Physics NCERT Class 12 Chapter 7 focuses on Alternating Currents (AC). This chapter deals with AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor, Representation of AC Current & Voltage by Rotating Vector, AC Voltage Applied to an Inductor, AC Voltage Applied to a Capacitor and other topics.
The NCERT exemplar for class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current consists of a series of questions based on the Alternating Current topics. Students solving the Physics NCERT exemplar class 12 chapter seven will master the theoretical concepts and improve their problem-solving skills. Class 12 Physics chapter 7 Ncert exemplar solutions will help in developing a deep understanding of Alternating Current. Moreover, students can prepare for competitive exams such as JEE Main, WBJEE, COMDEK, EAPCET, and more through the Physics NCERT exemplar class 12 pdf with solutions. Check the article for Physics NCERT exemplar solutions class 12 chapter seven Alternating Current on this page.
Students must also read NCERT Solutions given on Shiksha's website and they should also refer to Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current for a better understanding of this chapter.
- Chapters List
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Alternating Current – Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Alternating Current – Very Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 – Long Answer Type Question
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Alternating Current – Objective Type Questions
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 7 NCERT Exemplar
- Alternating Current Question and Answer
- 26th February 2021 (Second Shift)
Chapters List
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current
A free PDF download of the NCERT exemplar for Physics Class 12 Chapter 7 is provided below. No credential is required to download the NCERT exemplar for Physics Class 12 Chapter 7 Alternating Current pdf. Click on the link provided below, and the NCERT Physics Class 12 exemplar will be downloaded.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Alternating Current – Short Answer Type Questions
Find below the questions:
Commonly asked questions
A device ‘X is connected to an AC source. The variation of voltage, current and power in one complete cycle is shown in figure.
(a) Which curve shows power consumption over a full cycle?
(b) What is the average power consumption over a cycle?
(c) Identify the device X
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) We know that P= VI
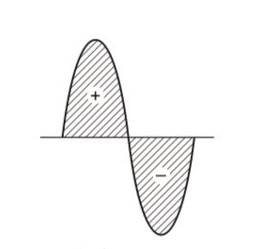
that is curve of power will be having maximum amplitude, equals to multiplication of amplitudes of voltage (V)and current (I) curve. So, the curve will be represented by A.
(b) As shown by shaded area in the diagram, the full cycle of the graph consists of one positive and one negative symmetrical area. Hence average power over a cycle is zero.

(c) As the average power is zero, hence the device may be inductor (L) or capacitor (C) or the series combination of L and C.
Both alternating current and direct current are measured in amperes. But how is the ampere defined for an alternating current?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
For a Direct Current (DC),
1ampere= 1coulomb/sec
An AC current changes direction with the source frequency and the attractive force would average to zero. Thus, the AC ampere must be defined in terms of some property that is independent of the direction of current.
Joule’s heating effect is such property and hence it is used to define rms value of AC.
A coil of 0.01 H inductance and 1 ω resistance is connected to 200 V, 50 Hz AC supply. Find the impedance of the circuit and time lag between maximum alternating voltage and current.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
L= 0.01H
R= 1ohm
Voltage =200V
Frequency = 50Hz
Z= = = =3.3ohm
tan = = 3.14
= tan-13.14=72
=72
= /w= = s
A 60 W load is connected to the secondary of a transformer whose primary draws line voltage. If a current of 0.54 A flows in the load, what is the current in the primary coil? Comment on the type of transformer being used.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ps=60W, Is= 0.54 A
P=VI, V= 60/0.54= 110V
Voltage in the secondary is less than voltage in primary so transformer is step down transformer
As transformation ratio is, k = Es/Ep= Ip/Is
110/220=Ip/0.54A
Ip= 0.27A
Explain why the reactance provided by a capacitor to an alternating current decreases with increasing frequency.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A capacitor does not allow flow of direct current through it as the resistance across the gap is infinite. When an alternating voltage is applied across the capacitor plates, the plates are alternately charged and discharged. The current through the capacitor is a result of this changing voltage (or charge).
Thus, a capacitor will pass more current through it if the voltage is changing at a faster rate, i.e. if the frequency of supply is higher. This implies that the reactance offered by a capacitor is less with increasing frequency.
Mathematically, the reactance can be written as XC=1/wC
Explain why the reactance offered by an inductor increases with increasing frequency of an alternating voltage.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
An inductor opposes flow of current through it by developing a back emf according to Lenz’s law. The induced voltage has a polarity so as to maintain the current at its present value. If the current is decreasing, the polarity of the induced emf will be so as to increase the current and vice -versa.
Since, the induced emf is proportional to the rate of change of current, it will provide greater reactance to the flow of current if the rate of change is faster, i.e., if the frequency is higher. The reactance of an inductor, therefore, is proportional to the frequency. Mathematically, the Reactance offered by the inductor is given by XL= ωL
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Alternating Current – Very Short Answer Type Questions
Here are the VSA questions:
Commonly asked questions
Draw the effective equivalent circuit of the circuit shown in figure, at very high frequencies and find the effective impedance
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If we consider a L-C circuit analogous to a harmonically oscillating spring block system. The electrostatic energy CV2 is analogous to potential energy and energy associated with moving charges (current) that is magnetic energy LI2 is analogous to kinetic energy.
Study the circuits (a) and (b) shown in figure and answer the following questions.
(a) Under which conditions would the rms currents in the two circuits be the same?
(b) Can the rms current in circuit (b) be larger than that in (a)?
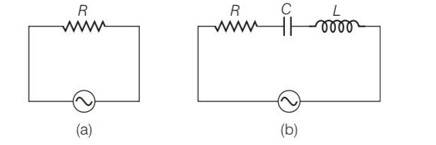
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(Irms)a= =
(Irms)b= =
When = (Irms)b
Then R=
XL=Xc resonance condition
As Z>R = = >1
(Irms)a > (Irms)b
Can the instantaneous power output of an AC source ever be negative? Can the average power output be negative?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
E=E0sinwt
And current I=I0sin (wt )
Power, P= EI = E0sinwt = E0I0sinwtsin (wt+ )
= [cos ]………… (1)
Pav= cos =VrmsIrmscos ………. (2)
From eqn 1 ……But when cos < cos (2wt+
P<0 power can be nagative of an AC source
From eqn 2……… Pav>0
cos =R/Z>0 average power can not be negative
In a series LCR circuit, the plot of Imaxversus co is shown in figure. Find the bandwidth and mark in the figure.
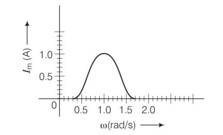
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In the figure
Band width = w2-w1 where these two corresponds to frequencies at which magnitude of current is 1/ times of maximum value
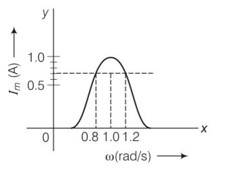
Irms= = 1/ = 0.7A
From the diagram the corresponding frequencies are 0.8 and 1.2rad/s
The alternating current in a circuit is described by the graph shown in figure. Show rms current in this graph.
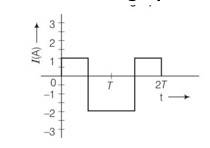
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Irms= = = 1.58A = 1.6 approx
This value is indicating in graph
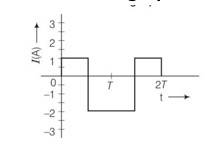
How does the sign of the phase angle ?, by which the supply voltage leads the current in an L-C-R series circuit, change as the supply frequency is gradually increased from very low to very high values?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar

NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 – Long Answer Type Question
See below the LA type questions with solutions:
Commonly asked questions
An electrical device draws 2KW power from AC mains (voltage 223V(rms)=) . The current differs (lags) in phase by (tan ) as compared to voltage . find
(a) R
(b) XL-XC (c) Im. Another device has twice the values for R,XcandXL. how the answer affected?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Power drawn, p= 2KW= 2000W
tan =-3/4
P=V2/Z
Z=V2/P= =25
Z =
25=
625 = ………… (1)
tan = = ¾
XL-XC= 3R/4
Use this in eqn 1
625= R2+ (3R/4)2 = R2+9R2/16
625 = 25R2/16, R= 20ohm
XL-XC=15ohm
Im= I= = = 12.6A
If R, XL and Xc are all doubled, tan does not change . Z is doubled, current is halved. So power is also halved.
MW power is to be delivered from a power station to a town 10 km away. One uses a pair of Cu wires of radius 0.5 cm for this purpose. Calculate the fraction of ohmic losses to power transmitted if
(i) Power is transmitted at 220V. Comment on the feasibility of doing this.
(ii) A step-up transformer is used to boost the voltage to 11000V, power transmitted, then a step-down transformer is used to bring voltage to 220 V. (ρcu= 1.7×10-8 SI unit)
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
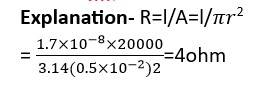

Consider the LCR circuit shown in figure find the net current I and the phase of i. show that i=V/Z. find the impedance Z for this circuit.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Total current i=i1+i2
Vmsinwt=Ri1
I1=
If q2 is charge on the capacitor at any time t then for series combination of C and L
Applying KVL in below circuit
So q2=qmsin(wt )……….1
qm[ sin(wt+ )]= Vmsinwt
if
qm=
from above equation i2=
i2= when
so total current I = i1+i2
I=
I= i1+i2= Ccos +Csin
I= Csin(wt+ )
C=
1/2
= tan-1
1/2
This is the expression for impedance.2
For a LCR circuit at frequency w the equation reads
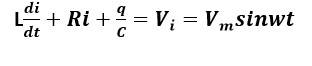
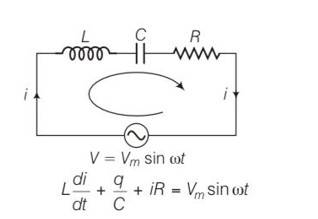
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar

In the LCR circuit shown in figure the AC driving voltage isV=Vmsinwt
Write the equation of motion for q(t) describe subsequent motion of charges.
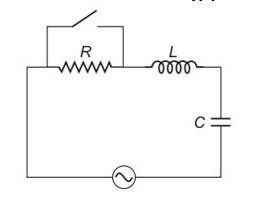
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar

NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Alternating Current – Objective Type Questions
Here are the objective type questions:
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 7 NCERT Exemplar
The following are the important formulas of Class 12 Physics Chapter 7:
Alternating Voltage and Current (Instantaneous Values)
RMS (Root Mean Square) Values
Mean/ Average Value over Half Cycle
Impedance in LCR Circuit
Current in LCR Circuit
Phase Angle
Power Factor
Average Power in AC Circuit
Resonance in Series LCR Circuit
Alternating Current Question and Answer
Commonly asked questions
If the rms current in a 50 Hz AC circuit is 5 A, the value of the current 1/300 s after its value becomes zero is
(a) 5
(b) 5 A
(c) 5/6A
(d) 5/ A
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) I0= Irms= (5)A
I=I0sinwt = 5 sin = 5 A
An alternating current generator has an internal resistance Rgand an internal reactance XgIt is used to supply power to a passive load consisting of a resistance Rg and a reactance XL. For maximum power to be delivered from the generator to the load, the value of XL is equal to
(a) Zero
(b) Xg
(c) -Xg
(d) Rg
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) For delivering maximum power from the generator to the load, total internal reactance must be equal to conjugate of total external reactance.
XL=-Xg
When a voltage measuring device is connected to AC mains, the meter shows the steady input voltage of 220 V. This means
(a) Input voltage cannot be AC voltage, but a DC voltage
(b) Maximum input voltage is 220 V
(c) The meter reads not v but < v2> and is calibrated to read v2
(d) The pointer of the meter is stuck by some mechanical defect
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) The voltmeter connected to AC Mains reads mean value (
To reduce the resonant frequency in an L-C-R series circuit with a generator
(a) The generator frequency should be reduced
(b) Another capacitor should be added in parallel to the first
(c) The iron core of the inductor should be removed
(d) Dielectric in the capacitor should be removed
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As we know resonant frequency is v0=
To increase capacitance we must connect it to another capacitor parallel to the first.
Which of the following combinations should be selected for better tuning of an L-C-R circuit used for communication?
(a) R = 20 ?, L = 1.5 H, C = 35μF
(b) R = 25 ?, L = 2.5 H, C = 45 μF
(c) R=15?, L = 3.5H, C = 30 μF
(d) R = 25 ?, L = 1.5 H, C = 45 μF
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) As we know that Q= to make Q high R should be low, L should be high and C should be low.
An inductor of reactance 1 ? and a resistor of 2 ? are connected in series to the terminals of a 6 V (rms) AC source. The power dissipated in the circuit is
(a) 8 W
(b) 12 W
(c) 14.4 W
(d) 18 W
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Average power dissipated is ErmsIrmscos
Z=
= =
Irms= 6/ A
cos =R/Z=2/
pav= 6 = 14.4W
The output of a step-down transformer is measured to be 24 V when connected to a 12 W light bulb. The value of the peak current is
(a) 1/ A
(b) A
(c) 2A
(d) 2 A
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Secondary voltage Vs= 24V
Power associated with secondary Ps = 12W
Is= = 12/24= 0.5A
I0= Is = 1/ A
As the frequency of an AC circuit increases, the current first increases and then decreases. What combination of circuit elements is most likely to comprise the circuit?
(a) Inductor and capacitor
(b) Resistor and inductor
(c) Resistor and capacitor
(d) Resistor, inductor and capacitor
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, d) inductive reactance XL= 2 L
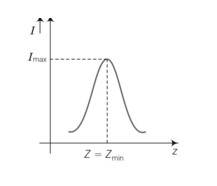

As frequency (ν) increases, Z decreases and at certain value of frequency know as resonant frequency (ν0), impedance Z is minimum that is Zmin= R current varies inversely with impedance and at Zmin current is maximum.
In an alternating current circuit consisting of elements in series, the current increases on increasing the frequency of supply. Which of the following elements are likely to constitute the circuit?
(a) Only resistor
(b) Resistor and an inductor
(c) Resistor and a capacitor
(d) Only a capacitor
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c, d) According to the question, the current increases on increasing the frequency of supply. Hence, the reactance of the circuit must be decreases as increasing frequency.
For a capacitive circuit, capacitive reactance Xc=
For an CR circuit Z= when frequency increases X decreases.
Electrical energy is transmitted over large distances at high alternating voltages. Which of the following statements is (are) correct?
(a) For a given power level, there is a lower current
(b) Lower current implies less power loss
(c) Transmission lines can be made thinner
(d) It is easy to reduce the voltage at the receiving end using step-down transformers
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
We have to transmit energy (power) over large distances at high alternating voltages, so current flowing through the wires will below because for a given power (P).
P= ErmsIrms, Irms is low when Erms is high.
Power loss= I 2 rms R= low
For an L-C-R circuit, the power transferred from the driving source to the driven oscillator is P = I2Z cos ?.
(a) Here, the power factor cos ? > 0, P > 0
(b) The driving force can give no energy to the oscillator (P = 0) in some cases
(c) The driving force cannot syphon out (P < 0) the energy out of oscillator
(d) The driving force can take away energy out of the oscillator
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
According to the question power transferred Is P = I2 Z cos?
as we know cos? = R/Z
R>0 and Z>0
cos? >0 so P>0
When an AC voltage of 220 V is applied to the capacitor C
(a) The maximum voltage between plates is 220 V
(b) The current is in phase with the applied voltage
(c) The charge on the plates is in phase with the applied voltage
(d) The power delivered to the capacitor is zero
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c, d) When the AC voltage is applied to the capacitor, the plate connected to the positive terminal will be at higher potential and the plate connected to the negative terminal will be at lower potential.
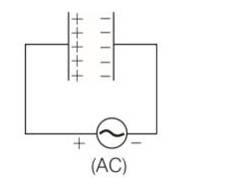
The plate with positive charge will be at higher potential and the plate with negative charge will be at lower potential. So, we can say that the charge is in phase with the applied voltage.
P= ErmsIrmscos
=90
So power, P = 0
If an L-C circuit is considered analogous to a harmonically oscillating spring- block system, which energy of the L-C circuit would be analogous to potential energy and which one analogous to kinetic energy?
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, d) For house hold supplies, AC currents are used which are having zero average value over a cycle.
The line is having some resistance so power factor cos φ = R/Z≠0
so, φ not equal to π /2 ⇒ φ < π/2
i.e., phase lies between 0 and π /2.
26th February 2021 (Second Shift)
Commonly asked questions
A cord is wound round the circumference of wheel of radius r. The axis of the wheel is horizontal and the moment of inertial about it is I. A weight mg is attached to the cord at the end. The weight falls from rest. After falling through a distance ‘h’, the square of angular velocity of wheel will be
mg – T = ma. (1)
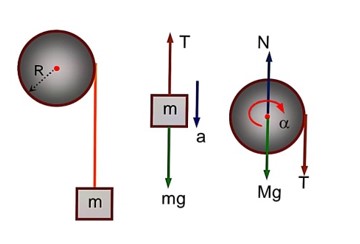
T × R = l α. (2)
a = α R. (3)
With the help of equations (1), (2) and (3), we get
A tuning fork A of unknown frequency produces 5 beats/s with a fork of known frequency 340 Hz. When fork A is filed, the beat frequency decreases to 2 beats/s. What is the frequency of fork A?
Frequency increases on filing. So, initial frequency of A is 335 Hz.
f = 340 – 5 = 335 Hz
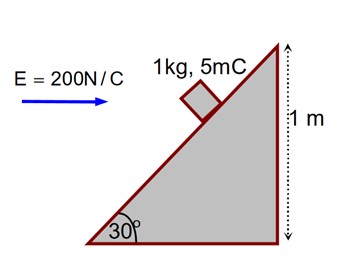
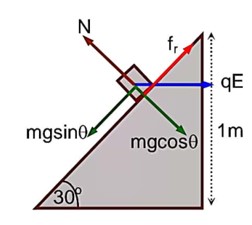
An inclined plane making an angle of 30° with the horizontal is placed in a uniform horizontal electric field as shown in the figure. A body of mass 1kg and charge 5 mC is allowed to slide down from rest at a height of 1m. If the coefficient of friction is 0.2, find the time taken by the body to reach the bottom.
A particle executes S.H.M., the graph of velocity as a function of displacement is
Path is ellipse.
If ‘C’ and ‘V’ represent capacity and voltage respectively then what are the dimensions of where C/V =
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : A second’s pendulum has a time period of 1 second.
Statement II : It takes precisely one second to move between the two extreme positions.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
Time period of second pendulum is 2 seconds.
Time period of a simple pendulum is T. The time taken to complete oscillations starting from mean position is The value of a is
Total oscillation =
= 7
The volume V of a given mass of monoatomic gas changes with temperature T according to the relation The work done when temperature changes by 90 K will be xR. The value of x is……..
[R = universal gas constant]
Work done =
n = 60
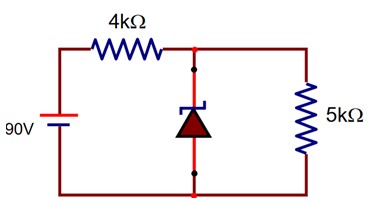
The zener diode has a Vz = 30V. The current passing through the diode for the following circuit is…………mA.
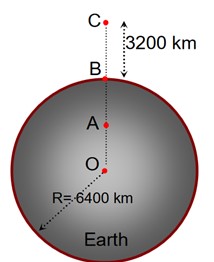
In the reported figure of earth, the value of acceleration due to gravity is same at point A and C but it is smaller than that of its value at point B (surface of the earth). The value of OA: AB will be x : y. The value of x is
The trajectory of a projectile in an vertical plane is y = ax - bx2, where a and b are constants and x & y are respectively the horizontal and vertical distances of the projectile from the point of projection. The angle of projection q and the maximum height attained H are respectively given by
Range =
On comparing with
y = x tan θ-
The length of metallic wire is when tension in it is . It is when the tension is T2. The original length of the wire will be
Stress = Y × strain
A radioactive simple is undergoing decay. At any time t1, its activity is A and another time t2, the activity is What is the average life time for the sample?
[Radio active decay law]
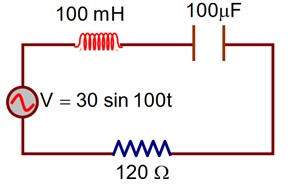
Find the peak current and resonant frequency of the following circuit (as shown in figure).
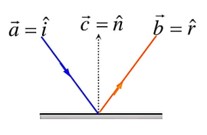
The incident ray, reflected ray and the outward drawn normal are denoted by the unit vectors respectively. Then choose the correct relation for these vectors.
Two masses A and B, each of mass M are fixed together by a massless spring. A force acts on the mass B as shown in figure. If the mass A starts moving away from mass B with acceleration ‘a’, then the acceleration of mass B will be
Let the spring is in extension state and
Hence we can say that block moves away from block B in the frame of B
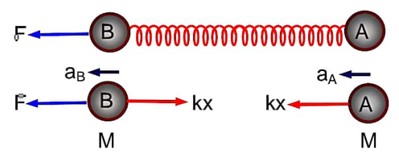
F – kx = MaB . (1)
kx = Ma . (2)
A scooter accelerates from rest for time t1 at constant rate a1 and then retards at constant rate a2 for time t2 and comes to rest. The correct value of will be
The internal energy (U), pressure (P) and volume (V) of an ideal gas are related as U = 3PV + 4. The gas is
U = 3PV + 4
An aeroplane, with its wings spread 10m, is flying at a speed of 180 km/h in a horizontal direction. The total intensity of earth’s field at that part is 2.5 × 10-4Wb/m2 and the angle of dip is 60°. The emf induced between the tips of the plane wings will be
Bv = B sin 60°
Given below are two statements : one is labeled as Assertion A and the other is labeled as Reason R.
Assertion A : For a simple microscope, the angular size of the object equals the angular size of the image.
Reason R : Magnification is achieved as the small object can be kept much closer to the eye that 25cm and hence it subtends a large angle.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Consider the following image dddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddd
The recoil speed of a hydrogen atom after it emits a photon in going from n = 5 state to n = 1 state will be
With the help of conservation of linear momentum, we can write
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : An electric dipole is placed at the centre of a hollow sphere. The flux of electric field through the sphere is zero but the electric field is not zero anywhere in the sphere.
Statement II : If R is the radius of a solid metallic sphere and Q be the total charge on it. The electric field at any point on the spherical surface of radius r ( In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the option given below
All the charge given to a conducting sphere resides on outer surface.
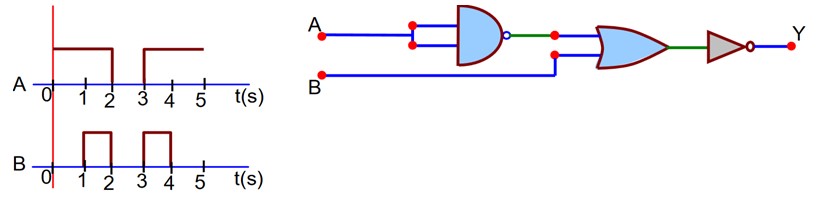
Draw the output signal Y in the given combination of gates.
Two stream of photons, possessing energies equal to twice and ten times the work function of metal are incident on the metal surface successively. The value of ratio of maximum velocities of the photoelectrons emitted in the two respective cases is x : y. The value of x is
Case I :-
Case II :-
x = 1
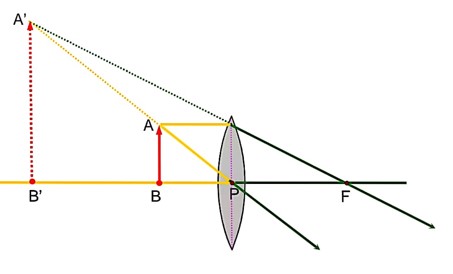
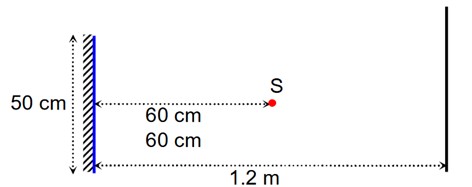
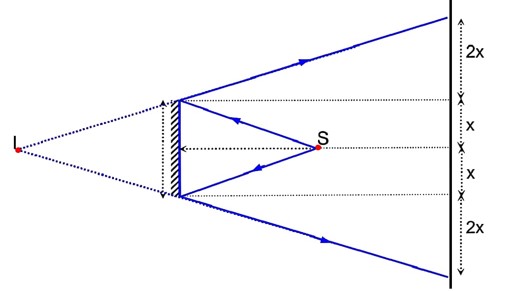
A point source of light S, placed at a distance 60cm infront of the centre of a plane mirror of width 50cm, hangs vertically on a wall. A man walks inform of the mirror along a line parallel to the mirror at a distance 1.2m from it (see in the figure). The distance between the extreme points where he can the image of the light source in the mirror is…………..cm
If the highest frequency modulating a carrier is 5 kHz, then the number of AM broadcast stations accommodated in a 90 kHz bandwidth are
Band Width = 2 × n × the highest modulation frequency
1 mole of rigid diatomic gas performs a work of when heat Q is supplied to it. The molar heat capacity of the gas during this transformation is The value of x is
[R = universal gas constant]
A particle executes S.H.M. with amplitude ‘a’ and time period ‘T’. The displacement of the particle when its speed is half of maximum speed is The value of x is
27 similar drops of mercury are maintained at 10V each. All these spherical drops combine into a single big drop. The potential energy of the bigger drop is……… times that of a smaller drop.
With the help of conservation of volume, we can write
With the help of conservation of charge, we can write
Q = 27 q. (2)
Potential energy of single drop = U1 =
Potential energy of bigger drop =
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Seven Exam