Ncert Solutions Physics Class 12th
Get insights from 218 questions on Ncert Solutions Physics Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Physics Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.25 Excess electrons on an oil drop, n = 12
Electric field intensity, E = 2.55
Density of oil, 1.26 g / = 1.26 g/
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/
Charge of an electron, e = 1.60C
Let the radius of the oil drop be r
Force (F) due to electric field (E) is equal to the weight of the oil drop (W)
F = W
Eq = mg
Ene =
= =
r = 9.815 m = 9.815 mm
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.24 The given conditions are explained in the adjacent diagram
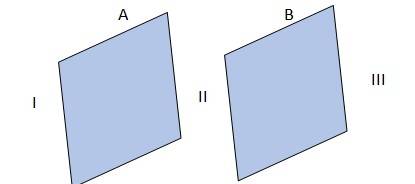
Where A and B represent two large, thin metal plates, parallel and close to each other. The outer surface of A is shown as I, outer surface of B is shown as II and the surface in between A and B is shown as III.
Charge density of plate A, = 17.0 C/
Charge density of plate B, = 17.0
C/
(a) & (b) In the region, I and III, electric field E is zero, because charge is not enclosed by the respective plates.
(c) Electric field, E in the region II is given by
E =
, where
= Permittivity of free space = 8.854
E = N/C = 1.92 N/C
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.23 Electric field produced by the infinite line charge at a distance d having linear charge density
is given by
E = , where
E = Electric field = 9 N/C
= Permittivity of free space = 8.854
d = 2 cm = 0.02 m
Hence, = 9
8.854
0.02 = 10
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.22
(a) Diameter of the sphere, d = 2.4 m, Radius, r = 1.2 m
Surface charge density, = 80 μC/
Total charge on the surface of the sphere is given by Q =
Hence Q = 80
(b) The total electric flux (
where
Q = 1.447
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.21 Electric field intensity, E, at a distance d, from the centre of a sphere containing net charge q is given by the relation,
E =
Where
q= Net charge
E = 1.5
d = 2r = 20 cm = 0.2 m
q = E
= 6.67 nC
The net charge on the sphere is 6.67 nC
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.20 Electric flux,
Radius of Gaussian surface, r = 10 cm = 0.1 m
(a) Electric flux piercing through a surface depends on the net charge enclosed inside a body, not on the size of the body. Hence, if the radius is doubled, the net flux passing does not change. The net flux passing will remain as -1 N
(b) The relation between point charge and the electric flux is given by
Where
Hence point charge q = φ
= - 8.854
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.19 Net electric flux (
where
q= 2.0 μC
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.18 The square can be considered as one face of a cube of edge 10 cm with a centre where charge q is placed.
According to Gauss's theorem for a cube, total electric flux is through all its six faces.
We have q = +10
Hence, =
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.17 (a) Net outward flux through the surface of the box ,
For a body containing net charge q, flux is given by the relation,
where
Hence q =
= 7.0832
(b) Net flux piercing out through a body depends on the net charge contained in the body. If net flux is zero, then it can be inferred that the net charge inside the body is zero. The body may have equal amount of positive and negative charges.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.16 When the cube side is oriented so that its faces are parallel to the coordinate planes, number of field lines entering the cube is equal to the number of field lines piercing out of the cube. A as a result, net flux through the cube is zero.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers