Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12 Chapter Five Magnetism And Matter offers great practice material to deepen your understanding of the main concepts of Ch 5 Physics Class 12. It also helps in improving teaching/learning qualities in schools. By practicing these questions, the students will understand how magnetic forces operate in various artificial and natural systems. This exemplar provides a wide range of numerical, conceptual, and application-based problems to boost students' problem-solving and analytical skills.
Students can also download the Magnetism and Matter Class 12 PDF from here and practice it offline at their convenience time without the need for any internet connection. The PDF has all types of questions, including Multiple Choice Questions, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, and Long Answer Type Questions. All are important for an overall understanding of the chapter.
Students can use this exemplar for self-assessment and quick revision. It saves a lot of time as it offers exam-focused preparation. It also prepares them for the entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
For quick revision of Class 11 and Class 12, do check out - NCERT Notes for Class 11 & 12.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Five Magnetism And Matter
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Magnetism and Matter Multiple Choice Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Magnetism and Matter Long Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Magnetism and Matter Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Magnetism and Matter Very Short Answer Type Questions
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 5 NCERT Exemplar
- JEE Mains 2022
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Five Magnetism And Matter
One of the biggest benefits of downloading the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Five is that you can study it from anywhere and you do not need internet connectivity. Whether one is traveling, at home, or at school, one can revise the concepts by practicing the questions. It is based on the CBSE curriculum. It ensures that students focus on exam-related topics like Earth’s magnetism, magnetic dipoles, and magnetization. By offering a mix of various types of questions, it provides clarification of core concepts. Using the PDF, students can practice and revise the questions repeatedly.
Students should also practice the Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter NCERT Solutions. It will help them to further understand the concepts.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Magnetism and Matter Multiple Choice Questions
The following are the MCQs related to Class 12 Physics Chapter 5
| 1. Verify the Ampere’s law for magnetic field of a point dipole of dipole moment m = mk . Take C as the closed curve running clockwise along . (i) The z-axis from z = a > 0 to z = R; (ii) Along the quarter circle of radius R and centre at the origin, in the first quadrant of x-z plane; (iii) Along the x-axis from x = R to x = a, and (iv) along the quarter circle of radius a and centre at the origin in the first quadrant of x-z plane. |
| Explanation- the magnetic field induction at a pojnt z distance from dipole moment is B= Along z axis from p to q = = = (b) the point A lies on the equatorial line of the magnetic dipole of moment Msin B= dl= Rd |
| 2. What are dimensions of , the magnetic susceptibility ? consider an hydrogen atom. Gives an expression for χ, upto a constant by constructing a quantity of dimensions of χ, out of parameters of the atom e,m,v,R and μ0. Here, m is the electronic mass, v is electronic velocity, R is Bohr radius. Estimate the number so obtained and compare with the value of ∣χ∣∼10−5 for many solid materials. |
| Explanation- as is dimensionless quantity , it should have no involvement of charge Qin its dimensional formula Let [ ]= [ML ] = [ ] After solving we get a=-1 , b= 0, c =-1 Putting these values in equations
By using their standard values we get =10 which proves it is dimensionless quantity |
| 3. Assume the dipole model for earth’s magnetic field B which is given by BV = vertical component of magnetic field = BH = Horizontal component of magnetic field = θ = 90° – lattitude as measured from magnetic equator. Find loci of points for which (i) |B| is minimum; (ii) dip angle is zero; and (iii) dip angle is ± 45°. |
| Explanation- Bv= BH= adding and squaring both equations we get Bv2+BH2= B= = 1/2 The value of B is minimum if cos (b) tan = 2cot For dip angle is zero cot =0 and = (c) tan if angle of dip is 45 tan so Bv=BH 2cot =1 Cot =1/2 and tan = 2 So tan-12 |
| 4. Consider the plane S formed by the dipole axis and the axis of earth. Let P be a point on the magnetic equator and in S. Let Q be the point of intersection of the geographical and magnetic equators. Obtain the declination and dip angles at P and Q. |
| Explanation- P is also on the magnetic equator, so the angle of dip= 0, because the value of angle of Dip at equator is zero. Q is also on the magnetic equator, thus the angle of dip is zero. As earth tilted on its axis by 11.3°, thus the declination at Q is11.3°. |
Commonly asked questions
A toroid of n turns, mean radius R and cross-sectional radius a carries current I. It is placed on a horizontal table taken as xy-plane. Its magnetic moment m
(a) Is non-zero and points in the z-direction by symmetry
(b) Points along the axis of the toroid (m = m?)
(c) Is zero, otherwise there would be a field failing as 1/r3 at large distances outside the toroid
(d) Is pointing radially outwards.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (c)
Explanation- magnetic field outside the toroid is inversely proportional to distance
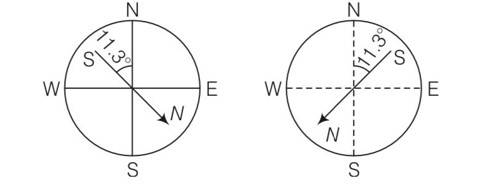
The magnetic field of the earth’ can be modelled by that of a point dipole placed at the centre of the earth. The dipole axis makes an angle of 11.3° with the axis of the earth. At Mumbai, the declination is nearly zero. Then
(a) The declination varies between 11,3°W to 11.3°E
(b) The least declination is 0°
(c) The plane defined by dipole axis and the earth axis passes through Greenwich
(d) Declination averaged over the earth must be always negative
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a)
Explanation- for the earth's magnetism, the magnetic field lines of the earth resemble that of a hypothetical magnetic dipole located at the centre of earth.
The axis of the dipole not coincide with the axis of rotation of the earth but is presently tilted 11.30 with respect to the later or it is either towards east or towards west
In a permanent magnet at room temperature,
(a) Magnetic moment of each molecule is zero
(b) The individual molecules have non-zero magnetic moment which are all perfectly aligned
(c) Domains are partially aligned
(d) Domains are all perfectly aligned
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (d)
Explanation- the individual atoms in a ferromagnetic material possess dipole moment as in a paramagnetic material.
However they interact with one another in such a way that they spontaneously align themselves in a common direction over a microscopic volumes called domain. Thus they align perfectly.
Consider the two idealised systems (i) A parallel plate capacitor with large plates and small separation and (ii) A long solenoid of length L>>R, radius of cross-section. In (i) E is ideally treated as a constant between plates and zero outside. In (iii) Magnetic field is constant inside the solenoid and zero outside. These idealised assumptions, however, contradict fundamental laws as below:
(a) Case I contradicts gauss’s law for electrostatic fields
(b) Case ii contradicts gauss’s law for magnetic fields
(c) Case(i) agrees with
(d) Case(ii) contradicts with en
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (b)
Explanation- as gauss’s law states = q/ 0 for electrostatic field. It does not contradicts for electrostatic fields as the electric field lines do not form continuous closed path
According to gauss’s law in magnetic field
=0
It contradicts for magnetic field, because there is a magnetic field inside the solenoid and no field outsid the solenoid carrying current but the magnetic field lines from the closed path.
A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of 8 Am-1 when placed in an external magnetic field of 0.6 T at a temperature of 4 K. When the same sample is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.2 T at a temperature of 16 K, the magnetisation will be
(a) 32/3 Am-1 (b) 2/3 Am-1
(c) 6 Am-1 (d) 2.4 Am-1
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (b)
Explanation- as curie law explains B
1 =8Am-1, B1= 0.6T, t1=4K
B2= 0.2T, t2=16K
So after solving we get I2= 2/3Am-
S is the surface of a lump of magnetic material.
(a) Lines of B are necessarily continuous across S
(b) Some lines of B must be discontinuous across S
(c) Lines of H are necessarily continuous across S
(d) Lines of H cannot all be continuous across S
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (a, d)
Explanation – magnetic field lines for magnetic induction B form continuous lines. So lines of B are necessarily continuous across S.
Also H varies inside and outside. So lines of H cannot all be continuous across S
The primary origin(s) of magnetism lies in
(a) Atomic currents
(b) Pauli exclusion principle
(c) polar nature of molecules
(d) Intrinsic spin of electron
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a, d)
Explanation- The primary origin of magnetism lies in the fact that the electrons are revolving and spinning of an atom, which gives rise to current called atomic current.
This atomic current gives rise to magnetism. The revolving and spinning about nucleus of
An atom is called intrinsic spin of electron.
A long solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 1 A. It has a soft iron core of μr = 1000. The core is heated beyond the Curie temperature, Tc.
(a) The H field in the solenoid is (nearly) unchanged but the B field decreases drastically
(b) The H and B fields in the solenoid are nearly unchanged
(c) The magnetisation in the core reverses direction
(d) The magnetisation in the core diminishes by a factor of about 108
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a, d)
Explanation- for solenoid H=nI
H= 1000 1= 1000 Am
Thus H is a constant, so it is nearly unchanged
B= n I
So B
( )m)fero = 103
( )m)para = 10-5
= = 108
Essential difference between electrostatic shielding by a conducting shell and magnetostatic shielding is due to
(a) Electrostatic field lines can end on charges and conductors have free charges
(b) Lines of B can also end but conductors cannot end them
(c) Lines of B cannot end on any material and perfect shielding is not possible
(d) Shells of high permeability materials can be used to divert lines of B from the interior region
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a, c, d)
Explanation- Electrostatic shielding is the phenomenon to block the effects of an electric field. The conducting shell can block the effects of an external field on its internal content or the effect of an internal field on the outside environment.
Magnetostatic shielding is done by using an enclosure made of a high permeability
magnetic material to prevent a static magnetic field outside the enclosure from reaching
objects inside it or to confine a magnetic field with in the enclosure.
Let the magnetic field on the earth be modelled by that of a point magnetic dipole at the centre of the earth. The angle of dip at a point on the geographical equator (a) Is always zero (b) Can be zero at specific points (c) Can be positive or negative (d) Is bounded
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (b, c, d)
Explanation- If the total magnetic field of the earth is modelled by a point magnetic dipole at the centre, then it is in the same plane of geographical equator, thus the angle of dip at a point on the geographical equator is bounded in a range from positive to negative value.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Magnetism and Matter Long Answer Type Questions
See the questions below:
Commonly asked questions
Verify the Ampere’s law for magnetic field of a point dipole of dipole moment m = mk . Take C as the closed curve running clockwise along .
(i) The z-axis from z = a > 0 to z = R;
(ii) Along the quarter circle of radius R and centre at the origin, in the first quadrant of x-z plane;
(iii) Along the x-axis from x = R to x = a, and (iv) along the quarter circle of radius a and centre at the origin in the first quadrant of x-z plane.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- the magnetic field induction at a pojnt z distance from dipole moment is
B=
Along z axis from p to q
=
=
=
(b) the point A lies on the equatorial line of the magnetic dipole of moment Msin
B= dl= Rd
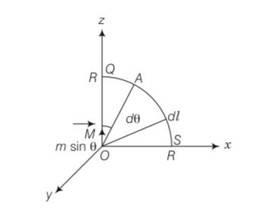
Circular arc = =
(c) along x axis over the path ST
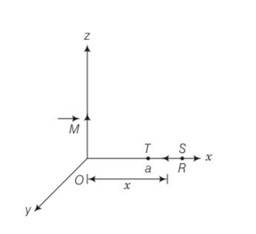
From figure every point lies on the equatorial line of magnetic dipole so
B= the value of B is zero as the angle between M and dl is 90
(d)along the quarter circle TP of radius a
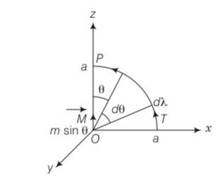
B along circular arc d
B =
Net magnetic field through PQST is zero
What are dimensions of , the magnetic susceptibility ? consider an hydrogen atom. Gives an expression for χ, upto a constant by constructing a quantity of dimensions of χ, out of parameters of the atom e,m,v,R and μ0?. Here, m is the electronic mass, v is electronic velocity, R is Bohr radius. Estimate the number so obtained and compare with the value of ?χ?∼10−5 for many solid materials.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- as is dimensionless quantity , it should have no involvement of charge Qin its dimensional formula
Let
[ ]= [ML ]
= [ ]
After solving we get a=-1 , b= 0, c =-1
Putting these values in equations
By using their standard values we get =10 which proves it is dimensionless quantity
Assume the dipole model for earth’s magnetic field B which is given by
BV = vertical component of magnetic field =
BH = Horizontal component of magnetic field = θ = 90° – lattitude as measured from magnetic equator.
Find loci of points for which (i) |B| is minimum; (ii) Dip angle is zero; and (iii) Dip angle is ± 45°.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Bv=
BH= adding and squaring both equations we get
Bv2+BH2=
B= = 1/2
The value of B is minimum if cos
(b) tan = 2cot
For dip angle is zero
cot =0 and =
(c) tan if angle of dip is 45
tan so Bv=BH
2cot =1
Cot =1/2 and tan = 2
So tan-12
Consider the plane S formed by the dipole axis and the axis of earth. Let P be a point on the magnetic equator and in S. Let Q be the point of intersection of the geographical and magnetic equators. Obtain the declination and dip angles at P and Q.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- P is also on the magnetic equator, so the angle of dip= 0, because the value of angle of Dip at equator is zero. Q is also on the magnetic equator, thus the angle of dip is zero.
As earth tilted on its axis by 11.3°, thus the declination at Q is11.3°.
There are two current carrying planar coil made each from identical wires of length L. C1is circular (radius R) and C2 is square (side a). They are so constructed that they have same frequency of oscillation when they are placed in the same uniform B and carry the same current. Find a in terms of R.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- as we know n = L/2
Magnetic moment of circle = m1= n1IA1= L.I .2/2 R = LIR/2………(1)
Magnetic moment of square = m2= n2IA2= .I.a2= Lia/4……………..(2)
Moment of inertia of circle = MR2/2……………..(3)
Moment of inertia of square = Ma2/12…………….(4)
Frequency of circle f1= 2
Frequency of square f2= 2
As f1=f2
2 =2
So m2/m1= I2/I1
From eqn 1,2,3 and 4
=
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Magnetism and Matter Short Answer Type Questions
Find below the questions with solutions:
Commonly asked questions
Use (i) The Ampere’s law for H and (ii) Continuity of lines of B, to conclude that inside a bar magnet, (a) Lines of H run from the A-pole to S-pole, while (b) Lines of B must run from the S-pole to A-pole
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- in the given figure let C be the amperian loop then,
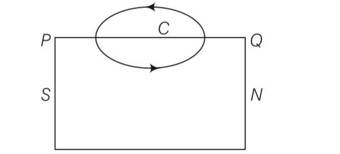
= .dl
between B and dl is less than 90 degree so
= . dl>0
So magnetic field from south pole to north pole inside the bar magnet
So according to ampere law
=0
= + = 0
>0, so <0,
It will be so if the angle between H and dl is more than 90 degree so cos is negative . it means H must run from north to south pole .
A bar magnet of magnetic moment M and moment of inertia 1 (about centre, perpendicular to length) is cut into two equal pieces, perpendicular to length. Let T be the period of oscillations of the original magnet about an axis through the mid-point, perpendicular to length, in a magnetic field B. What would be the similar period T for each piece?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- I= moment of inertia of the bar magnet
m= mass of bar magnet
l= length of magnet about an any passing through its centre and perpendicular to its
length
M= magnetic moment of the magnet
B= uniform magnetic field in which magnet Is oscillating
T= 2
I= ml2/12
When magnet is cut into two equal pieces
I1= = ml2/96= I/8
Magnetic dipole moment M’= M/2
Its time period oscillation is T’= 2 = 2 =
Suppose we want to verify the analogy between electrostatic and magnetostatic by an explicit experiment. Consider the motion of (i) Electric dipole p in an electrostatic field E and (ii) Magnetic dipole M in a magnetic field B. Write down a set of conditions on E, B, p, M so that the two motions are verified to. be identical. (Assume identical initial conditions).
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-
From these two we can say that
=
pE= MB
E=cB
pcB=MB
p=M/c
Three identical bar magnets are rivetted together at centre in the same plane as shown in figure. This system is placed at rest in a slowly varying magnetic field. It is found that the system of magnets does not show any motion. The north-south poles of one magnet is shown in the figure. Determine the poles of the remaining two
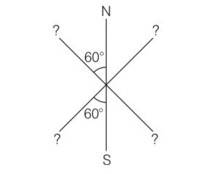
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- the system will be in stable equilibrium if the net force on the system is zero and net torque on the system is also zero.
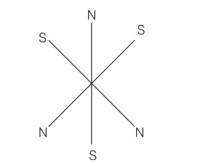
Verify the Gauss’s law for magnetic field of a point dipole of dipole moment m at the origin for the surface which is a sphere of radius R.
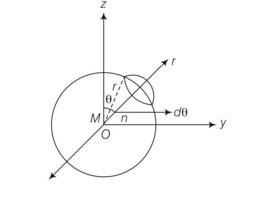
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- magnetic moment of dipole at origin o is
M=Mk
Magnetic field induction at p due to dipole moment
B= r
dS= r(rsin )r = (r2 sind )
= r(r2sin )
{cos4 }
(1-1)= 0
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Magnetism and Matter Very Short Answer Type Questions
Here are the questions:
Commonly asked questions
A proton has spin and magnetic moment just like an electron. Why then its effect is neglected in magnetism of materials?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – M= or M 1/m
= = <<1
Mp<
A permanent magnet in the shape of a thin cylinder of length 10 cm has M = 106A/m. Calculate the magnetisation current IM.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- M (intensity of magnetisation) = 106A/m
Length = 10cm = 10 10-2= 0.1m
M= Im/l
Im= M l= 106 0.1 = 105A
Explain quantitatively the order of magnitude difference between the diamagnetic susceptibility of N2 (~5 X 10-9) (at STP) and Cu (~10-5).
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- density of nitrogen = 28g/22.4L= 28g/22400cc
density of copper = 8g/22.4L= 8g/22400cc
on comparing = = 1.6 10-4
= = 5 10-4
As we know
= 1.6 10-4
From molecular view point, discuss the temperature dependence of Susceptibility for diamagnetism, paramagnetism and ferromagnetism.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation - = I/H
Diamagnetism is due to orbital motion of electrons in an atom developing magnetic moments opposite to applied field. Thus, the resultant magnetic moment of the diamagnetic material is zero and hence, the susceptibility χ of diamagnetic material is not much affected by temperature.
Paramagnetism and ferromagnetism is due to alignments of atomic magnetic moments in the direction of the applied field. As temperature is raised, the alignment is disturbed, resulting decrease in susceptibility of both with increase in temperature.
A ball of superconducting material is dipped in liquid nitrogen and placed near a bar magnet.
(i) In which direction will it move?
(ii) What will be the direction of its magnetic moment?
Explanation- When a diamagnetic material is dipped in liquid nitrogen, it again behaves as a diamagnetic material. Thus, superconducting material will again behave as a diamagnetic material. When this diamagnetic material is placed near a bar magnet, it will be feebly magnetised opposite to the direction of magnetising field.
(i) Thus, it will be repelled.
(ii) Also its direction of magnetic moment will be opposite to the direction of magnetic field of magnet.
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 5 NCERT Exemplar
The following are the important formulas of Chapter 5:
Magnetic Dipole Moment
Torque on a Magnetic Dipole in a Uniform Magnetic Field
Potential Energy of a Magnetic Dipole
Magnetic Field Due to a Magnetic Dipole on the Axis
Magnetic Field Due to a Magnetic Dipole on the Equatorial Line
Gauss’s Law for Magnetism
Magnetic Susceptibility
Magnetic Permeability
Relation Between Relative Permeability and Susceptibility
Earth’s Magnetic Field Components
Magnetic Moment of Electron
To get the notes of Physics, Chemistry and Maths, students should read the NCERT Solutions Class 11 and 12.
JEE Mains 2022
JEE Mains 2022
Commonly asked questions
The bulk modulus of a liquid is 3 × 1010 Nm-2. The pressure required to reduce the volume of liquid by 2% is :
We know,
Given below are two statements : One is labeled as Assertion (A) and the other is labeled as Reason (R). (Magnetism)
Assertion (A) : In an uniform magnetic field, speed and energy remains the same for a moving charged particle.
Reason (R) : Moving charged particle experiences magnetic force perpendicular to its direction of motion.
Work done in magnetic field zero.
Two identical cells each of emf 1.5 V are connected in parallel across a parallel combination of two resistors each of resistance 20Ω . A voltmeter connected in the circuit measures 1.2 V. The internal resistance of each cell is :
Eeq = E = 1.5 v
req =
12 + 0.6r = 15
0.6r = 3
Identify the pair of physical quantities which have different dimensions
A projectile is projected with velocity of 25m/s at an angle θ with the horizontal. After t seconds its inclination with horizontal becomes zero. If R represents horizontal range of the projectile, the value of θ will be :
[Use g = 10 m/s2]
T = 2t =
R = u cos θ (T)
cot θ =
A block of mass 10 kg, starts sliding on a surface with an initial velocity of 9.8 ms-1. The coefficient of friction between the surface and block is 0.5. The distance covered by the block before coming to rest is :
[used g = 9.8 ms-2]
a µg = 0.5 × 9.8 = 4.9 m/sec2
u = 9.8 m/sec
S =?
v = 0
v2 = u2 + 2as
s =
A boy ties a stone of mass 100 g to the end of 2 m long string and whirls it around in a horizontal plane. The string can withstand the maximum tension of 8 N. If the maximum speed with which the stone can revolve is rev. /min. The value of K is :
(Assume the string is massless and unstretchable)
By N L M : T sin θ = - (1)
& R = sin θ - (2)
From (1) & (2)
And,
A vertical electric field of magnitude 4.9 × 105 N/C just prevents a water droplet of a mass 0.1 g from falling. The value of charge on the droplet will
(Given g = 9.8 m/s2)
qE = mg
q = 2 × 10-9 C
A particle experiences a variable for in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force is Newton. if the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane, then kinetic Energy changes by :
= 6 + 19 = 25 J
The approximate height from the surface of earth at which the weight of the body becomes of its weight on the surface of earth is :
[Radius of earth R = 6400 km and
1 +
h = 0.732 × 6400
= 4684.8 km » 4685 km
A resistance of 40Ω is connected to a source of alternating current rated 220 V, 50 Hz. Find the time taken by the current to charge from its maximum value to the rms value :
Let l = l0 cos wt
l = l0, at t1 = 0
&
= 0.25 × 10-2
t2 = 2.5 ms
The equations of two waves are given by :
These waves are simultaneously passing through a string. The amplitude of the resulting wave is :
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in a medium of relative permeability 1.61 and relative permittivity 6.44. If magnitude of magnetic intensity is 4.5 × 10-2 Am-1 at a point, what will be the approximate magnitude of electric field intensity at that point ?
(Given : Permeability of free space µ0 = 4p × 10-7 NA-2, speed of light in vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
Velocity of wave in a medium =
E = vB = 0.931 × 108 × 1.61 × 4p × 4.5 × 10-9
= [0.931 × 1.61 × 4p × 4.5] × 10-1
= 8.476
» 8.476 v m-1
Choose the correct option from the following options given below :
According to Rutherford, e- revolves around in nucleus in circular orbit. Thus e- is always accelerating (centripetal acceleration). An accelerating change emits EM radiation and thus e- should loose energy and finally should collapse in the nucleus.
Nucleus A is having mass number 220 and its binding energy per nucleon is 5.6 MeV. It splits in two fragments ‘B’ and ‘C’ of mass numbers 105 and 115. The binding energy of nucleons in (B) and ‘C’ 6.4 MeV per nucleon. The energy Q released per fission will be :
Q = 176 MeV
A baseband signal of 3.5 MHz frequency is modulated with a carrier signal of 3.5 GHz frequency using amplitude modulation method. What should be the minimum size of antenna required to transmit the modulated signal?
Baseband Signal frequency 3.5 MHz
& Carrier signal frequency = 3.5 GHz
=
Size of antenna =
= 21.4 mm
A cornot engine whose heat sinks at 27°C has an efficiency of 25%. By how many degrees should the temperature of the source be changed to increase the efficiency by 100% of the original efficiency?
0.25 = 1 -
0.25 = 1 -
T1 = 400 k
Now, efficiency increases by 100%
= 0.25 × 2
= 0.50
0.50 = 1 -
(600 – 400) = 200 k or 200° C
A parallel plate capacitor is formed by two plates each of area 30πcm2 separated by 1 mm. A material of dielectric strength 3.6 × 107 Vm-1 is filled between the plates. If the maximum charge that can be stored on the capacitor without causing any dielectric breakdown is 7 × 10-6 C, the value of dielectric constant of the material is [Use ]
A = 30p cm2 = 30p × 10-4 m2
d = 1mm = 10-3 m
E = (dielectric strength for breakdown)
= 3.6 × 107 v/m
Q = 7 × 10-6 C
The magnitude field at the centre of a circular coil of radius r, due to current I flowing through it, is B. The magnetic field at a point along the axis at a distance from the centre is :
-(1)
Two metallic blocks M1 and M2 of same area of cross – section are connected to each other (as shown in figure). If the thermal conductivity of M2 is K then thermal conductivity of M1 will be :
[Assume steady state heat conduction]
At steady state condition -> Heat conducted through slab AB = Heat conducted though slab BC
->
k1 = 8 k
0.056 kg of Nitrogen is enclose in a vessel at a temperature of 127°C. The amount of heat required to double the speed of its molecules is ___________ k cal.
Tf = 4Ti = 4 × 400 = 1600 k
=
=
Q = 12 × 103 cal
= 12 k cal
Two identical thin biconvex lenses of focal length 15 cm and refractive index 1.5 are in contact with each other. The space between the lenses is filled with a liquid of refractive index 1.25. The focal length of the combination is ________ cm.
f1 = 15 cm
A transistor is used in common-emitter mode in an amplifier circuit. When a signal of 10 mV is added to the base-emitter voltage, the base current changes by 10µA and the collector current changes by 1.5 mA. The load resistance is 5 kΩ. The voltage gain of the transistor will be ________.
Ib = 10 µA
IC = 1.5 mA
RL = 50 kW or (Rc)
Base – emitter voltage = 10 mv
=
Av = 750
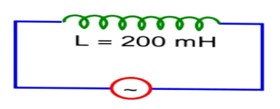
As shown in the figure an inductor of inductance 200 mH is connected to an AC source of emf 220 V and frequency 50 Hz. The instantaneous voltage of the source is 0 V when the peak value of current is The value of a is __________.
Let l = l0 cos wt
Then v = v0 sinwt
at t = 0, v = 0
but l = l0
a = 121 × 2
a = 242
Sodium light of wavelength 650nm and 655 nm is used to study diffraction at a single slit of aperture 0.5 mm. The distance between the slit and the screen is 2.0 m. The separation between the positions of the first maximum of diffraction pattern obtained in the two cases is _________× 10-5 m.
.For maxima = y = (2n + 1)
For 1st maxima for l1 wavelength (n = 1)
- (1)
First maxima for l2 wavelength
- (2)
When light of frequency twice the threshold frequency is incident on the metal plate, the maximum velocity of emitted electron is When the frequency of incident radiation is increased to five times the threshold value, the maximum velocity of emitted electron becomes If the value of x will be __________.
hu = hu0 + K.E
Cases u = 2u0
h2u0 = hu0 + K.E1
K.E1 = hu0
- (1)
Now, cases 2
h 5u0 = hu0 + k.E2
k.E2 = 4hu0
v2 =
v2 = 2v1
From the top of a tower, a ball is thrown vertically upward which reaches the ground in 6s. A second ball thrown vertically downward from the same position with the same speed reaches the ground in 1.5 s. A third ball released, from the rest from the same location, will reach the ground in __________ s.
For first ball
s = ut +
h = 180 - 6u -(1)
for second boy
h = 1.5u + 11.25 -(2)
from (1) & (2)
180 - 6u = 1.5u + 11.25
7.5u = 180 - 11.25
h = 180 - 6u
= 180 - 6 × 22.5
45m
for third ball
t2 = 9
t = 3 sec
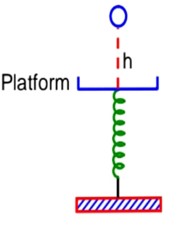
A ball of mass 100 g is dropped from a height h = 10 cm on a platform fixed at the top of a vertical spring (as shown in figure). The ball stays on the platform and the platform is depressed by a distance the spring constant is _________ Nm-1. (Use g = 10 ms-2)
COME
k = 120Nm-1
In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell gives a balancing point at 75 cm length of wire. This cell is now replaced by another cell of unknown emf. If the ratio of the emef’s of two cells respectively is 3:2, the difference in the balancing length of the potentiometer wire in above two cases will be __________ cm.
A metre scale is balanced on a knife edge at its centre. When two coins, each of mass 10 g are put one on the top of the other at the 10.0 cm mark the scale is found to be balanced at 40.0 cm mark. The mass of the metre scale is found to be x × 10-2 kg. The value of x is _________.
2mg ×30 = Mg ×10
M = 6 × 10-2kg
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Five Exam