Motion in a Plane
Get insights from 112 questions on Motion in a Plane, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Motion in a Plane
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a,b,c
Explanation – H=
H1=Vo2sin2 1/2g , H2=Vo2sin2 2/2g
H1>H2
Vo2sin2 1/2g= Vo2sin2 2/2g
Sin2 1>sin2 2
Sin2 1 – sin2 2>0
(Sin 1 – sin 2)( Sin 1 + sin 2)>0
Sin 1>sin 2 or 1 >2
T=
T1= , T2=
T1> T2
R=
Sin 1>sin 2
Sin2 1> sin2 2
R1>R2
Total energy for the first particle
U1=K.E+P.E=1/2m1
U2= K.E+P.E= 1/2m2
Total energy for the second particle
So m1= m2 then U1=U2
So m1>m2 then U1>U2
So m1
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a, b
Explanation - |A+B|= |A|or |A+B|2=|A|2
|A|2 +|B|2+2|A|B|cos = |A|2
|B| (|B|+2|A|cos )= 0
|B|=0 or |B|+2|A|cos =0
Cos =
If A and B are antiparallel then =180
-1=
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b, d
Explanation – given A+B+C = 0
B
B +B =0
B
B
A
(A )
It cannot be zero
(b) (A ).C= (B ).C=0 . if b|C then B =0 then (B )
(c) (A )=X=ABsin . The direction of X is perpendicular to the plane containing A and B (A )
(d) if c2= A2+B2, then angle between A and B is 900
(A ).C= (AB sin900X).C=AB (X.C)
= ABC cos900= 0
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-b, d
Explanation- as given motion is two-dimensional motion and given that instantaneous speed vo is positive constant. Acceleration is rate of change of velocity. hence it will also be in the plane of motion.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- d
Explanation – speed = total distance travelled /time taken
Total distance travelled = path length
= speed time
We should be very careful with the fact, that speed is related with total distance covered not with displacement.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation – we know that impulse J= f. = , where F is force . is time duration and is change in momentum. As is a vector quantity, hence impulse is also a vector quantity. Sometimes area can also be treated as vector.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- c
Explanation - we know that =150 and R= 50m
Range, R=
50 =
So u2= 980
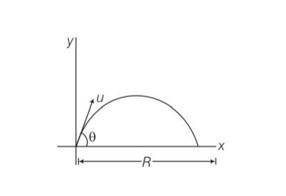
So u = m/s
So u= 14 = 31.304m/s
= 450, R=
R= = =
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation – ler r makes an angle with positive x axis component if r along x-axis.
So rx= |r|cos
(rx)maximum= |r| (cos )maximum
= |r|cos = r
=00
R is along positive x-axis.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
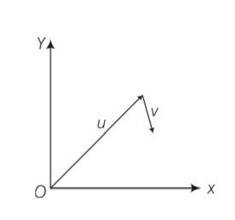
Explanation – u= a? + b? as u in the first quadrant, hence both components a and b will be positive. For v= p? + q? , as it is positive x direction and located downward hence x component p will be positive and y component q will be negative.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
