Physics Ncert Solutions Class 12th
Get insights from 1.2k questions on Physics Ncert Solutions Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Ncert Solutions Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation- F=GMm/r2
M=effective mass of hydrogen atom=mass of electron +mass of proton -B2/c
B.E of hydrogen atom = 13.6eV
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer (c)
Explanation- it is a process in which metal decays spontaneously . so during a span of 1 year it will decay almost half of its original value so it will come close to 5000.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- a nuclide 1 is said to be mirror isobar of nuclide 2, if Z1=N2 and Z2= N1
Now 11Na23, 12Mg23 for which Z2=12=N1 and N2 =23-12=11=Z1
(b) As 12Mg23 contain even number of protons against 11Na23 which has odd number of protons (11), therefore Mg has greater binding energy than sodium.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Each particle (neutron and proton) present inside the nucleus is called nucleon .
Let
and KE= PE
= eV
K.E= 109eV
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- R= 12dis/min per gm and R0= 16dis/min per gm T1/2= 5760yr
R=
By taking log
= log1016/12
= 2.303 (0.6020-4.771)5760/0.6931
= 2391.20yr
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
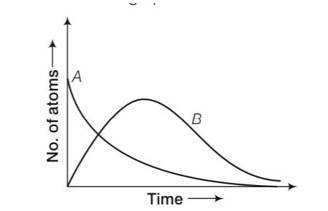
by considering the graph at t=0 NA= No while NB=0 but when time increases the atoms in B also increases and becomes maximum and then drop to zero by radioactive decay law.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-because more number of protons means more repulsive force which leads to instability.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- during the collision of electron and positron they form gamma radiation and these gamma particle travels in opposite direction to conserve the momentum.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- electron cannot emit radiation while exiting because they absorbs energy in eV which is very low as compared to gamma particle . as they contain energy in MeV
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
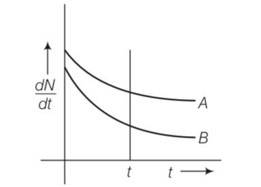
Explanation- at t=0 (dN/dt)A= (dN/dt)B
By drawing a perpendicular line across graph (dN/dt)A> (dN/dt)B so decay is faster in A than B
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers