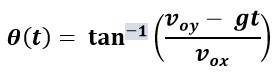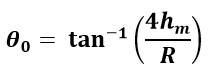Motion in a Plane
Get insights from 112 questions on Motion in a Plane, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Motion in a Plane
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
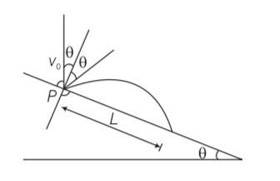
Explanation- y=O, uy= Vocos
ay=-gcos , t =T
applying equation of kinematics
y=uyt+ t2
0 = Vocos +T2
T=
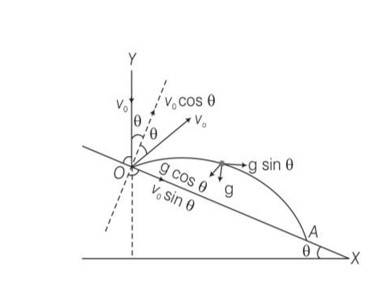
T= 2V0/g
X= L, ux=Vosin , ax= gsin , t=T=
X=uxt+
L= Vosin
L= sin
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
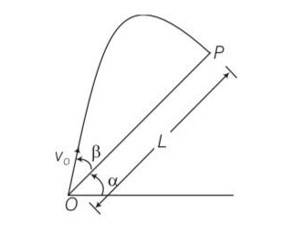
Explanation – particle is projected from the point O.
Let time taken in reaching from point O to point P is T.
for journey O to P
y=0,uy= Vosin ,ay= -gcos
y=uyt +
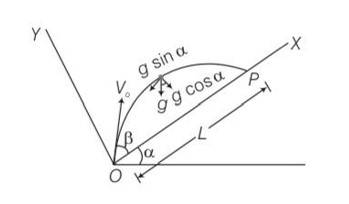
0= Vosin
T[Vosin T]=0
T = time of flight =
Motion along OX
x= L ,ux= Vocos , ax= -gsin
t =T =
x= uxt+
L= V0cos +
L= T[V0cos ]
L= [Vocos ]
L=
Z= sin
= sin
=
= ½ [sin2]
=
= [sin(2 )-sin ]
For z maximum
2 ,
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – target T is at horizontal distance x= R+ and between point of projection y= -h
Maximum horizontal range R= …………1
Horizontal component of initial velocity = Vocos
Vertical component of initial velocity = -Vosin
So h = (-Vosin )t + 2………….2
R+ = Vocos
So t=
Substituting value of t in 2 we get
So h = (-V0sin )
H = -(R+ )tan +
, h = -(R+ )tan +
So h = -(R+ ) +
So h = -(R+ )+
So h = -R- +(R+ )
h=
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- speed of jackets = 125m/s
Height of hill = 500m
To cross the hill vertical component of velocity should be grater than this value uy=
So u2= ux2+uy2
Horizontal component of initial velocity ux =
Time taken to reach the top of hill t=
Time taken to reach the ground in 10 sec = 75 (10)= 750m
Distance through which the canon has to be moved =800-750=50m
Speed with which canon can move = 2m/s
Time taken canon = 50/2= 25s
Total time t= 25+10+10= 45s
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.32
(a) Let be the angle at which the projectile is fired w.r.t. the x-axis, since depends on t
Therefore tan since (Vy=Voy -gt and Vx = Vox)
(b) Since = sin2 /2g…….(1)
R = sin2 /g …….(2)
Dividing (1) by (2)
( /R) = [ sin2 /2g]/[ sin2 /g] = / 4
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.31
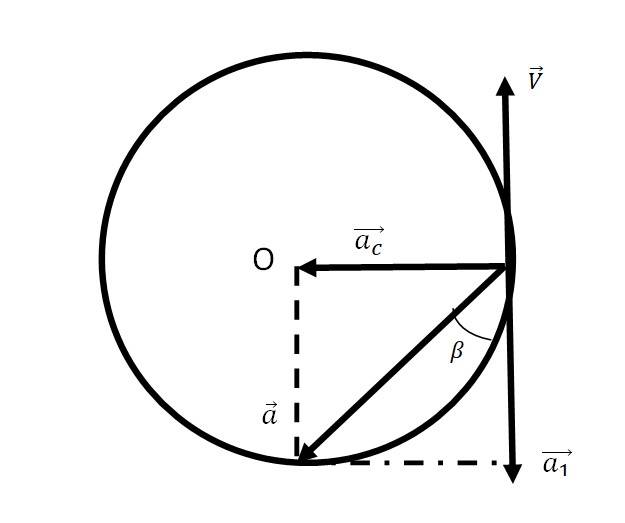
Speed of the cyclist = 27 km/h = 7.5 m/s
Radius of the road = 80m
The net acceleration is due to braking and the centripetal acceleration
Acceleration due to braking = 0.5 m/s2
Centripetal acceleration a = v2r = (7.5)2/80= 0.703 m/s2
The resultant acceleration is given by a = sqrt ( + ) = sqrt ( + ) = 0.86 m/s2
tan = AC / at = 0.7/0.5, = 54.5
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.30
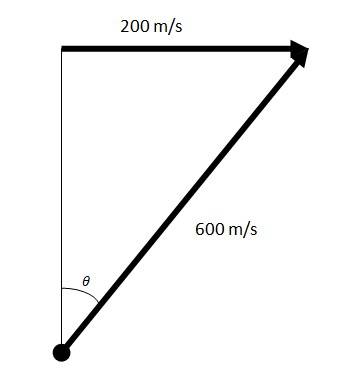
Speed of the fighter plane = 720 km/h = 200 m/s
The altitude of the plane = 1.5 km =1500 m
Velocity of the shell = 600 m/s
= 200/600
Let H be the minimum altitude for the plane to fly, without being hit
Using equation H = sin2 (90-
= (6002cos2 )/2g
= 360000 { ( 1 + cos2 )/2}/2 10
= 16000 m = 16 km
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.29 The angle of projectile = 30
The bullet hits the ground at a distance of 3 km, Range R = 3 km
We know horizontal range for a projectile motion, R = sin2 / g
3 = sin60 / g
= 3/ sin60 = 3.464 …………… (1)
To hit a target at 5 km,
Max Range, = …………. (2)
On comparing equation (1) and (2), we get
= 3.464
Hence, the bullet will not hit the target even by adjusting its angle of projection.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers