Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Seven
Get insights from 66 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Seven, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Seven
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
The capacitive reactance is equal to the inductive reactance at resonance:
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
In an AC circuit, the power factor cos? measures the efficiency of power usage. Between the current and voltage, it is the cosine of the phase angle. A power factor of 1 means all the supplied power is used effectively and a low power factor means more energy is wasted.
Average power:
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
The alternating current's RMS (Root Mean Square) value or voltage offers the equivalent DC value that would generate the same power in a resistive circuit. The RMS is used in most practical measurements and is calculated as:
Where ?0 and ?0 are the peak current and voltage, respectively.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
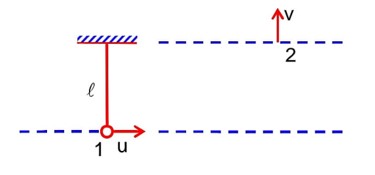
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, d) For house hold supplies, AC currents are used which are having zero average value over a cycle.
The line is having some resistance so power factor cos φ = R/Z≠0
so, φ not equal to π /2 ⇒ φ < /2
i.e., phase lies between 0 and π /2.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c, d) When the AC voltage is applied to the capacitor, the plate connected to the positive terminal will be at higher potential and the plate connected to the negative terminal will be at lower potential.
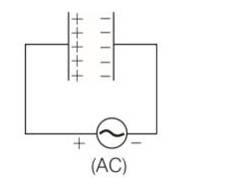
The plate with positive charge will be at higher potential and the plate with negative charge will be at lower potential. So, we can say that the charge is in phase with the applied voltage.
P= ErmsIrmscos
=90
So power, P = 0
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
According to the question power transferred Is P = I2 Z cos?
as we know cos? = R/Z
R>0 and Z>0
cos? >0 so P>0
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
We have to transmit energy (power) over large distances at high alternating voltages, so current flowing through the wires will below because for a given power (P).
P= ErmsIrms, Irms is low when Erms is high.
Power loss= I 2 rms R= low
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c, d) According to the question, the current increases on increasing the frequency of supply. Hence, the reactance of the circuit must be decreases as increasing frequency.
For a capacitive circuit, capacitive reactance Xc=
For an CR circuit Z= when frequency increases X decreases.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers