Physics Ncert Solutions Class 12th
Get insights from 1.2k questions on Physics Ncert Solutions Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Ncert Solutions Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
9.1 Size of the candle, h = 2.5 cm
Let the image size be = h'
Object distance, u = 27 cm
Radius of curvature of the concave mirror, R = 36 cm
Focal length of the concave mirror, f = = 18 cm
Image distance = v
The image distance can be obtained by using mirror formula: = +
= =
v = −54 cm
Therefore, the screen should be placed 54 cm away from the mirror to obtain a sharp image.
The magnification of the image is given as:
m = =
h' = = = - 5 cm
The height of the candle's image i
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ans.1.10 Electric dipole moment, p = 4
C m
Angle made by p with a uniform electric field, = 30
Electric field, E = 5 N
Torque acting on the dipole is given by = pE = 4 5
= 1 Nm
Therefore, the magnitude of the torque acting on the dipole is Nm
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.9
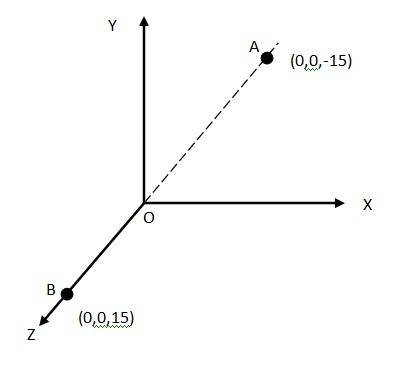
At A, the amount of charge,
At B, the amount of charge,
= –2.5
Total charge of the system, q =
+
Distance between two charges at point A and B = 15 + 15 = 30 cm = 0.3 m
Electric dipole moment of the system is given by p =
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.8 (a) The situation is represented in the following figure.
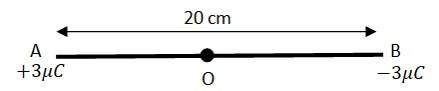
O is the midpoint of AB, hence OA = OB = 10 cm = 10
The electric field at O caused by the charge at A is given by
where
Net electric field at point O, E =
=5.39
(b) A test charge of amount 1.5
So the force experienced by the test charge, F = q
= 1.5
N = 8.088
N
This force is directed along the line OA, this is because th
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.7
(a) An electrostatic field line is a continuous curve because a charge experiences a continuous force when traced in an electrostatic field. The field line cannot have sudden breaks because the charge moves continuously and does not jump from one point to another.
(b) The electric field intensity will show two directions at that point where two filed lines crosses. This is not possible. Hence they do not cross.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.6
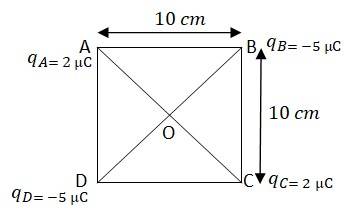
In the adjoining figure ABCD is a square with sides AB = BC = CD = DA = 10 cm
Diagonals, AC = BD =
AO = OC = DO = BO =
At the centre of the square ABCD, O, a charge of 1
The force of repulsion between the charges placed at A and at O is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction between the charges placed at point C and centre O. Similarly ,the force of attraction between the charges placed at B & O and D & O will be equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. These charges will cancel each other.
Hence, the net charge at centre O will be zero.
Here is a deeper explanation.
What you just saw is the us
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ans.1.5 When two bodies are rubbed against each other, it produces charges of equal magnitude in both the bodies but of opposite in nature. Hence the net charges of the two bodies are zero. When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, similar phenomena occur. This is as per the law of conservation of energy.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.4
(a) Electric charge of a body is quantized, this means that only integers (1,2,3, ….n) number of electrons can be transferred from one body to the other. Charges are not transferred in fraction. Hence, a body possesses total charge only in integers.
(b) In macroscopic i.e. large scale charges, the charges used are huge as compared to the electric charge of electrons or protons. Therefore, it is ignored and it is considered that electric charge is continuous.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.3 The units of the given equation
e = Electric charge in C
k =
G = Gravitational constant = N
Therefore
So the given equation is dimensionless
We have the following values
e = 1.6
G = 6.67
The numerical value of this ratio is given by
= 2.284
New answer posted
9 months agoBeginner-Level 5
The Davisson-Germer experiment was conducted to test the De-broglie hypothesis and know wave nature of electrons. In this experiment, a beam of electrons was emitted from an electron gun with known acceleration to strike a nickel crystal placed inside a vacuum chamber.
After striking the surface, electrons are scattered from the crystal surface at different angles. The diffraction pattern obtained through this experiment was similar to that produced by X-rays, which is wave.
The Davisson-Germer experiment provided the first experimental proof of the wave nature of matter and de Broglie's hypothesis right.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
