Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Nine
Get insights from 101 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Nine, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Nine
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
apparent depth = real depth / refractive index
Since, the image formed by Medium1, O2 act as an object for Medium2.
If seen from µ3 ,the apparent depth is O2.
Similarly, the image formed by Medium2, O2 act as an object for Medium3
O2= ( )
= (
Seen from outside the apparent height is
O3 = ( =
= )
This is the expression for required depth.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
no reversibility of lens maker formula is not possible.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
m=v/u = D/f
So m = 25/10 = 2.5= 0.025m
P= 1/0.025= 40D
This is the required power of lens.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As the refractive index for red is less than that for blue, parallel beams of light incident on a lens will be bent more towards the axis for blue light compared to red.
By lens makers formula 1/f=
So fb
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
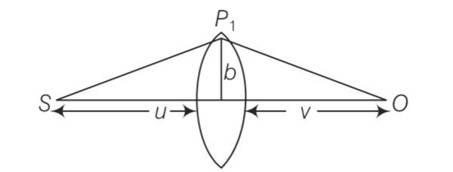
Time from S to P1 is
t1 =
Time from P1 to O is
t2 = ;
the time required travel through lens is t1 =
so total time is t=1/c(u+v+b2/2D+(n-1)(wo+b2/ ))
after solving we get
differentiating with respect to time
t=1/c(u+v+b2/2D+(n-1)K1In(K2b))
dt/db=0=b/D-(n-1)K1/b
b2= (n-1)K1D
b=
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
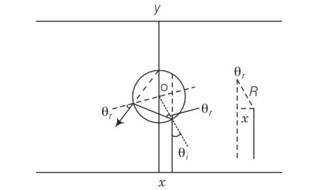
Since the material is of refractive index , is negative and is positive
| |= | |=| |
Explanation- since the material is of refractive index , is negative and is positive
| |= | |=| |
The total deviation of the outcoming ray from the incoming ray is 4 rays shall not receive if
<4 <
<4 <
sin =x/R
Light emitted from the source shall not reach the receiving plate under this condition
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let us consider planes r and r+dr. let the light be incident at an angle
n (r)sin
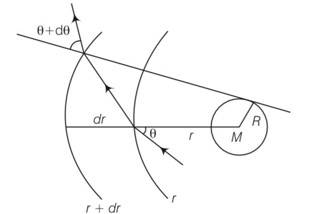
n (r)sin
-dn/drtan
So after integral r2=x2+R2 and tan
2rdr=2xdx
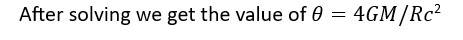
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let us consider a portion of a ray between x and x+dx inside the liquid. Let the angle of incidence at x be θ and let it enter the thin column at height y. Because of the bending it shall emerge at x+dx with an angle θ+dθ and at a height y+dy . From Snell's law,
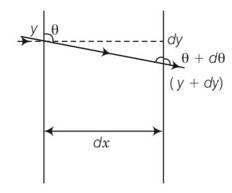
d
tan
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Any ray entering at an angle I shall be guided along AC if the angle ray makes with the face AC (φ) is greater than the critical angle as per the principle of total internal reflection φ +r =900, therefore sinφ = cosr
Sinφ>
Cosr>
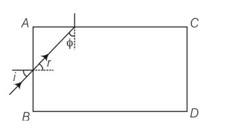
1-cos2r<1-1/
Sin2r<1-1/
Sin2r<1-1/
Sini = sinr
I=
If that is greater than the critical then all other angle of incidence shall be more than the critical angle.
1< -1
>
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) As we know that power Pf=1/f=1/0.1+1/0.02=60D
By corrective lens the object distance at far pointP'f=1/f'=1/1/0.02=50D
Total power P'f=Pf+Pg
Pg=-10D
(ii) This power of accommodation is 4D for the normal eye then
4=Pn-Pf where Pn power of near point
So Pn= 64D
1/xn+1/0.002=64 then xn= 1/14=0.07m
(iii) Pn'=Pf'+4=54
After solving xn'=4=0.25m
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers