Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Seven
Get insights from 106 questions on Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Seven, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Seven
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
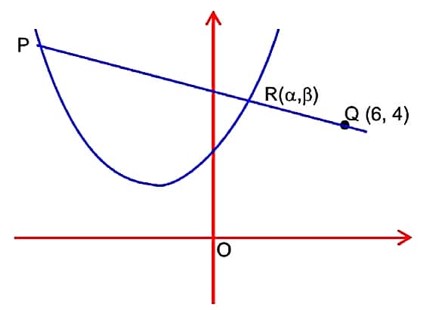
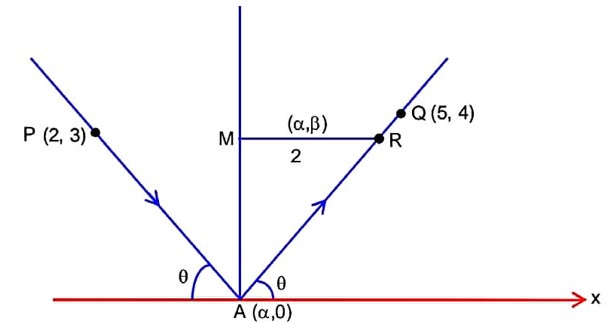
………(i)
………(ii)
………(iii)
Centre of the circle given by solving (i) & (ii)
Again is tangent to the circle.
New question posted
4 months agoNew question posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
gen term = 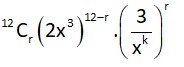
For constant term
36 – 3r – rk = 0
for r = 1, 2, 4
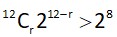
Possible values of k = 3, 1
New question posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
A = {1, 2, 3, ….50}
R1 = (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 4)…. (2, 32)
(3, 1) (3, 3) (3, 9) (3, 27)
(13, 1) (13, 13) etc.
R2 = { (2, 1), (2, 2), (3, 1), (3, 3), (5, 1), (5, 5), (7, 1), (7, 7), (1, 1), (11, 11)…}
contains only 9 elements.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers