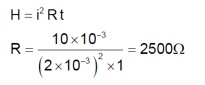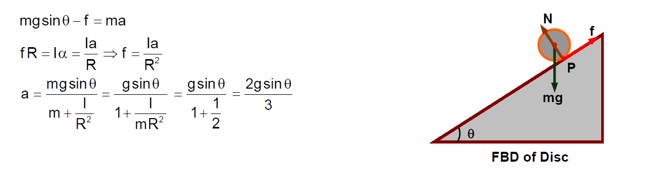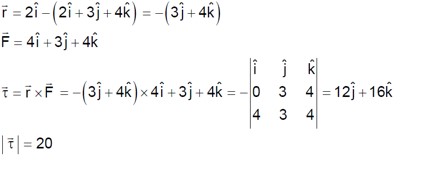- Thermodynamics Questions and Answers
Thermodynamics Questions and Answers
| 1. Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in Fig. |
| Explanation- pV1/2= constant P=k/ Work done from 1 to 2 W= from ideal equation = pV=nRT T= pV/nR= T= T1= , T1= = U=
= RT1( ) =2p1V11/2( ) = 2p1V11/2(2 ) = 2p1V1( )= 2RT1( ) = = RT1( )+ 2RT1( ) = |
| 2. A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in Fig . A to B : volume constant B to C : adiabatic C to D : volume constant D to A : adiabatic Vc=VD=2VA=2VB (a) In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside? (b) In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine? (c) What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA. (d) What is the efficiency of the engine? [γ =5/3 for the gas], (Cv= 3/2R for one mole) |
| Explanation-a) for the process AB dV=0 and dW=0 dQ=dU+dW=dU dQ=dU= change in internal energy , so heat utilised is equal to change in internal energy. Since p= in adiabatic temperature is directly proportional to pressure. So heat is supplied to the system in process AB. b) for the process CD volume is constant but the pressure decreases, hence temperature also decreases . so heat is also given to the surroundings. c) WAB= , WCD= WBC= = [pV]= WDA= B and C lies on adiabatic curve BC PBVBY= PCVCY PC = PB( )Y = PB( )Y= 2-YPB Total work done by the engine in one cycle ABCDA W= WAB+WBC+WCD+WDA= WBC+WDA = W = W = W= 2/3]( )VA |
| 3. A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in Fig.. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2) R) |
| Explanation-a) for process AB Volume is constant , hence work done dW=0 dQ=dU+dW=dU+0=dU = nCvdT= nCv(TB-TA) = = Heat exchanged = b) for process BC , p =constant dQ= dU+dW = heat exchanged = c) for process CD , because CD is adiabatic , dQ= heat exchanged =0 d) DA involves compression of gas from VD to VA at constant pressure PA heat transferred as similar way as BC1 hence dQ = PA(VA-VD) |
| 4. Consider that an ideal gas (n moles) is expanding in a process given by P = f ( V ), which passes through a point (Po, V0 ). Show that the gas is absorbing heat at (P0, Vo ) if the slope of the curve P = f (V ) is larger than the slope of the adiabat passing through (Po, V0 ). |
| Explanation- slope of the curve = f(V) , where V is the volume Slope of P = f(V) curve at ((Po, V0 )= f(Vo) Slope of adiabatic at (Po, V0 )= k(-Y)Vo-1-Y =-YPo/Vo Now heat absorbed in the process P= f(V) dQ=dU+dW= nCvdT+pdV pV=nRT T= pV/nR T= nCv
After solving we get
= Heat is absorbed where dQ/dV>0 when gas expands Hence YPo+Vof’(Vo)>0 or f’(Vo)>(-Y ) |
Commonly asked questions
Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in Fig.
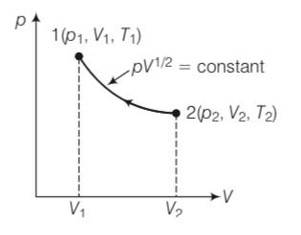
(a) Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
(b) What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
(c) Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
pV1/2= constant
P=k/
Work done from 1 to 2
W=
from ideal equation = pV=nRT
T= pV/nR=
T=
T1= , T1=
=
U=
= RT1( )
=2p1V11/2( )
= 2p1V11/2(2 )
= 2p1V1( )= 2RT1( )
=
= RT1( )+ 2RT1( )
=
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in Fig .
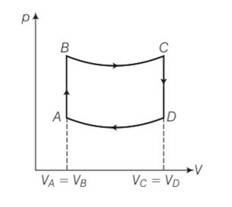
A to B : volume constant B to C : adiabatic C to D : volume constant D to A : adiabatic Vc=VD=2VA=2VB
(a) In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
(b) In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
(c) What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA
(d) What is the efficiency of the engine? [γ =5/3 for the gas], (Cv= 3/2R for one mole)
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) For the process AB
dV=0 and dW=0
dQ=dU+dW=dU
dQ=dU= change in internal energy , so heat utilised is equal to change in internal energy.
Since p= in adiabatic temperature is directly proportional to pressure. So heat is supplied to the system in process AB.
(b) For the process CD volume is constant but the pressure decreases, hence temperature also decreases . so heat is also given to the surroundings.
(c) WAB= , WCD=
WBC=
= [pV]=
WDA=
B and C lies on adiabatic curve BC
PBVBY= PCVCY
PC = PB( )Y = PB( )Y= 2-YPB
Total work done by the engine in one cycle ABCDA
W= WAB+WBC+WCD+WDA= WBC+WDA
=
W =
W =
W= 2/3]( )VA
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in Fig.. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2) R)
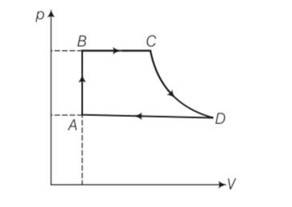
AB : constant volume
BC : constant pressure
CD : adiabatic
DA : constant pressure
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) For process AB
Volume is constant , hence work done dW=0
dQ=dU+dW=dU+0=dU
= nCvdT= nCv(TB-TA)
=
=
Heat exchanged =
(b) For process BC , p =constant
dQ= dU+dW =
heat exchanged =
(c) For process CD , because CD is adiabatic , dQ= heat exchanged =0
(d) DA involves compression of gas from VD to VA at constant pressure PA
heat transferred as similar way as BC1
hence dQ = PA(VA-VD)
Consider that an ideal gas (n moles) is expanding in a process given by P = f ( V ), which passes through a point (Po, V0 ). Show that the gas is absorbing heat at (P0, Vo ) if the slope of the curve P = f (V ) is larger than the slope of the adiabat passing through (Po, V0 ).
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Slope of the curve = f(V) , where V is the volume
Slope of P = f(V) curve at ((Po, V0 )= f(Vo)
Slope of adiabatic at (Po, V0 )= k(-Y)Vo-1-Y =-YPo/Vo
Now heat absorbed in the process P= f(V)
dQ=dU+dW= nCvdT+pdV
pV=nRT
T= pV/nR
T=
nCv
After solving we get
=
Heat is absorbed where dQ/dV>0 when gas expands
Hence YPo+Vof’(Vo)>0 or f’(Vo)>(-Y )
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached . A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched length L ) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from Vo to V1.
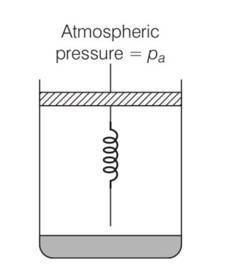
(a) What is the initial pressure of the system?
(b) What is the final pressure of the system?
(c) Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q, Pa, V, Vo and k.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Initially the piston is in equilibrium Pi=Pa
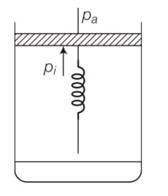
(b) On supplying heat , the gas expands from Vo to Vi
so increase in volume of the gas =Vi-Vo
as the piston is of unit cross sectional area hence extension in the spring
x=
force exerted by the spring on the piston= F= kx= K(Vi - Vo)
hence final pressure =Pf =Pa +kx
= Pa+K ( )
(c) From first law of thermodynamics
dQ=dU+dW
dU=Cv(T-To) = Cv(T-To)
T=
Work done by the gas =pdV+ increase in PE of the spring
= Pa(V1-Vo) + x2
dQ=dU+dW
= Cv(T-To)+Pa(V-Vo)+ x2
= Cv(T-To)+Pa(v-Vo)+1/2 ( )2
Can a system be heated and its temperature remains constant?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Yes this is possible when the entire heat supplied to the system is utilised in expansion.
So its working against the surroundings.
A system goes from P to Q by two different paths in the P-V diagram as shown in Fig. 12.8. Heat given to the system in path 1 is 1000 J. The work done by the system along path 1 is more than path 2 by 100 J. What is the heat exchanged by the system in path 2?
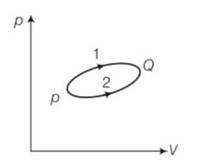
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
For path1
Heat Q1= 1000J
Work done =W1
For path 2
Work done W2= W1-100
As change in internal energy is same
dU=Q1-W1=Q2-W2
1000-W1=Q2-W1+100
Q2= 1000-100= 900J
If a refrigerator’s door is kept open, will the room become cool or hot? Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If a refrigerator's doors is kept open, then room will become hot, because amount of heat removed would be less than the amount of heat released in the room.
Is it possible to increase the temperature of a gas without adding heat to it? Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Yes during adiabatic compression the temperature of a gas increases while no heat is
In adiabatic compression dQ=0
From the first law of thermodynamics dU= dQ-dW
dU=-dW
in compression work is done on the gas i.e work done is negative
dU=positive
hence internal energy of the gas increases due to which its temperature increases.
Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving. Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
During driving temperature of the gas increases while volume remains constant. So according charle's law, at constant volume V.
Pressure is directly proportional to temperature. Therefore pressure of gas increases.
Consider a Carnot’s cycle operating between T1 = 500K and T2=300K producing 1 k J of mechanical work per cycle. Find the heat transferred to the engine by the reservoirs.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Temperature of the source T1= 500K and sink T2= 300K
Work done W= 1000J
Efficiency of Carnot engine = 1-T2/T1= 1-300/500= 200/500= 2/5
Efficiency = W/Q1
So Q1= W/efficiency = 1000
A person of mass 60 kg wants to lose 5 kg by going up and down a 10m high stairs. Assume he burns twice as much fat while going up than coming down. If 1 kg of fat is burnt on expending 7000 kilo calories, how many times must he go up and down to reduce his weight by 5 kg?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Height of stairs h= 10m
Energy produced by burning 1 kg of fat = 7000Kcal
Energy produced by burning 5kg of fat = 5
Energy utilised in going up and down one time
= mgh + =
=
= 9000J= 9000/4.2=3000/1.4cal
Number of times, the person has to go up and down the stairs
= = 16.3 times
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ?V V ( ) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
For adiabatic change process we know
P1V1y= P2V2y
P (V+ )y = (P+ )Vy
PVy (1+ ) y=p (1+ )Vy
PVy (1+ ) PVy (1+ )
Y
dV=
hence work done increasing the pressure from P1 to P2
W=
=
W=
In a refrigerator one removes heat from a lower temperature and deposits to the surroundings at a higher temperature. In this process, mechanical work has to be done, which is provided by an electric motor. If the motor is of 1kW power, and heat is transferred from –3°C to 27°C, find the heat taken out of the refrigerator per second assuming its efficiency is 50% of a perfect engine.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Temperature of the source is 270C
T1= 27+273= 300K
T2= -3+273= 270K
Efficiency of heat engine = 1-T2/T1= 1-270/300=1/10
Efficiency of refrigerator is 50% of a perfect engine
= 0.5 = 1/20
Coefficient of performance of the refrigerator
=
Q2= =19W
= 19 1KW=19KW= 19kJ/s
If the co-efficient of performance of a refrigerator is 5 and operates at the room temperature (27 °C), find the temperature inside the refrigerator.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Coefficient of
T1= 27+273=300K
Coefficient of performance
1500-5T2=T2
6T2=1500
T2= 250K
T2= 250-273=-23oC
The initial state of a certain gas is (Pi , Vi , Ti ). It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes Vf . Consider the following two cases:
(a) The expansion takes place at constant temperature.
(b) The expansion takes place at constant pressure. Plot the P-V diagram for each case. In which of the two cases, is the work done by the gas more?
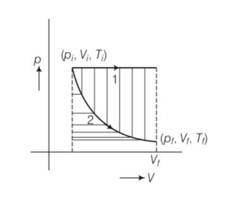
process 1 isochoric and process 2 is isothermal .
Since, work done = area under P-V curve . here area under the pV curve 1 is more . so work done is more when the gas expands in isochoric process.
An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (Fig. 12.1). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of 1, 2, 3 and 4 which one is adiabatic.
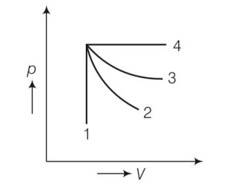
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 1
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) For the curve 1 volume is constant so it is isochoric process. But in curve 2 and 3 curve 2 is steeper so 2 is adiabatic and 3 is isothermal.
If an average person jogs, he produces 14.5 × 103 cal/min. This is removed by the evaporation of sweat. The amount of sweat evaporated per minute (assuming 1 kg requires 580 × 103 cal for evaporation) is
(a) 0.25 kg
(b) 2.25 kg
(c) 0.05 kg
(d) 0.20 kg
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Amount of sweat evaporated /minute =
=
Consider P-V diagram for an ideal gas shown in Out of the following diagrams , which represents the T-P diagram?
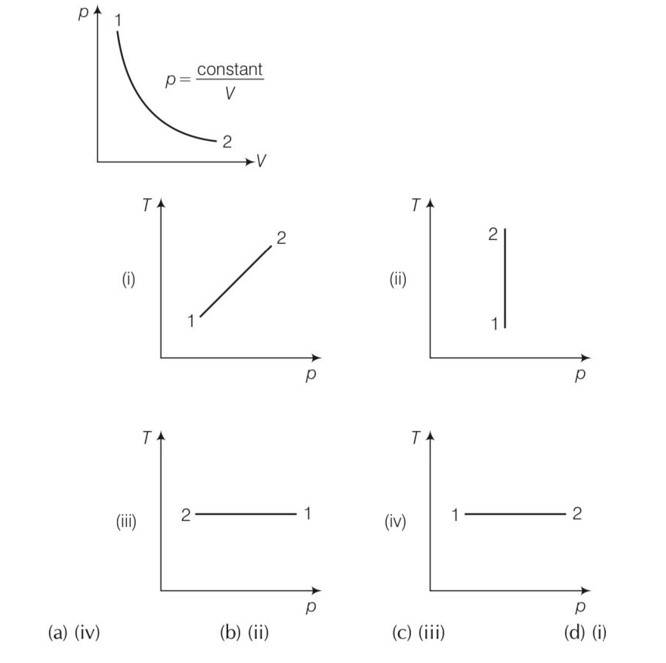
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) As we know PV =constant
Hence we can say that gas is going through an isothermal process.
Clearly from the graph that between process 1 and 2 temperature is constant and the gas expands and pressure decreases. So density of 2 is less than 1 so option ii
An ideal gas undergoes cyclic process ABCDA as shown in given P-V diagram (Fig. 12.4). The amount of work done by the gas is
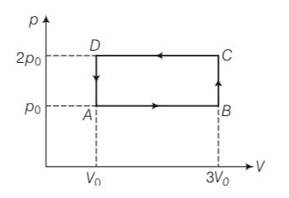
(a) 6 PoVo
(b) –2 PoVo
(c) + 2 PoVo
(d) + 4 PoVo
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Work done ABCD = area of rectangle ABCDA
= AB = (3Vo-Vo) (2po-po)
= 2V0 Po= 2poVo
And work done by the gas =- 2poVo
Consider two containers A and B containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container A is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container B is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in B to that of gas in A is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Container A is isothermal and container B is adiabatic
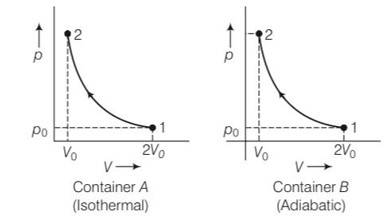
For isothermal process P1V1=P2V2
Po (2Vo)= P2 (Vo)
P2= 2Po
for adiabatic process
P1V1y= P2V2y
Po (2Vo)y=P2 (Vo)y
P2= ( )yPo= 2yPo
Hence ratio of final pressure =
Three copper blocks of masses M1, M2 and M3 kg respectively are brought into thermal contact till they reach equilibrium. Before contact, they were at T1, T2, T3 (T1 > T2 > T3 ). Assuming there is no heat loss to the surroundings, the equilibrium temperature T is (s is specific heat of copper)
(a) T=
(b) T=
(c) T=
(d) T=
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Let us assume that T1, T2T3
According to questions there is no loss of heat in the surroundings
Heat lost by M3 = heat gained by M1+ heat gained by M2
M3s (T3-T)= M1s (T-T1)+M2s (T-T2)
T [M1+M2+M3]= M3T3+M1T1+M2T2
T =
Which of the processes described below are irreversible?
(a) The increase in temperature of an iron rod by hammering it
(b) A gas in a small container at a temperature T1 is brought in contact with a big reservoir at a higher temperature T2 which increases the temperature of the gas
(c) A quasi-static isothermal expansion of an ideal gas in cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston
(d) An ideal gas is enclosed in a piston cylinder arrangement with adiabatic walls. A weight W is added to the piston, resulting in compression of gas
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (b), (d) When the rod is hammered the external work is done on the rod which increases its temperature.
Heat is transferred to the gas in the small container by big reservoir at temperature T2
As the weight is added to the cylinder arrangement in the form of external pressure so it cannot reversed.
An ideal gas undergoes isothermal process from some initial state i to final state f. Choose the correct alternatives.
(a) dU = 0
(b) dQ= 0
(c) dQ = dU
(d) dQ = dW
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (d) For isothermal dT= 0 so T=constant
For an ideal gas dU = change in internal energy = nCvdT=0
From first law of thermodynamics dQ= dU+dW
dQ= dW
Figure 12.5 shows the P-V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of state from A to B. Four different parts I, II, III and IV as shown in the figure may lead to the same change of state.
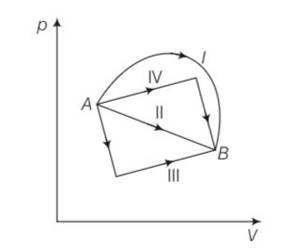
(a) Change in internal energy is same in IV and III cases, but not in I and II
(b) Change in internal energy is same in all the four cases
(c) Work done is maximum in case I
(d) Work done is minimum in case II
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b), (c) Change in internal energy for process A to B
dU=nCvdT=nCv (dT)=nCv (TB-TA)
work done from A to B = area under the PV curve which is maximum for path I
Consider a cycle followed by an engine 1 to 2 is isothermal 2 to 3 is adiabatic 3 to 1 is adiabatic Such a process does not exist because
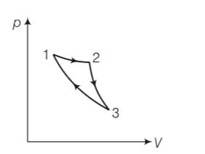
(a) Heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
(b) Mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process, which is not possible.
(c) Curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
(d) Curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) the given process is a cyclic process i.e returns to the original state 1
Hence change in internal energy dU =0
dQ= dU+dW=0+dW
hence total heat supplied is converted to work done by the gas which is not possible by second law of thermodynamics.
(c) When the gas expands adiabatically from 2 to 3 . it is not possible to return to the same state without being heat supplied hence 3 to 1 cannot be adiabatic.
Consider a heat engine as shown in Fig. Q1 and Q2 are heat added to heat bath T1 and heat taken from T2 in one cycle of engine. W is the mechanical work done on the engine. If W > 0, then possibilities are:
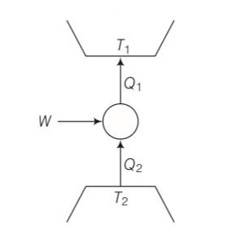
(a) Q1 > Q2 > 0
(b) Q2 > Q1 > 0
(c) Q2 < Q1 < 0
(d) Q1 < 0, Q2 > 0
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (c) Q1= W+Q2
W=Q1-Q2>0
Q1>Q2>0
We can also write Q21
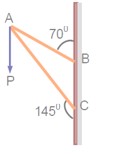
Consider a frame that is made up of two thin massless rods AB and AC as shown in the figure. A vertical force of magnitude 100N is applied at point A of the frame. Suppose the force is resolved parallel to the arms AB and AC of the frame. The magnitude of the resolved component along the arm AC is xN. The value of x, to the nearest integer, is------------. [Given : sin(35° ) = 0.573, cos(35° )= 0.819 sin(110° )= 0.939, cos(110° )= -0.342 ]
Kindly consider the following Image
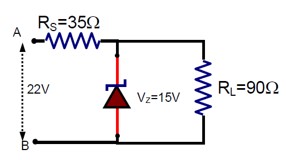
The value of power dissipated across the Zener diode ( Vz = 15V) connected in the circuit as shown in the figure is x x10-1 watt. The value of x, to the nearest integer, is--------.
Kindly consider the following Image
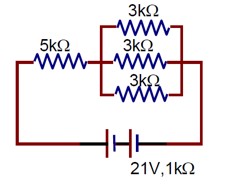
In the figure given, the electric current flowing through the 5 k Ω resistor is ‘x’ mA. The value of x to the nearest integer is --------.
Kindly consider the following Image
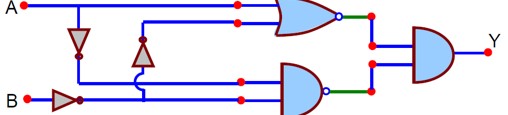
In the logic circuit shown in the figure, if input A and B are 0 to 1 respectively, then output at Y would be ‘x’.
The value of x is ----------.
Kindly consider the following Image
The resistance R = V/I where V =(50 ± 2V) and I = (20 ± 0.2)A. The percentage error in R is ‘x’ %. The value of ‘x’ to the nearest integer is ----------.
Kindly consider the following Image
A sinusoidal voltage of peak value 250V is applied to a series LCR circuit, in which R = 8Ω, L = 24mH andC = 60μF. The value of power dissipated at resonant condition is ‘x’ kW. The value of x to the nearest integer is-----------.
Kindly consider the following Image
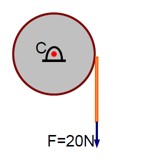
Consider a 20 kg uniform circular disk of radius 0.2 m. It is pin supported at its centre and is at rest initially. The disk is acted upon by a constant force F = 20 N through a massless string wrapped around its periphery as shown in the figure. Suppose the disk makes n number of revolutions to attain an angular speed of 50 rad s-1. The value of n, to the nearest integer, is ---------.
[Given : In one complete revolution, the disk rotates by 6.28 rad ]
Kindly consider the following Image
The first three spectral of H-atom in the Balmer series are given λ1 , λ2 , λ3 considering the Bohr atomic model, the wave lengths of first and third spectral lines (λ1/ λ2) are related by a factor of approximately ‘x’ ×10-1. The value of x, to the nearest integer, is-----------.
Kindly consider the following Image
A fringe width of 6 mm was produced for two slits separated by 1 mm apart. The screen is placed 10 m away. The wavelength of light used is ‘x’ nm. The value of ‘x’ to the nearest integer is----------.
Kindly consider the following Image
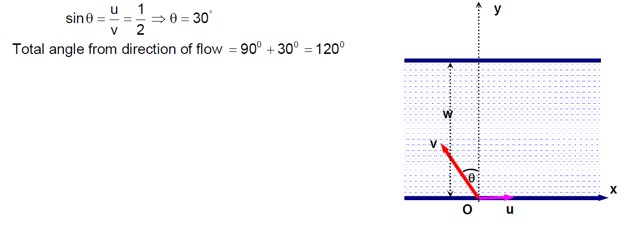
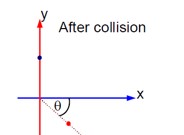
A ball of mass 10 kg moving with a velocity10√3ms-1along X – axis, hits another ball of mass 20 kg which is at rest. After collision, the first ball comes to rest and the second one disintegrates into two equal pieces. One of the pieces starts moving along Y– axis at a speed of 10m/s. The second piece starts moving at a speed of 20m/s at an angle θ° with respect to the X –axis. The configuration of pieces after collision is shown in the figure. The value of θ to the nearest integer is----------.
Kindly consider the following Image
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Twelve Exam