Mechanical Properties of Solids
Get insights from 66 questions on Mechanical Properties of Solids, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Mechanical Properties of Solids
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Length of steel cable l=9.1m
Radius r= 5mm=
Tension in the cable F =800N
Young's modulus of steel Y= 2
So
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Bulk modulus of rubber is 9.8*108 N/m2
density of sea water is 103 kg m-3
percentage decrease in volume
Let the rubber ball be taken up to depth h.
Change in pressure =h g
Bulk modulus K=
So h =
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Young's modulus of steel Y= 2
Coefficient of thermal expansion = 10-5
Length =1m
Area = 10-4m2
Increase in temperature t= 2000C
Tension produced in steel rod F = YA =2
= 4
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Young's modulus Y=
For first wire Y=
For second wire Y=
From above equations
So l=l' hence Y will also same.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Young's modulus Y=
For a perfectly rigid body change in length
Y= so young's modulus for perfectly rigid body is infinite
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Work done =1/2F l
As spring of both are equally compressed
So Young's modulus Y= as is inversely proportional to young's modulus
And also we know W is inversely proportional to young's modulus
So
Wsteel
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
stress=
Therefore stress is scalar quantity not vector quantity.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Young's modulus Y= stress/longitudinal strain
For same longitudinal strain,
Ysteel>Yrubber
so we can say that stresssteel > stressrubber
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
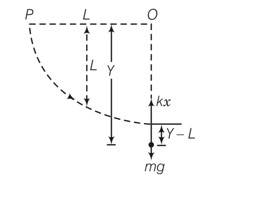
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Till the stone drops through a length L it will be in free fall. After that the elasticity of the spring will force it to a SHM. Let the stone come to rest instantaneously at y.
The loss in PE of the stone is the PE stored in the stretched string .
Mgy=1/2 k(y-L)2
Mgy =
=
Y=
b)in SHM the maximum velocity is attained when the body passes through the equilibrium position i.e when instantaneous acceleration is zero. That is mg-kx=0
so mg=kx
from the conservation of energy
mg=kx
x=mg/k
v2=2gL+mg2/K
v= (2gL+mg2/K)1/2
c)when stone is at lowest position i.e at instantaneo
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Consider the diagram according, the bending torque on the trunk of radius r of the tree =
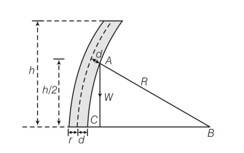
When the tree is about to buckle Wd=
If R>>h, then the centre of gravity is at a height l
From 2+ (h/2)2
If d <2+
So d = h2/8R
If wo is the weight /volume
h= ( )1/3r2/3
critical height = h= ( )1/3r2/3
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers