- Thermal Properties of Matter Questions and Answers
- JEE Mains 2021
- JEE Mains 01 MT
Thermal Properties of Matter Questions and Answers
| 11.1 We would like to prepare a scale whose length does not change with temperature. It is proposed to prepare a unit scale of this type whose length remains, say 10 cm. We can use a bimetallic strip made of brass and iron each of different length whose length (both components) would change in such a way that difference between their lengths remain constant. If 5 αiron =1.2 10-5/K and αbrass 1.8 10-5 /K , what should we take as length of each strip? |
| Explanation- As liron-lbrass =10cm= constant at all temperature Let lo be the length of temperature at 00C and l be the length after change in temperature liron-lbrass =10cm liron(1+ )-lbrass(1+ )=10cm Iiron iron= Ibrass brass =1.8/1.2=3/2
Lbrass=20cm and liron=30cm |
| 11.2 We would like to make a vessel whose volume does not change with temperature (take a hint from the problem above). We can use brass and iron ( βvbrass = 6 × 10-5/K and βviron = 3.55 ×10-5/ K) to create a volume of 100 cc. How do you think you can achieve this. |
| Explanation- As difference in volume is constant By considering the diagram Let Vio , Vbo be the volume of iron and brass vessel at 00C Vi,Vb be the volume of iron and brass vessel at 0C be the coefficient of volume expansion of iron and brass. Vio -Vbo= 100cc= Vi-Vb Vi =Vio(1+ i ) Vb =Vbo(1+ b ) Vi-Vb = (Vio -Vbo)+ Since Vi-Vb= constant Vio i= Vbo
Using above equations
Vbo = 144.9cc |
| 11.3 Calculate the stress developed inside a tooth cavity filled with copper when hot tea at temperature of 57 0C is drunk. You can take body (tooth) temperature to be 370 C and α = 1.7× 10-5 / 0C , bulk modulus for copper = 140 × 109 N/m2. |
| Explanation- Decrease in temperature = 57-37= 200C Coefficient of linear expansion = 1.7 oC Bulk modulus for copper B = 140 Coefficient of cubical expansion = 3 = 5.1 Let initial volume of the cavity be V and its volume increases by due to increase in temperature.
Thermal stress produced = B = B = 140 = 1428 2 |
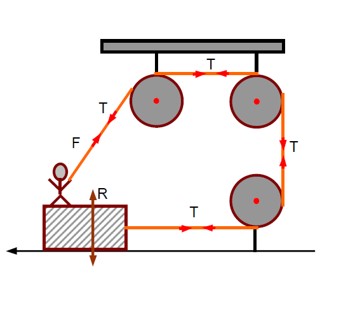
| 11.4 A rail track made of steel having length 10 m is clamped on a railway line at its two ends (Fig). On a summer day due to rise in temperature by 20° C , it is deformed as shown in figure. Find x (displacement of the centre) if αsteel = 1.2× 10-5 /°C. |
| Explanation- By applying Pythagoras theorem in given figure 2 x= =1/2 = ½ =1/2 As Increase in is very small so we neglect it =1/2
By using this value in above in equation x=1/2 = ½ L = = 5 = 5 |
Commonly asked questions
A glass full of hot milk is poured on the table. It begins to cool gradually. Which of the following is correct?
(a) The rate of cooling is constant till milk attains the temperature of the surrounding
(b) The temperature of milk falls off exponentially with time
(c) While cooling, there is a flow of heat from milk to the surrounding as well as from surrounding to the milk but the net flow of heat is from milk to the surrounding and that is why it cools
(d) All three phenomenon, conduction, convection and radiation are responsible for the loss of heat from milk to the surroundings
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b), (c), (d) When the hot milk in the table is transferred to the surroundings by conduction, convection and radiation.
According to newton's law of cooling temperature of the milk falls of exponentially. Heat also will be transferred from surroundings to the milk but will be lesser than that of transferred from milk to surroundings. So option b, c, d satisfy.
We would like to prepare a scale whose length does not change with temperature. It is proposed to prepare a unit scale of this type whose length remains, say 10 cm. We can use a bimetallic strip made of brass and iron each of different length whose length (both components) would change in such a way that difference between their lengths remain constant. If 5 αiron =1.2 10-5/K and αbrass 1.8 10-5 /K , what should we take as length of each strip?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As liron-lbrass =10cm= constant at all temperature
Let lo be the length of temperature at 00C and l be the length after change in temperature
liron-lbrass =10cm
liron (1+ )-lbrass (1+ )=10cm
Iiron iron= Ibrass brass
=1.8/1.2=3/2
Lbrass=20cm and liron=30cm
We would like to make a vessel whose volume does not change with temperature (take a hint from the problem above). We can use brass and iron ( βvbrass = 6 × 10-5/K and βviron = 3.55 ×10-5/ K) to create a volume of 100 cc. How do you think you can achieve this.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As difference in volume is constant
By considering the diagram
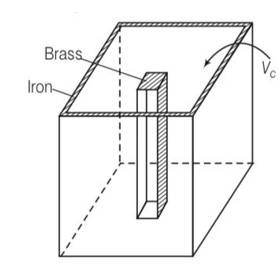
Let Vio , Vbo be the volume of iron and brass vessel at 00C
Vi,Vb be the volume of iron and brass vessel at 0C
be the coefficient of volume expansion of iron and brass.
Vio -Vbo= 100cc= Vi-Vb
Vi =Vio(1+ i )
Vb =Vbo(1+ b )
Vi-Vb = (Vio -Vbo)+
Since Vi-Vb= constant
Vio i= Vbo
Using above equations
Vbo = 144.9cc
Calculate the stress developed inside a tooth cavity filled with copper when hot tea at temperature of 57 0C is drunk. You can take body (tooth) temperature to be 370 C and α = 1.7× 10-5 / 0C , bulk modulus for copper = 140 × 109 N/m2.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Decrease in temperature = 57-37= 200C
Coefficient of linear expansion = 1.7 oC
Bulk modulus for copper B = 140
Coefficient of cubical expansion = 3 = 5.1
Let initial volume of the cavity be V and its volume increases by due to increase in temperature.
Thermal stress produced = B
= B
= 140
= 1428 2
A rail track made of steel having length 10 m is clamped on a railway line at its two ends (Fig). On a summer day due to rise in temperature by 20° C , it is deformed as shown in figure. Find x (displacement of the centre) if αsteel = 1.2× 10-5 /°C.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
By applying Pythagoras theorem in given figure
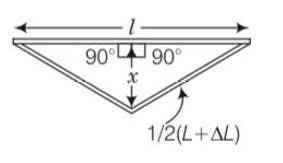
2
x=
=1/2
= ½
=1/2
As Increase in is very small so we neglect it
=1/2
By using this value in above in equation
x=1/2 = ½ L
=
= 5
= 5
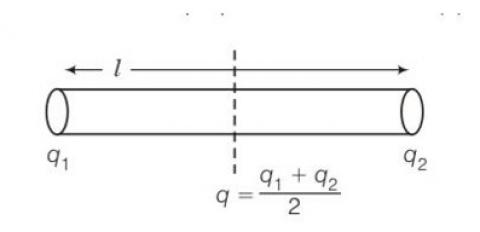
A thin rod having length L0 at 0° C and coefficient of linear expansion α has its two ends maintained at temperatures θ1 and θ2, respectively. Find its new length.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Consider the diagram

Θ= θ1+ θ2/2
Let temperature varies linearly in the rod from its one end to other end, let θ be the temperature of the midpoint of the rod. At steady state
Rate of flow of heat,
dQ/dt =
where k is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the rod
so θ1- θ= θ- θ2
θ= θ1+ θ2/2
L=L0 (1+ )
L= Lo (1+ )
According to Stefan’s law of radiation, a black body radiates energy σT 4 from its unit surface area every second where T is the surface temperature of the black body and σ = 5.67 × 10-8 W/m2K4 is known as Stefan’s constant. A nuclear weapon may be thought of as a ball of radius 0.5 m. When detonated, it reaches temperature of 106K and can be treated as a black body.
(a) Estimate the power it radiates.
(b) If surrounding has water at 30 C° , how much water can 10% of the energy produced evaporate in 1 s? Sw 4186.0 J/kg K and Lv 22.6
(c) If all this energy U is in the form of radiation, corresponding momentum is p = U/c. How much momentum per unit time does it impart on unit area at a distance of 1 km?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Power radiated by stefan’s law
P= 4 R2)T4
= 5.67
= 1.78 =1.8
(b) Energy available per second U= 1.8 = 18 16J/s
Actual energy required to evaporate water = 10%of 18
=1.8 J/s
Energy used per second to raise the temperature of m kg of water from 300C to 1000C and then into vapour at 1000C
=msw +mL= m
= 2.93
As per question , 25.53 = 1.8
m=
(c) Momentum per unit time
P= U/c= 2
Momentum per unit time
Area p= p/4
d=47.7N/m2
Is the bulb of a thermometer made of diathermic or adiabatic wall?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As diathermic walls allow exchange of heat energy between two systems and adiabatic walls do not, hence diathermic walls are used to make the bulb of a thermometer.
A student records the initial length l, change in temperature ?T and change in length ?l of a rod as follows:
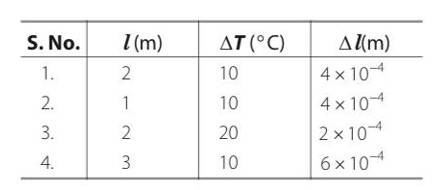
If the first observation is correct, what can you say about observations 2, 3 and 4.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
= oC-1
From next observation
From next observation
From next observation = so this value satisfies the equation.
Why does a metal bar appear hotter than a wooden bar at the same temperature? Equivalently it also appears cooler than wooden bar if they are both colder than room temperature.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Due to difference in conductivity metals having high conductivity compared to wood. On touch with a finger heat from the surroundings flows faster to the finger from metals and so one feels the heat.
Similarly when one touches a cold metal the heat from the finger flows away to the surroundings faster.
Calculate the temperature which has same numeral value on celsius and Fahrenheit scale.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
According to the formula
F=C=Q
= Q=-40C or 40F
These days people use steel utensils with copper bottom. This is supposed to be good for uniform heating of food. Explain this effect using the fact that copper is the better conductor.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As copper is a good conductor of heat as compared to steel. The steel utensils with copper bottom absorbs heat more quickly than steel and give it to food in utensils. So, food heated uniformly and quickly.
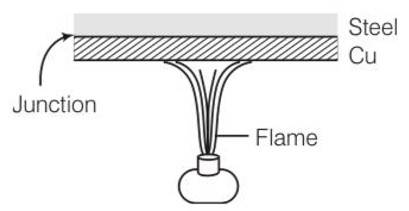
Find out the increase in moment of inertia I of a uniform rod (coefficient of linear expansion α ) about its perpendicular bisector when its temperature is slightly increased by ?T.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let the mass and length of a uniform rod be M and l respectively.
Moment of inertia of the rod about its perpendicular bisector I= ml2/12
Increase in length of the rod when temperature is increased by T is given by
So new moment of inertia of the rod = =
As change in length is very small therefore neglecting so we get
I’= = l+mI
Increase in moment of inertia =
During summers in India, one of the common practice to keep cool is to make ice balls of crushed ice, dip it in flavoured sugar syrup and sip it. For this a stick is inserted into crushed ice and is squeezed in the palm to make it into the ball. Equivalently in winter, in those areas where it snows, people make snow balls and throw around. Explain the formation of ball out of crushed ice or snow in the light of P–T diagram of water.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Increasing pressure at 00C and 1 atm takes ice into liquid state and decreasing pressure in liquid state at 00C and 1 atm takes to ice state.
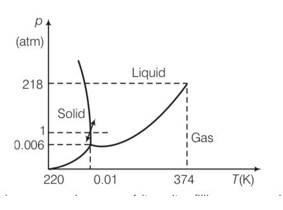
When crushed ice is squeezed, some of it melts, filling up the gap between ice flakes upon releasing pressure. This water freezes, binding all ice flakes and making the ball more stable.
100 g of water is supercooled to –10° C. At this point, due to some disturbance mechanised or otherwise some of it suddenly freezes to ice. What will be the temperature of the resultant mixture and how much mass would freeze? [Sw=1cal/g/ and Lfusion= 80cal/g]
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Mass of water m =100
Change in temperature
Specific heat of water Sw= 1cal/g C
Latent heat of fusion of water Lfusion= 80cal/g
Heat required to bring water in super cooling from -10 to 0
Q= ms
Let m gram of ice be melted Q= mL
m=Q/L=1000/80= 12.5g
One day in the morning, Ramesh filled up 1/3 bucket of hot water from geyser, to take bath. Remaining 2/3 was to be filled by cold water (at room temperature) to bring mixture to a comfortable temperature. Suddenly Ramesh had to attend to something which would take some times, say 5-10 minutes before he could take bath. Now he had two options:
(i) Fill the remaining bucket completely by cold water and then attend to the work,
(ii) First attend to the work and fill the remaining bucket just before taking bath. Which option do you think would have kept water warmer ? Explain
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The first option kept water warmer because according to newton's law of cooling the rate of loss of heat is directly proportional to the difference of temperature of the body and the surroundings and in the first case temperature difference is less. So rate of loss of heat will be less.
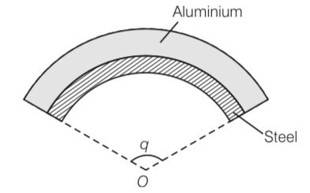
A bimetallic strip is made of aluminium and steel (αAl > αsteel ) . On heating, the strip will
(a) Remain straight
(b) Get twisted
(c) Will bend with aluminium on concave side
(d) Will bend with steel on concave side
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) As , aluminium will expand more . so it would have larger radius of curvature. So aluminium will expand and will outside region.
A uniform metallic rod rotates about its perpendicular bisector with constant angular speed. If it is heated uniformly to raise its temperature slightly
(a) Its speed of rotation increases
(b) Its speed of rotation decreases
(c) Its speed of rotation remains same
(d) Its speed increases because its moment of inertia increases
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
L = angular momentum = Iw = constant
I1w1=I2w2
Due to expansion of the rod I2>I1
w2
The graph between two temperature scales A and B is shown in Fig. Between upper fixed point and lower fixed point there are 150 equal division on scale A and 100 on scale B. The relationship for conversion between the two scales is given by
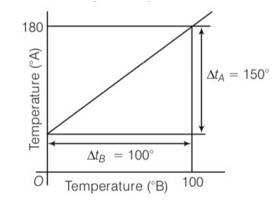
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Lowest point for scale A is 300 and lowest point for scale B is 00. Highest point for the scale A is 1800 and for scale B is 1000
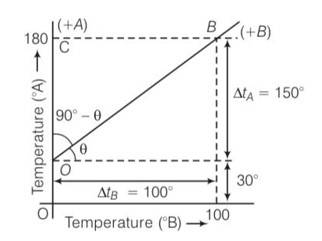
,LFP= lower fixed point , UFP= upper fixed point
An aluminium sphere is dipped into water. Which of the following is true?
(a) Buoyancy will be less in water at 0°C than that in water at 4°C.
(b) Buoyancy will be more in water at 0°C than that in water at 4°C.
(c) Buoyancy in water at 0°C will be same as that in water at 4°C.
(d) Buoyancy may be more or less in water at 4°C depending on the radius of the sphere.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) F= V
F
Hence buoyancy will be less in water at 00C than that in water at 40C.
As the temperature is increased, the time period of a pendulum
(a) Increases as its effective length increases even though its centre of mass still remains at the centre of the bob
(b) Decreases as its effective length increases even though its centre of mass still remains at the centre of the bob
(c) Increases as its effective length increases due to shifting of centre of mass below the centre of the bob
(d) Decreases as its effective length remains same but the centre of mass shifts above the centre of the bob
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As the temperature is increased length of the pendulum increases.
T=2
Heat is associated with
(a) Kinetic energy of random motion of molecules
(b) Kinetic energy of orderly motion of molecules
(c) Total kinetic energy of random and orderly motion of molecules
(d) Kinetic energy of random motion in some cases and kinetic energy of orderly motion in other
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) We know that temperature increases vibrations of molecules about their mean position increases. Hence kinetic energy associated with random motion of molecules increases.
The radius of a metal sphere at room temperature T is R, and the coefficient of linear expansion of the metal is α. The sphere is heated a little by a temperature ?T so that its new temperature is T+ ?T. The increase in the volume of the sphere is approximately
(a) 2παR?T
(b) πR2α?T
(c) 4πR3?T/3
(d) 4παR3 ?T
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) Let radius of sphere be R . as the temperature increases radius of the sphere increases.
Original volume Vo= 3
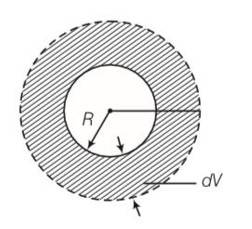
Coefficient linear expansion =
Coefficient of volume expansion =3
3 , dV= 4 R3 =increase in volume
A sphere, a cube and a thin circular plate, all of same material and same mass are initially heated to same high temperature.
(a) Plate will cool fastest and cube the slowest
(b) Sphere will cool fastest and cube the slowest
(c) Plate will cool fastest and sphere the slowest
(d) Cube will cool fastest and plate the slowest.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) density = mass/volume as density is same so volume is also same.
According to Stefan’s law H AT4 where A is the area and T is the temperature
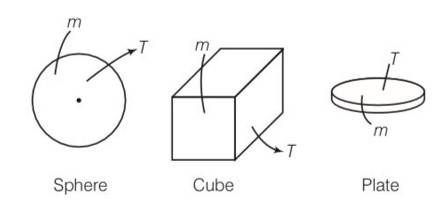
Hsphere:Hcube:Hplate= Asphere:Acube:Aplate
As Aplate is maximum.
Hence the plate will cool the fastest.
Mark the correct options:
(a) A system X is in thermal equilibrium with Y but not with Z. System Y and Z may be in thermal equilibrium with each other
(b) A system X is in thermal equilibrium with Y but not with Z. Systems Y and Z are not in thermal equilibrium with each other
(c) A system X is neither in thermal equilibrium with Y nor with Z. The systems Y and Z must be in thermal equilibrium with each other
(d) A system X is neither in thermal equilibrium with Y nor with Z. The system Y and Z may be in thermal equilibrium with each other
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b), (d) Tx=Ty when x and y are in thermal equilibrium.
Tx TZ when x and z are not in thermal equilibrium.
Ty TZ
Hence y and z are not In thermal equilibrium.
Given Tx Ty
And Tx TZ
We cannot say about equilibrium of y and z.
They may or may not in thermal equilibrium
‘Gulab Jamuns’ (assumed to be spherical) are to be heated in an oven. They are available in two sizes, one twice bigger (in radius) than the other. Pizzas (assumed to be discs) are also to be heated in oven. They are also in two sizes, one twice big (in radius) than the other. All four are put together to be heated to oven temperature. Choose the correct option from the following:
(a) Both size gulab jamuns will get heated in the same time
(b) Smaller gulab jamuns are heated before bigger ones
(c) Smaller pizzas are heated before bigger ones
(d) Bigger pizzas are heated before smaller ones
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b), (c) Smaller gulab jamun having least surface area hence they will be heated first. As in case of smaller gulab jamun heat radiates will be less.
Similarly smaller pizzas are heated before bigger ones because of smaller surface area.
Refer to the plot of temperature versus time (Fig) showing the changes in the state of ice on heating (not to scale) Which of the following is correct?
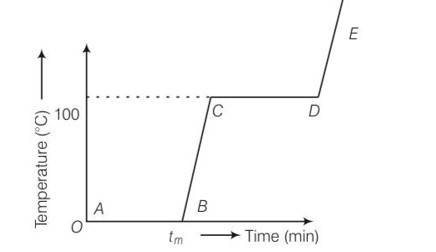
(a) The region AB represents ice and water in thermal equilibrium
(b) At B water starts boiling
(c) At C all the water gets converted into steam
(d) C to D represents water and steam in equilibrium at boiling point
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (d) During the process AB temperature of the system is 00C . hence it represents phase change that is transformation of ice into water while temperature remains 00C.
BC represents rise in temperature of water from 00C to 1000C. now water starts converting into steam which is represented by CD.
Which is only represents by a, d options
A fighter jet is flying horizontally at a certain with a speed of 200ms-1. When it passes directly overhead ad anti-aircraft gun, a bullet is fired from the gun, at an angle (θ)with the horizontal, to hit the jet. If the bullet speed is 400m/s, the value of (θ)will be _____________.
B → fighter jet
A → anti-Air craft gun
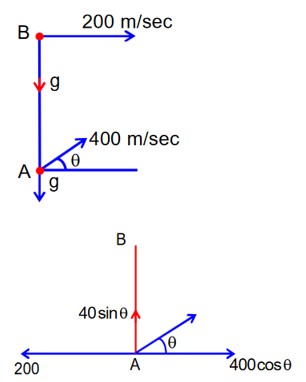
Draw velocity diagram of A w.r.t. B
If A hits B
Then Relative velocity perpendicular to the line joining A to B will be zero.
That means 400 cos q = 200
A ball of mass 0.5 kg is dropped from the height of 10m. The height, at which the magnitude of velocity becomes equal to the magnitude of acceleration due to gravity, is __________m.
[Use g = 10m/s2]
Let ‘h’ be the height at which velocity becomes equal to magnitude of Acceleration
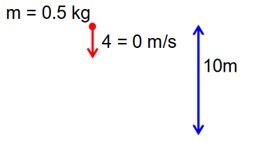
v = g = 10
v = u + at
10 = 0 + 10t
t = 1 sec
= 5m
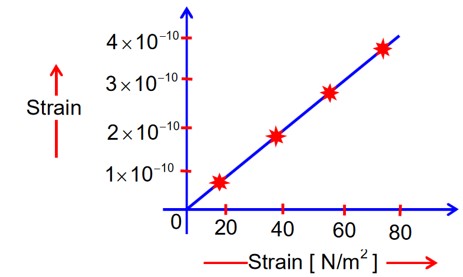
The elastic behavior of material for linear stress and linear strain, is shown in the figure. The energy density for a linear strain of 5 × 10-4 is __________KJ/m3. Assume that material is elastic upto the linear strain of 5 × 10-4.
Y → young’s modules of elasticity.
Stress at strain 5 × 10-4
=
= 108
The elongation of a wire on the surface of the earth is 10-4m. The same wire of same dimensions is elongated by 6 × 10-5 m on another planet. The acceleration due to gravity on the planet will be__________ms-2. (Take acceleration due to gravity on the surface of earth = 10 ms-2)
(change in length)
6 m/sec2
A 20 mH coil carrying constant current is connected to a battery of 20 V through a switch. Now after switch is opened current becomes zero in 100 The average e.m.f. induced in the coil is__________V.
Decay of current in Inductor is given by,
At t = 100
i = 0
i.e. i = i0 -(1)
e.m.f induced
=
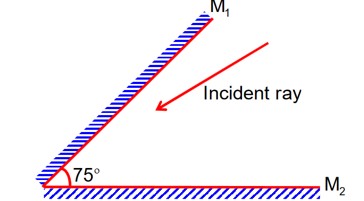
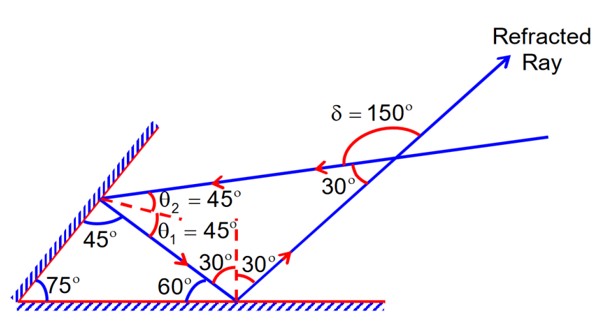
A light ray is incident, at an incident angle q1, on the system of two plane mirrors M1 and M2 having an inclination angle 75° between them (as shown in figure). After reflecting from mirror M1 it gets reflected back by the mirror M2 with an angle of reflection 30°. The total deviation of the ray will be ___________ degree.
= 360 – 2 × 75° = 210°
Total deviation =
In a vernier calipers, each cm on the main scale is divided into 20 equal parts. If tenth vernier scale division coincides with nineth main scale division. Then the value of vernier constant will be__________× 10-2mm.
Let ‘x’ he the value of one division of main scale
Let y be value of one division on venire scale given
10 y = 9 x
Least count =
= 0.005 cm
= 5 × 10-2 mm
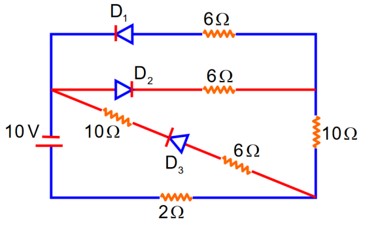
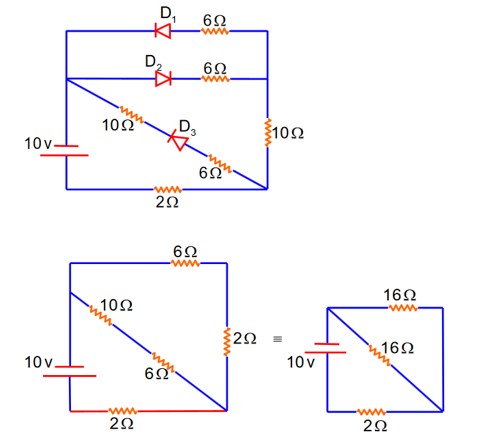
As per the given circuit, the value of current through the battery will be__________A.
Forward biased offer zero Resistance
D2} Reversed biased offers Infinite Resistance
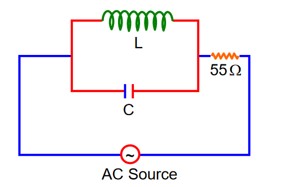
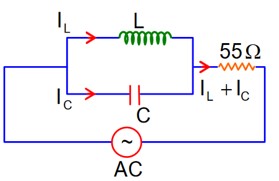
A 110 V, 50Hz, AC source is connected in the circuit (as shown in figure). The current through the resistance at resonance in the circuit, will be__________A.
At Resonance
XL = XC
then lL = lC
Now phasor diagram
for L & C
So, Net current = zero
Therefore current through R circuit at resonance will be zero
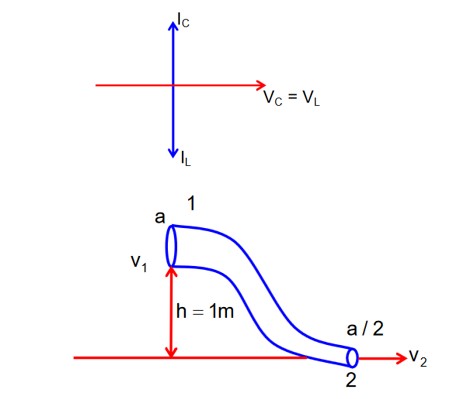
An ideal fluid of density 800kgm-3, flows smoothly through a bent pipe (as shown in figure) that tapers in cross-sectional area from a to The pressure difference between the wide and narrow sections of pipe is 4100 Pa. At wider section, the velocity of fluid is for x = ________. (Given g = 10 ms-2)
JEE Mains 2021
JEE Mains 2021
Commonly asked questions
A 2 µF capacitor C₁ is first charged to a potential difference of 10V using a battery. Then the battery is removed and the capacitor is connected to an uncharged capacitor C₂ of 8 µF. The charge in C₂ on equilibrium condition is --------- µC. (Round off to the Nearest integer)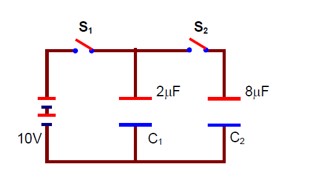
Let the charge on C? be q µC. For the capacitor network:
q/C? = (C? * 10 - q) / C? ⇒ q/8 = (2 * 10 - q) / 2 ⇒ q = 16
A body of mass 1 kg rests on a horizontal floor with which it has a coefficient of static friction 1/√3. It is desired to make the body move by applying the minimum possible force F N. The value of F will be ______. (Round off to Nearest Integer) [Take g = 10 ms?²]
The minimum force F? is calculated as:
F? = (μmg) / √* (1 + μ²)* = ( (1/√3) * 1 * 10 ) / √* (1 + (1/√3)²) = 5N
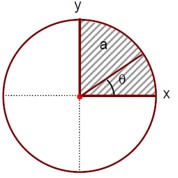
The disc of mass M with uniform surface mass density σ is shown in the figure. The centre of mass of the quarter disc (the shaded area) is at the position (xa/3π, xa/3π) where x is---------. (Round off to the Nearest integer) [a is an area as shown in the figure]
The x and y coordinates of the center of mass are given by:
x? = y? = 4a / 3π
The image of an object placed in air formed by a convex refracting surface is at a distance of 10 m behind the surface. The image is real and is at 2/3 of the distance of the object from the surface. The wavelength of light inside the surface is 2/3 times the wavelength in air. The radius of the curved surface is x/13 m. The value of 'x' is _____.
Given the refractive index μ = λ? / λ = 3/2 and v = 10m, the object distance is u = - (3/2)v = -15m.
Using the lens maker's formula:
μ/v - 1/u = (μ - 1)/R
(3/2)/10 - 1/ (-15) = (3/2 - 1)/R
This gives the radius of curvature R:
R = -30/13 m
A boy of mass 4 kg is standing on a piece of wood having mass 5 kg. If the coefficient of friction between the wood and the floor is 0.5, the maximum force that boy can exert on the rope so that the piece of wood does not move from its place is _____ N. (Round off to the Nearest Integer) [Take g = 10 ms?²]
Assuming the rope in the boy's hand is vertical and using a Free Body Diagram (FBD):
f? = T
R + T = 90 ⇒ R = 90 - T
For the piece of wood not to move, f? ≤ µR:
T ≤ 0.5 (90 - T) ⇒ T ≤ 30N
The electric field intensity produced by the radiation coming from a 100W bulb at a distance of 3 m is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiation coming from 60 W at the same distance is √(x/5) E. Where the value of x = ______.
Electric field squared is proportional to the power P of the bulb (E² ∝ P).
(E' / E)² = (60 / 100) ⇒ E' = E * √* (3/5)*
Sea-water at a frequency f = 9 × 10² Hz, has permittivity ε = 80ε₀ and resistivity ρ = 0.25Ωm. Imagine a parallel plate capacitor is immersed in seawater and is driven by an alternating voltage source V(t) = V₀sin(2πft). Then the conduction current density become 10ˣ times the displacement current density after time t = 1/800 s. The value of x is ______. [Given: 1/(4πε₀) = 9 × 10⁹ Nm²C⁻²]
Conduction current density, J? = E/ρ = (V/d) / ρ = (V? sin (2πft) / (pd)
Displacement current density, J? = ε (dE/dt) = (ε/d) (dV/dt) = (2πfε/d) * V? cos (2πft)
The ratio of their magnitudes is:
J? / J? = tan (2πft) / (2πfε? ρ) = tan (2π * 900) / (2π * 9 * 10? * 80ε? * 0.25) = 10?
Suppose you have taken a dilute solution of oleic acid in such a way that its concentration becomes 0.01cm³ of oleic acid per cm³ of the solution. Then you make a thin film of this solution (monomolecular thickness) of area 4cm² by considering 100 spherical drops of radius ³√(3/(40π)) × 10⁻³ cm. Then the thickness of oleic acid will be x × 10⁻¹⁴ m. Where x is ______.
4t = 100 * (4/3)π * (40π * 10? * 0.01)³
t = 2.5 * 10? ¹¹ cm = 2.5 * 10? ¹³ m
A particle of mass m moves in a circular orbit in a central potential field U(r) = U₀r⁴. If Bohr's quantization conditions are applied, radii of possible orbitals rₙ vary with nᵃ, where α is---------.
From the given relations:
mv²/r = |dU/dr| = 4|U? |r³ . (1)
mvr = nh / 2π . (2)
By combining equations (1) and (2), we can derive the radius r:
r = ( (nh)² / (4π√* (U? )*) )¹/³ ⇒ r ∝ n²/³
The electric field in a region is given by E⃗ = (2/5)E₀ î + (3/5)E₀ ĵ with E₀ = 4.0 × 10³ N/C. The flux of this field through a rectangular surface area 0.4m² parallel to the Y-Z plane is _____ Nm²C⁻¹.
The flux φ is calculated as:
φ = (2/5) * 4 * 10³ * 0.4 = 640 Nm²C? ¹
JEE Mains 01 MT
JEE Mains 01 MT
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Eleven Exam