=1-cost
Acceleration =sint
When t=o x=o
When t=, x=
When t=0.x= 2
(b) x=sint so velocity becomes v=cost as displacement and velocity contain sin and cos so equation is periodic.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If effect of gravity is neglected then ball moving uniformly turned back with same speed when a ball hit it. Acceleration of the ball is zero just before it hits the bat and due to the repulsive force it gets accelerated.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
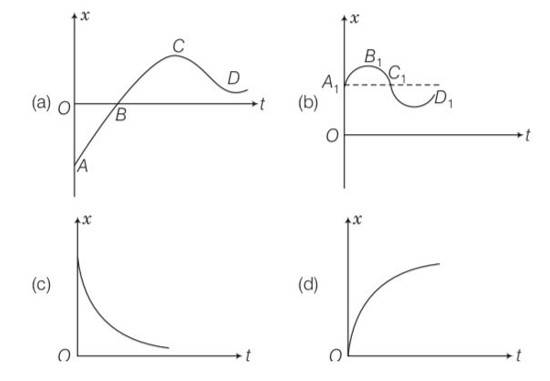
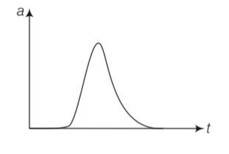
We have to analyse slope of each curve i.e= dx/dt . for peak values dx/dt will be zero as x is maximum at peak points.
For graph (a) there is appoint for which displacement is zero so a matches with (iii)
In graph b, x is positive throughout and at point B, V=dx/dt=0
Since at point of curvature changes a=0, so b matches with (ii)
displacement is zero in only first graph so it matches with the (iii) point.
And slope of d graph v=dx/dt is positive so v>0 so acceleration will be negative so matches with I but in graph c it matches with iv as its slope is negative.
New question posted
7 months agoNew answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
let speed of two balls be V1and V2
Where v1=2v and v2=v and y1and y2 be the distance covered
So y1= and y2=
So y1-y2= 15
V2=
So clearly we can say v1=20 and v2=10
And y1=20m and y2=5m
If t2 is the time taken by ball 2 through a distance of 5m, y2=v2t-1/2gt2
5=10t2-5t22 so t2 will be 15
Then time covered by ball 1 in 2 sec between two throws = t1-t2= 2-1=1s
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) for maximum velocity dv/dt=0
d/dt (6t-2t2)=0
6-4t=0 t= 6/4=1.5s
(b) v=6t-2t2
ds/dt=6t-2t2
ds=6t-2t2dt
distance in 3s, S= 30
s= 27-18=9m
average velocity = distance /time =9/3 = 3m/s
x= 6t-2t2
3=6t-2t2
After solving we get t= 9/4s approx.
(c) in periodic motion when velocity is zero
0=6t-2t2
0=t (6-2t)
So t=0, 3 sec
(d) distance covered from 0 to 3s=9m
distance covered in 3 to 6s=
S= (18t- )6
S= 108-9 (18)+
S= -4.5m
So total distance covered = 9+ (-4.5)=4.5m
No of cycles covered in that distance =20/4.5=4.44approx
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
speed of car and truck = 72km/h = 72 (5/18) =20m/s
V= u+at
0=20+a (5) so a=-4m/s2
But retarted acceleration will be v=u+at
0=20+a (3)
So a= -20/3m/s2
We also need to consider human response time = 0.5 s
V=u-at (for retarded motion)
V= 20- ….1
Vt=20-4t ….2
From 1 and 2
20-=20-4t
After solving we get t= 5/4s
Distance travelled by truck in time t, S=ut+1/2at2
= 20
To avoid the bump onto the truck car must maintain distance = 23.125-21.875=1.250m
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) velocity attained by a falling rain drop will be =
=
(b) diameter of the rain drop = 2r=4mm
Radius = 2mm= 2
Mass of rain drop = V
Momentum of rain drop= mv= 3.4
(c) time ,t = d/v=
(d) force exerted, F = change in momentum /time=
(e) area =
number of drops striking the the umbrella with separation of 5
so net force =
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b, d) We know that one light year = 9.46 = distance that light travels in 1 year with a speed 3 m/s
1 par sec =3.08 = distance at which average radius of earth's orbit subtends an angle of par second.
Here second and year represent time.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers