physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Yes during adiabatic compression the temperature of a gas increases while no heat is
In adiabatic compression dQ=0
From the first law of thermodynamics dU= dQ-dW
dU=-dW
in compression work is done on the gas i.e work done is negative
dU=positive
hence internal energy of the gas increases due to which its temperature increases.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If a refrigerator's doors is kept open, then room will become hot, because amount of heat removed would be less than the amount of heat released in the room.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
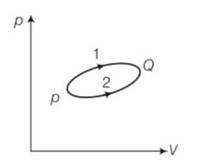
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
For path1
Heat Q1= 1000J
Work done =W1
For path 2
Work done W2= W1-100
As change in internal energy is same
dU=Q1-W1=Q2-W2
1000-W1=Q2-W1+100
Q2= 1000-100= 900J
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Yes this is possible when the entire heat supplied to the system is utilised in expansion.
So its working against the surroundings.
New answer posted
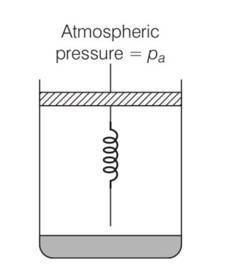
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Initially the piston is in equilibrium Pi=Pa
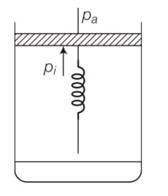
(b) On supplying heat , the gas expands from Vo to Vi
so increase in volume of the gas =Vi-Vo
as the piston is of unit cross sectional area hence extension in the spring
x=
force exerted by the spring on the piston= F= kx= K(Vi - Vo)
hence final pressure =Pf =Pa +kx
= Pa+K ( )
(c) From first law of thermodynamics
dQ=dU+dW
dU=Cv(T-To) = Cv(T-To)
T=
Work done by the gas =pdV+ increase in PE of the spring
= Pa(V1-Vo) + x2
dQ=dU+dW
= Cv(T-To)+Pa(V-Vo)+ x2
= Cv(T-To)+Pa(v-Vo)+1/2 ( )2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Slope of the curve = f(V) , where V is the volume
Slope of P = f(V) curve at ((Po, V0 )= f(Vo)
Slope of adiabatic at (Po, V0 )= k(-Y)Vo-1-Y =-YPo/Vo
Now heat absorbed in the process P= f(V)
dQ=dU+dW= nCvdT+pdV
pV=nRT
T= pV/nR
T=
nCv
After solving we get
=
Heat is absorbed where dQ/dV>0 when gas expands
Hence YPo+Vof'(Vo)>0 or f'(Vo)>(-Y )
New answer posted
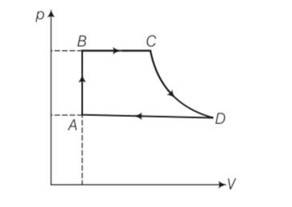
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) For process AB
Volume is constant , hence work done dW=0
dQ=dU+dW=dU+0=dU
= nCvdT= nCv(TB-TA)
=
=
Heat exchanged =
(b) For process BC , p =constant
dQ= dU+dW =
heat exchanged =
(c) For process CD , because CD is adiabatic , dQ= heat exchanged =0
(d) DA involves compression of gas from VD to VA at constant pressure PA
heat transferred as similar way as BC1
hence dQ = PA(VA-VD)
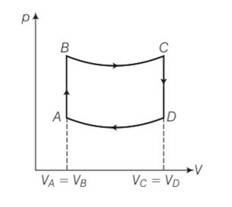
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) For the process AB
dV=0 and dW=0
dQ=dU+dW=dU
dQ=dU= change in internal energy , so heat utilised is equal to change in internal energy.
Since p= in adiabatic temperature is directly proportional to pressure. So heat is supplied to the system in process AB.
(b) For the process CD volume is constant but the pressure decreases, hence temperature also decreases . so heat is also given to the surroundings.
(c) WAB= , WCD=
WBC=
= [pV]=
WDA=
B and C lies on adiabatic curve BC
PBVBY= PCVCY
PC = PB( )Y = PB( )Y= 2-YPB
Total work done by the engine in one cycle ABCD
New answer posted
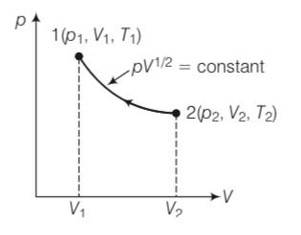
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
pV1/2= constant
P=k/
Work done from 1 to 2
W=
from ideal equation = pV=nRT
T= pV/nR=
T=
T1= , T1=
=
U=
= RT1( )
=2p1V11/2( )
= 2p1V11/2(2 )
= 2p1V1( )= 2RT1( )
=
= RT1( )+ 2RT1( )
=
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b), (c), (d) When the hot milk in the table is transferred to the surroundings by conduction, convection and radiation.
According to newton's law of cooling temperature of the milk falls of exponentially. Heat also will be transferred from surroundings to the milk but will be lesser than that of transferred from milk to surroundings. So option b, c, d satisfy.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers