Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Five
Get insights from 90 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Five, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Five
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
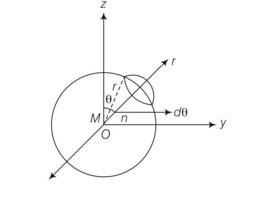
Explanation- magnetic moment of dipole at origin o is
M=Mk
Magnetic field induction at p due to dipole moment
B= r
dS= r(rsin )r = (r2 sind )
= r(r2sin )
{cos4 }
(1-1)= 0
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
Explanation- When a diamagnetic material is dipped in liquid nitrogen, it again behaves as a diamagnetic material. Thus, superconducting material will again behave as a diamagnetic material. When this diamagnetic material is placed near a bar magnet, it will be feebly magnetised opposite to the direction of magnetising field.
(i) Thus, it will be repelled.
(ii) Also its direction of magnetic moment will be opposite to the direction of magnetic field of magnet.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation - = I/H
Diamagnetism is due to orbital motion of electrons in an atom developing magnetic moments opposite to applied field. Thus, the resultant magnetic moment of the diamagnetic material is zero and hence, the susceptibility χ of diamagnetic material is not much affected by temperature.
Paramagnetism and ferromagnetism is due to alignments of atomic magnetic moments in the direction of the applied field. As temperature is raised, the alignment is disturbed, resulting decrease in susceptibility of both with increase in temperature.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- density of nitrogen = 28g/22.4L= 28g/22400cc
density of copper = 8g/22.4L= 8g/22400cc
on comparing = = 1.6 10-4
= = 5 10-4
As we know
= 1.6 10-4
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- M (intensity of magnetisation) = 106A/m
Length = 10cm = 10 10-2= 0.1m
M= Im/l
Im= M l= 106 0.1 = 105A
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – M= or M 1/m
= = <<1
Mp<
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- as we know n = L/2
Magnetic moment of circle = m1= n1IA1= L.I .2/2 R = LIR/2………(1)
Magnetic moment of square = m2= n2IA2= .I.a2= Lia/4…………….(2)
Moment of inertia of circle = MR2/2…………….(3)
Moment of inertia of square = Ma2/12…………….(4)
Frequency of circle f1= 2
Frequency of square f2= 2
As f1=f2
2 =2
So m2/m1= I2/I1
From eqn 1,2,3 and 4
=
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- P is also on the magnetic equator, so the angle of dip= 0, because the value of angle of Dip at equator is zero. Q is also on the magnetic equator, thus the angle of dip is zero.
As earth tilted on its axis by 11.3°, thus the declination at Q is11.3°.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- as is dimensionless quantity , it should have no involvement of charge Qin its dimensional formula
Let
[ ]= [ML ]
= [ ]
After solving we get a=-1 , b= 0, c =-1
Putting these values in equations
By using their standard values we get =10 which proves it is dimensionless quantity
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- the magnetic field induction at a pojnt z distance from dipole moment is
B=
Along z axis from p to q
=
=
=
(b) the point A lies on the equatorial line of the magnetic dipole of moment Msin
B= dl= Rd
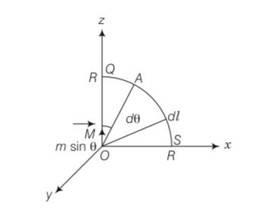
Circular arc = =
(c) along x axis over the path ST
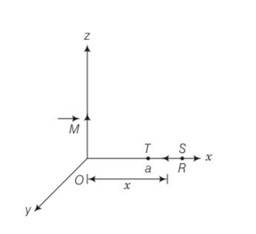
From figure every point lies on the equatorial line of magnetic dipole so
B= the value of B is zero as the angle between M and dl is 90
(d)along the quarter circle TP of radius a
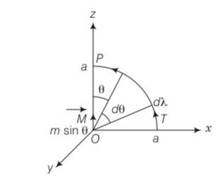
B along circular arc d
B =
Net magnetic field through PQST is zero
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers