Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Nine Ray Optics And Optical Instruments offers great preparation material for the Class 12 Board exams. It contains various types of questions, including multiple-choice questions, short-answer type questions, very short-answer type questions, and long-answer type questions. These questions cover all key concepts of Chapter Nine, and students' understanding of these concepts improves while practicing them. Students understand how and when to apply the concepts and formulas while solving complex problems during the exam.
Students can also download the Ch 9 Maths Class 12 PDF from here and study it anywhere without the requirement of any internet connection. The PDF is created by Shiksha's subject matter experts. The solutions given here are highly reliable and accurate. It is given in a step-by-step manner, which helps students to understand how to solve the problem.
Students can also check the NCERT solutions given on Shiksha's page. To have a better understanding of Class 12 Physics Chapter 9, they must also read Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Nine Ray Optics And Optical Instrument
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter Nine NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Ray Optics And Optical Instruments – Very Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Nine Long Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Objective Type Questions
- FAQs Related to Physics Chapter Nine NCERT Exemplar
- JEE Mains 2022
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Nine Ray Optics And Optical Instrument
One of the best things is that the PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Nine, once downloaded, can be accessed from anywhere without any internet connection. The students can read it while traveling and even if they are at a remote location. The PDF is well structured and neatly arranged, and contains all types of questions from very short, short, long, and objective types. The questions are concept and application-based, which deepens students' understanding of important topics like refraction, reflection, mirrors, lenses, and optical instruments. The PDF is ideal for preparing for various entrance exams like NEET and JEE. The PDF is available in a printable format. Students can also get the printout and practice on paper. Preparation from the NCERT Exemplar PDF boosts students' exam confidence.
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter Nine NCERT Exemplar
The following are the important formulas related to Class 12 Chapter 9 Physics:
Mirror Formula
Lens Formula
Magnification by Mirror
Magnification by Lens
Lens Maker’s Formula
Total Internal Reflection Condition
Power of a Lens (in diopters)
Angular Magnification (Simple Microscope)
Magnifying Power of Compound Microscope
Magnifying Power of Astronomical Telescope (Normal Adjustment)
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Short Answer Type Questions
Find below the answer:
Commonly asked questions
A circular disc of radius R is placed co-axially and horizontally inside an opaque hemispherical bowl of radius a (figure). The far edge of the disc is just visible when viewed from the edge of the bowl. The bowl is filled with transparent liquid of refractive index μ. and the near edge of the disc becomes just visible. How far below the top of the bowl is the disc placed?
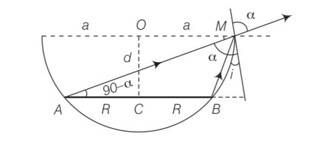
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Refering to the figure, AM is the direction of incidence ray before liquid is filled. After liquid is filled in, BM is the direction of the incident ray. Refracted ray in both cases is same as that along AM
N= 900, OM= a, CB = NB= a-R, AN= a+R
Sint=A short object of length L is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror away from focus. The object distance is u. If the mirror has a focal length f what will be the length of the image? You may take L << |v – f |.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Since, the object distance is u. Let us consider the two ends of the object be at distance
So u1= u+L/2 and u2=u+L/2 respectively so that|u1- u2| =L .
Let the image of the two
ends be formed at v1 and v2, respectively so that the image length would be
L’= |v1-v2|……… (1)
Applying mirror formula 1/v+1/u=1/f or v= fu/u-f
On solving two positions of image v1= v2=
For length substituting in equation 1
L’= |v1-v2|=
The objects is short and kept away from focus we have
<< (
Hence L’=
This is required expression.
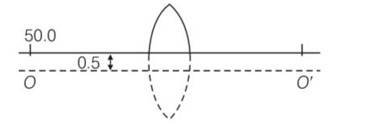
A thin convex lens of focal length 25 cm is cut into two pieces 0.5 cm above the principal axis. The top part is placed at (0, 0) and an object is placed at (-50 cm, 0). Find the coordinates of the image.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If there was no cut, then the object would have been at a height of 0.5 cm from the principal axis OO’.
Applying lens formula, we have
1/v-1/u=1/f Z
=
V= 50cm
Magnification m = v/u= 50/-50=-1
So coordinates of image are (50cm, -1cm)
In many experimental set-ups, the source and screen are fixed at a distance say D and the lens is movable. Show that there are two positions for the lens for which an image is formed on the screen. Find the distance between these points and the ratio of the image sizes for these two points.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
1/f=1/v-1/u
-u+V=D
U=-(D-v)
Putting
On solving v2-Dv+Dt=0
So v=
When the objects distance is
The image forms at
Similarly when the objects distance is
The image forms at
The distance between the poles for these two objects distance is
If u = D/2+d/2 then the image is at v=D/2-d/2
The magnification m1=
If u =D-d/2then v= D+d/2
The magnification m2=
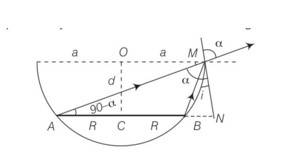
A jar of height h is filled with a transparent liquid of refraction index μ (figure). At the center of the jar on the bottom surface is a dot. Find the minimum diameter of a disc, such that when placed on the top surface symmetrically about the center, the dot is invisible.
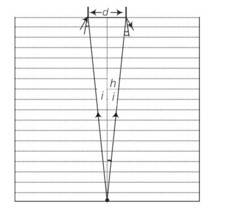
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let d be the diameter of the disc. The spot shall be invisible if the incident rays from the dot at O to the surface at d / 2 at the critical angle.
Let I be the angle of incidence. Using relationship between refractive index and critical angle,
SinC= 1/
= tani
D=
A myopic adult has a far point at 0.1 m. His power of accomodation is 4 diopters.
(i) What power lenses are required to see distant objects?
(ii) What is his near point without glasses?
(iii) What is his near point with glasses? (Take the image distance from the lens of the eye to the retina to be 2 cm.)
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) As we know that power Pf=1/f=1/0.1+1/0.02=60D
By corrective lens the object distance at far pointP’f=1/f’=1/1/0.02=50D
Total power P’f=Pf+Pg
Pg=-10D
(ii) This power of accommodation is 4D for the normal eye then
4=Pn-Pf where Pn power of near point
So Pn= 64D
1/xn+1/0.002=64 then xn= 1/14=0.07m
(iii) Pn’=Pf’+4=54
After solving xn’=4=0.25m
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Ray Optics And Optical Instruments – Very Short Answer Type Questions
Here are the solutions:
Commonly asked questions
Will the focal length of a lens for red light be more, same or less than that for blue light?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As the refractive index for red is less than that for blue, parallel beams of light incident on a lens will be bent more towards the axis for blue light compared to red.
By lens makers formula 1/f=
So fb
The near vision of an average person is 25 cm. To view an object with an angular magnification of 10, what should be the power of the microscope?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
m=v/u = D/f
So m = 25/10 = 2.5= 0.025m
P= 1/0.025= 40D
This is the required power of lens.
An unsymmetrical double convex thin lens forms the image of a point object on its axis. Will the position of the image change if the lens is reversed?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
no reversibility of lens maker formula is not possible.
Three immiscible liquids of densities d1> d2> d3and refractive indices μ1> μ2> μ3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is h/3. A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
apparent depth = real depth / refractive index
Since, the image formed by Medium1, O2 act as an object for Medium2.
If seen from µ3 ,the apparent depth is O2.
Similarly, the image formed by Medium2, O2 act as an object for Medium3
O2= ( )
= (
Seen from outside the apparent height is
O3 = ( =
= )
This is the expression for required depth.
For a glass prism (μ= √3 ), the angle of minimum deviation is equal to the angle of the prism. Find the angle of the prism.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Prism for is given by
Given that Dm= A
After substituting the values, =
On solving, = 2 cos A/2
So cos A/2 =
So A= 600 so this is the required prism angle
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Nine Long Answer Type Questions
See below the solutions:
Commonly asked questions
Show that for a material with refractive index μ ≥ √2, light incident at angle shall be guided along, a length perpendicular to the incident face.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Any ray entering at an angle I shall be guided along AC if the angle ray makes with the face AC (φ) is greater than the critical angle as per the principle of total internal reflection φ +r =900, therefore sinφ = cosr
Sinφ>
Cosr>
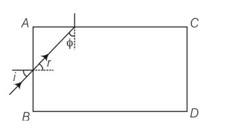
1-cos2r<1-1/
Sin2r<1-1/
Sin2r<1-1/
Sini = sinr
I=
If that is greater than the critical then all other angle of incidence shall be more than the critical angle.
1< -1
>
The mixture of a pure liquid and a solution in a long vertical column (i.e., horizontal dimensions << vertical dimensions) produces diffusion of solute particles and hence a refractive index gradient along the vertical dimension. A ray of light entering the column at right angles to the vertical is deviated from its original path. Find the deviation in travelling a horizontal distance d << h, the height of the column.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let us consider a portion of a ray between x and x+dx inside the liquid. Let the angle of incidence at x be θ and let it enter the thin column at height y. Because of the bending it shall emerge at x+dx with an angle θ+dθ and at a height y+dy . From Snell’s law,
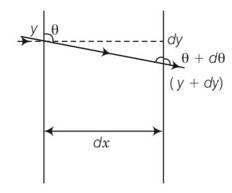
d
tan
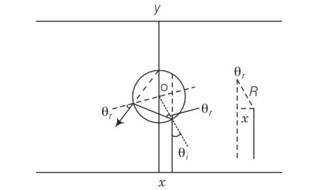
If light passes near a massive object, the gravitational interaction causes a bending of the ray. This can be thought of as happening due to a change in the effective refrative index of the medium given by n(r)=1+2GM/rc2 where r is the distance of the point of consideration from the centre of the mass of the massive body, G is the universal gravitational constant, M the mass of the body and c the speed of light in vacuum. Considering a spherical object find the deviation of the ray from the original path as it grazes the object.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let us consider planes r and r+dr. let the light be incident at an angle
n (r)sin
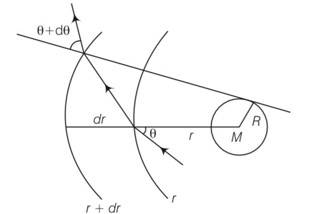
n (r)sin
-dn/drtan
So after integral r2=x2+R2 and tan
2rdr=2xdx
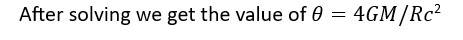
Infinitely long cylinder of radius R is made of an unusual exotic material with refractive index -1 (figure). The cylinder is placed between two planes whose normals are along the y-direction. The centre of the cylinder O lies along they-axis. A narrow laser beam is directed along the y-direction from the lower plate. The laser source is at a horizontal distance x from the diameter in the y direction. Find the range of x such that light emitted from the lower plane does not reach the upper plane.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Since the material is of refractive index , is negative and is positive
| |= | |=| |
Explanation- since the material is of refractive index , is negative and is positive
| |= | |=| |
The total deviation of the outcoming ray from the incoming ray is 4 rays shall not receive if
<4 <
<4 <
sin =x/R
Light emitted from the source shall not reach the receiving plate under this condition.
(i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O) (Figure). Let the thickness of the lens vary as w(b) =w0– b2/α , where b is the vertical distance from the pole, w0is a constant. Using Fermat’s principle, i.e., the time of transit fora ray between the source and observer is an extremum find the condition that all paraxial rays starting from the source will converge at a point O on the axis. Find the focal length.
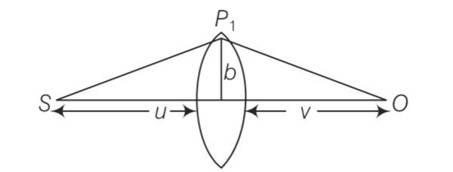
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Time from S to P1 is
t1 =
Time from P1 to O is
t2 = ;
the time required travel through lens is t1 =
so total time is t=1/c(u+v+b2/2D+(n-1)(wo+b2/ ))
after solving we get
differentiating with respect to time
t=1/c(u+v+b2/2D+(n-1)K1In(K2b))
dt/db=0=b/D-(n-1)K1/b
b2= (n-1)K1D
b=
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Objective Type Questions
Here are the questions and solutions:
Commonly asked questions
A ray of light incident at an angle d on a refracting face of a prism emerges from the other face normally. If the angle of the prism is 5° and the prism is mad? of a material of refractive index 1.5, the angle of incidence is
(a) 7.5°
(b) 5°
(c) 15°
(d) 2.5°
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) since deviation = (1.5-1)50= 2.50
But so
A‘ short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is
(a) Blue
(b) Green
(c) Violet
(d) Red
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) Since v ∝ λ, the light of red colour is of the highest wavelength and therefore of the highest speed. Therefore, after travelling through the slab, the red colour emerge first.
An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed 5 m/s and stops at the focus. The image
(a) Moves away from the lens with an uniform speed 5 m/s
(b) Moves away from the lens with an uniform acceleration
(c) Moves away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration
(d) Moves towards the lens with a non-uniform acceleration
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) When an object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed of 5 m/s, the image away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration.
A passenger in an aeroplane shall
(a) Never see a rainbow
(b) May see a primary and a secondary rainbow as concentric circles
(c) May see a primary and a secondary rainbow as concentric arcs
(d) Shall never see a secondary rainbow
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) A passenger in an aeroplane may see a primary and a secondary rainbow like concentric circles.
You are given four sources of light each one providing a light of a single colour—red, blue, green and yellow. Suppose the angle of refraction for a beam of yellow light corresponding to a particular angle of incidence at the interface of two media is 90°. Which of the following statements is correct if the source of yellow light is replaced with that of other lights without changing the angle of incidence?
(a) The beam of red light would undergo total internal reflection.
(b) The beam of red light would bend towards the normal while it gets refracted through the second medium.
(c) The beam of blue light would undergo total internal reflection.
(d) The beam of green light would bend away from the normal as it gets refracted through the second medium.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) According to VIBGYOR, among all given sources of light, the blue light have the smallest wavelength. According to Cauchy relationship, smaller the wavelength higher the refractive index and consequently smaller the critical angle. So, corresponding to blue colour, the critical angle is least which facilitates total internal reflection for the beam of blue light. The beam of green light would also undergo total internal reflection.
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, it will
(a) Act as a convex lens only for the objects that lie on its curved side
(b) Act as a concave lens for the objects that lie on its curved side
(c) Act as a convex lens irrespective of the side on which the object lies
(d) Act as a concave lens irrespective of side on which the object lies
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) R= 20cm, = 1.5, f= = =40cm so lens acts as convex lens.
The phenomena involved in the reflection of radio waves by ionosphere is similar to
(a) Reflection of light by a plane mirror
(b) Total internal reflection of light in air during a mirage
(c) Dispersion of light by water molecules during the formation of a rainbow
(d) Scattering of light by the particles of air
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) The phenomenon involved in the reflection of radio waves by ionosphere is similar to total internal reflection of light in air during a mirage i.e., angle of incidence is greater than critical angle.
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (figure). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
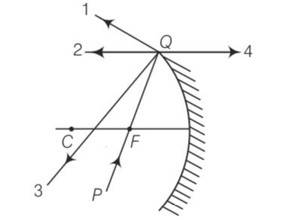
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) The PQ ray of light passes through focus F and incident on the concave mirror, after reflection, should become parallel to the principal axis and shown by ray-2 in the figure.
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path shown is correct?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
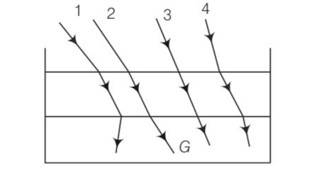
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Here, light ray goes from (optically) rarer medium air to optically denser terpentine, then it bends towards the normal i.e., i>r whereas when it goes from to optically denser medium terpentine to rarer medium water. then it bends away the normal i.e., i
A far is moving with a constant speed of 60 km h-1on a straight road. Looking at the rear view mirror, the driver finds that the car following him is at a distance of 100 m and is approaching with a speed of 5 km h-1.
In order to keep track of the car in the rear, the driver begins to glance alternatively at the rear and side mirror of his car after every 2 s till the other car overtakes. If the two cars were maintaining their speeds, which of the following statement (s) is/are correct?
(a) The speed of the car in the rear is 65 km h-1
(b) In the side mirror, the car in the-rear would appear to approach with a speed of 5 km h-1 to the driver of the leading car
(c) In the rear view mirror, the speed of the approaching car would appear to decrease as the distance between the cars decreases
(d) In the side mirror, the speed of the approaching car would appear to increase as the distance between the cars decreases
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) The speed of the image of the car would appear to increase as the distance between the cars decreases.
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index figure. A ray incident from air (Medium 1) into such a medium (Medium 2) shall follow a path given by
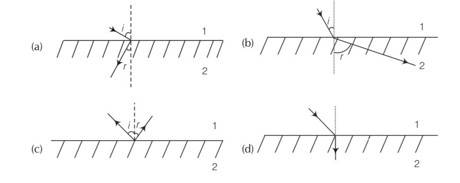
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) The negative refractive index metamaterials are those in which incident ray from air (Medium 1) to them refract or bend differently to that of positive refractive index medium.
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because
(a) The apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge
(b) The angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air
(c) Some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection
(d) Water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, c) When immersed object is seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
The angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air and some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is placed midway on the face AB of figure. When observed from the face AD, the pin shall
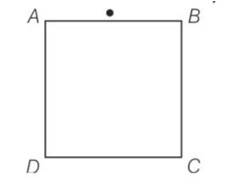
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) For µ = 16., the critical angle, µ = 1/ sin C, we have C = 38.7°, when viewed from AD, as long as angle of incidence on AD of the ray emanating from pin is greater than the critical angle, the light suffers from total internal reflection and cannot be seen through AD.
Between the primary and secondary rainbow, these is a dark band known as Alexandar’s dark band. This is because
(a) Light scattered into this region interfere destructively
(b) There is no light scattered into this region
(c) Light is absorbed in this region
(d) Angle made at the eye by the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42° and 50°
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, d) Alexandar’s dark band lies between the primary and secondary rainbows, forms due to light Scattered into this region interfere destructively.
Since, primary rainbows subtends an angle nearly 41° to 42° at observer's eye, whereas, secondary rainbows subtends an angle nearly 51° to 54° at observer’s eye w.r.t. incident light ray. So, the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42°and50°.
A magnifying glass is used, as the object to be viewed can be brought closer to the eye than the normal near point. This results in
(a) A larger angle to be subtended by the object at the eye and hence, viewed in greater detail
(b) The formation of a virtual erect image
(c) Increase in the field of view
(d) Infinite magnification at the near point
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b) A magnifying glass is used, as the object to be viewed can be brought closer to the eye than the normal near point. This results in a larger angle to be subtended by the object at the eye and hence, viewed in greater detail. Morever, the formation of a virtual erect and enlarged image, takes place.
An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length 20 m and an eyepiece of focal length 2 cm.
(a) The length of the telescope tube is 20.02 m
(b) The magnification is 1000
(c) The image formed is inverted
(d) An objective of a larger aperture will increase the brightness and reduce chromatic aberration of the
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, c) The length of the telescope tube L= f0+fe= 20+0.02= 20.02m
Also magnification is = 20/0.02= 1000
And image formed is inverted
FAQs Related to Physics Chapter Nine NCERT Exemplar
The following are the frequently asked questions related to NCERT Exemplar Ray Optics And Optical Instruments:
Commonly asked questions
A spherically symmetric charge distribution is considered with charge density varying
as
Where, r(r < R) is the distance from the centre O (as shown in figure). The electric field at point P will be:
As,
Find the ratio of energies of photos product due to transition of an electron of hydrogen atom from its (i) second permitted energy level to the first level. and (ii) the highest permitted energy level to the first permitted level.
Given below are two statements.
Statement I : Electric potential is constant within and at the surface of each conductor.
Statement II : Electric field just outside a charged conductor is perpendicular to the surface of the conductor at every point.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
‘A’ at static equilibrium, E (inside conductor) = 0
Two bodies of mass 1kg and 3kg have position vectors respectively. The magnitude of position vector of centre of mass of this system will be similar to the magnitude of vector:
=
Given below are two statements : One is labeled as Assertion (A) and the other is labeled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A) : Clothes containing oil grease statins cannot be cleaned by water wash.
Reason (R) : Because the angle of contact between the oil/grease and water is obtuse.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the option given below.
Water molecule doesn’t stick with oil/ grease drops due to obtuse angle of contact between then.
The time period of oscillation of a simple pendulum of length L suspended from the roof of a vehicle, which moves without friction down an inclined plane of inclination , is given by:
goff = g cos
Two metallic wires of identical dimensions are connected in series. If are the conductivities of these wires respectively, the effective conductivity of the combination is:
R = R1 + R2
An alternating emf E = 440 sin 100t is applied to a circuit containing an inductance of If an a.c. ammeter is connected in the circuit, its reading will be:
E = 440 sin 100 t
Match List – I with List – II:
List – I List – II
(A) UV rays (i) Diagnostic tool in medicine
(B) X-rays(ii) Water purification
(C) Microwave(iii) Communication, Radar
(D) Infrared wave(iv) Improving visibility in foggy daya
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Based an theoretical data.
The kinetic energy of emitted electron is E when the right incident on the metal has wavelength . To double the kinetic energy, the incident light must have wavelength:
-(i)
-(ii)
Find the modulation index of an AM wave having 8V variation where maximum amplitude to the wave is 9V.
Modulation Index,
Variation =
A traveling microscope has 20 divisions per cm on the main scale while its vernier scale has total 50 divisions and 25 vernier scale divisions are equal to 24 main scale divisions, what is the least count of the travelling microscope?
MSD = 20 divisions per cm 1 MSD =
VSD = 50 divisions
As, 25 VSD = 24 MSD
L.C. = 1 MSD – 1 VSD
=
In an experiment of find out diameter of wire using screw gauge, the following observations were noted:
(A) Screw moves 0.5mm on main scale in one complete rotation
(B) Total divisions on circular scale = 50
(C) Main scale reading is 2.5 mm
(D) 45th division of circular scale is in the pitch line
(E) Instrument has 0.03 mm negative error
Then the diameter of wire is:
MS – Reading = 2.5 mm.
50 division on CS = 0.5 mm on MS.
= .45 mm on M.S.
So, diameter = 2.5 mm
+0.45 mm
+0.03 mm
= 2.98 mm
Given below are two statements: One is labeled as Assertion (A) and other is labeler as Reason (R).
Assertion (A) : Time period of oscillation of a liquid drop depends on surface tension (S), if density of the liquid is and radius of the drop is r, then
is dimensionally correct, where K is dimensionless.
Reason (R) : Using dimensional analysis we get R.H.S. having different dimension than that of time period.
In the light of above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
A smooth circular groove has a smooth vertical wall as shown in figure. A block of mass m moves against the wall with a speed v. Which of the following curve represents the correct relation between the normal reaction on the block by the wall (N) and speed of the block (v)?
A ball is projected with kinetic energy E, at an angle of 60° to the horizontal. The kinetic energy of this ball at the highest point of its flight will become:
A coil of inductance 1H and resistance 100 is connected to a battery of 6.V. Determine approximately:
(A)The time elapsed before the current acquires half of its steady – state value.
(B)The energy stored in the magnetic field associated with the coil at instant 15ms after the circuit is switched on. (Given In 2 = 0.693, e3/2 = 0.25)
L = 1H, R = 100
So,
If the potential barrier across a p-n junction is 0.6 V. Then the electric field intensity, in the depletion region having the width of 6 × 10-6m, will be________ × 105 N/C.
As, Ed = VB
A ball is thrown up vertically with a certain velocity so that, it reaches a maximum height h. Find the ratio of the times in which it is at height while going up and coming down respectively.
If t =
then
= 0
An object is projected in the air with initial velocity u at an angle q. The projectile motion is such that the horizontal range R, in maximum. Another object is projected in the air with a horizontal range half of the range of first object. The initial velocity remains same in both the case. The value of the angle of projection, at which the second object is projected, will be_______degree.
If the acceleration due to gravity experienced by a point mass at a height h above the surface of earth is same as that of the acceleration due to gravity at a dept ah(h <
h << R
The pressure P1 and density d1 of diatomic gas changes suddenly to P2(>P1) and d2 respectively during an adiabatic process. The temperature of the gas increases and becomes ________times of its initial temperature. (given
For adiabatic process – PVY = const
One mole of a monoatomic gas is mixed with three moles of a diatomic gas. The molecular specific heat of mixture of constant volume is then the value of will be________.
(Assume that the given diatomic gas has no vibrational mode.)
As, Cv (mix) =
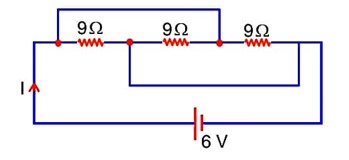
The current I flowing through the given circuit will be_________A.
A closely wounded circular coil of radius 5cm produces a magnetic field of 37.68 × 104 T at its centre. The current through the coil is_ A. [Given, number of turns in the coil is 100 and = 3.14]
Two light beams of intensities 4I and 9I interfere on a screen. The phase difference between these beams on the screen at point A is zero and at point B is . The difference of resultant intensities, at the point A and B, will be_________I.
A wire of length 314cm carrying current of 14A is bent to form a circle. The magnetic moment of the coil is_________ A -m2. [Given π = 3.14]
The X-Y plane be taken as the boundary between two transparent media M1 and M2. M1 in has a refractive index of and M2 with Z < 0 has refractive index of A ray of light travelling in M1 along the direction given by the vector is incident on the plane of separation. The value of difference between the angle of incident in M1 and the angle of refraction in M2 will be_______ degree.
For angle of incidence ‘i’ :-
cos I =
i = 60°
Using snell’s law :-
sin r =
So, difference, I – r = 60° - 452 = 15°
JEE Mains 2022
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Nine Exam