Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Thirteen Nuclei offers excellent preparation material for the CBSE exams and various entrance exams. The NCERT exemplar has all types of questions from Very-Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions and Multiple Choice Questions. Class 12 Science students must practice all these questions to boost their exam confidence and improve their understanding of the various key concepts.
The students can download the Nuclei NCERT PDF to thoroughly practice these questions. It will enhance their problem-solving skills and will also increase their understanding of when and how to use a particular formula or concept. Once downloaded, students can read from this PDF without the requirement of an internet connection. They can also take a printout of the PDF to practice on paper. To further improve their understanding of the key topics related to NCERT Chapter 13 Class 12 Physics, students must also check Chapter 13 Physics Class 12 Nuclei NCERT Solutions. They can also read the NCERT solutions on the Shiksha's page.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Thirteen Nuclei
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Nuclei Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Nuclei Very Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Long Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Nuclei Objective Type Questions
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter Thirteen NCERT Exemplar
- JEE Mains Solutions 2022,26th july , physics, second shift
- 27th July 2022 first shift
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Thirteen Nuclei
The students must download the Nuclei NCERT PDF from Shiksha's page. The Class 12th Chapter Thirteen Nuclei PDF contains all questions from the NCERT Exemplar book. By solving these questions, students can score high in their CBSE Board exams and other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE examinations. The PDF is well-structured and created by the subject matter expert, and hence it is highly reliable and accurate. Students can easily depend on the Shiksha's NCERT exemplar for their exam preparation. Once the student downloads the PDF, they can access it without the requirement of an internet connection. If they want, they can also take printouts of the PDF and practice the questions on paper. The PDF serves as an excellent exam preparation tool.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Nuclei Short Answer Type Questions
Here are the questions and solutions:
Commonly asked questions
Why do stable nuclei never have more neutrons than protons?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-because more number of protons means more repulsive force which leads to instability.
Consider a radioactive nucleus A which decays to a stable nucleus C through the following sequence:
A -> B -> C
Here B is an intermediate nuclei which is also radioactive. Considering that there are N0 atoms of A initially, plot the graph showing the variation of number of atoms of A and B versus time.
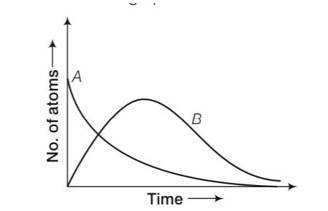
by considering the graph at t=0 NA= No while NB=0 but when time increases the atoms in B also increases and becomes maximum and then drop to zero by radioactive decay law.
A piece of wood from the ruins of an ancient building was found to have a 14 C activity of 12 disintegrations per minute per gram of its carbon content. The 14 C activity of the living wood is 16 disintegrations per minute per gram. How long ago did the tree, from which the wooden sample came, die? Given half-life of 14 C is 5760 yr.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- R= 12dis/min per gm and R0= 16dis/min per gm T1/2= 5760yr
R=
By taking log
= log1016/12
= 2.303 (0.6020-4.771)5760/0.6931
= 2391.20yr
Are the nucleons fundamental particles, or do they consist of still smaller parts? One way to find out is to probe a nucleon just as Rutherford probed an atom. What should be the kinetic energy of an electron for it to be able to probe a nucleon? Assume the diameter of a nucleon to be approximately 10-15
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Each particle (neutron and proton) present inside the nucleus is called nucleon .
Let
and KE= PE
= eV
K.E= 109eV
A nuclide 1 is said to be the mirror isobar of nuclide 2 if Z1=N2 and Z2 = N1 (a) What nuclide is a mirror isobar of 1123Na ? (b) Which nuclide out of the two mirror isobars have greater binding energy and why?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- a nuclide 1 is said to be mirror isobar of nuclide 2, if Z1=N2 and Z2= N1
Now 11Na23, 12Mg23 for which Z2=12=N1 and N2 =23-12=11=Z1
(b) As 12Mg23 contain even number of protons against 11Na23 which has odd number of protons (11), therefore Mg has greater binding energy than sodium.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Nuclei Very Short Answer Type Questions
See below the solutions:
Commonly asked questions
He23 and He13 nuclei have the same mass number. Do they have the same binding energy?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- nuclei 2He4 and 1He3 have the same mass number . the element having more number of proton having more repusion so less binding energy. So 2He4 have more number of proton so more repulsion so less binding energy.
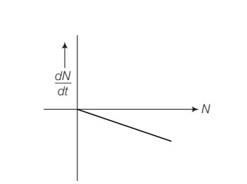
Draw a graph showing the variation of decay rate with number of active nuclei.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- dN/dt=
Which sample A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life?
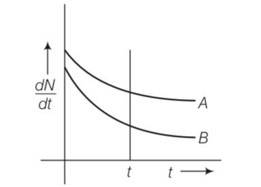
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- at t=0 (dN/dt)A= (dN/dt)B
By drawing a perpendicular line across graph (dN/dt)A> (dN/dt)B so decay is faster in A than B
Which one of the following cannot emit radiation and why? Excited nucleus, excited electron.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- electron cannot emit radiation while exiting because they absorbs energy in eV which is very low as compared to gamma particle . as they contain energy in MeV
In pair annihilation, an electron and a positron destroy each other to produce gamma radiations. How is the momentum conserved?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- during the collision of electron and positron they form gamma radiation and these gamma particle travels in opposite direction to conserve the momentum.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Long Answer Type Questions
These are the LA type questions and solutions:
Commonly asked questions
Sometimes a radioactive nucleus decays into a nucleus which itself is radioactive. An example is
38sulphur 38Cl 38Ar(stable)
Assume that we start 1000 38S nuclei at time t=0. The number of 38Cl is of count zero at t=0 and will be again zero at t= at what value of t, would the number of counts be a a maximum?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- let 38S have N1 active nuclei and 38Cl have N2 active nuclei
+
N1=N0
+
Multiplying by and then integrating both sides we got
N2=
After solving it we get time t= (log )/
t= =
Deuteron is a bound state of a neutron and a proton with a binding energy B = 2.2 MeV. A γ-ray of energy E is aimed at a deuteron nucleus to try to break it into a (neutron + proton) such that the n and p move in the direction of the incident γ-ray. If E = B, show that this cannot happen. Hence, calculate how much bigger than B must be E be for such a process to happen.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- B.E= 2.2MeV
E-B=Kn+KP=
Conservation of momentum= Pn+PP= E/C
E=B
It only happen if Pn=Pp=0
Let E=B+X where X<
X= (E/C-PP)/2m+
2 + =0
Pp=
= 4E2/c2
The deuteron is bound by nuclear forces just as H-atom is made up of p and e bound by electrostatic forces. If we consider the force between neutron and proton in a deuteron as given in the form a coulomb potential but with an effective charge e’.
F= ke’2/r estimate the value of e’/e given that the the binding energy of a duetron is 2.2MeV.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-E=
If proton and neutron had charge e each and were governed by the same electrostatic force, then in the above equation we would need relace m
So m’ = =M/2=918m
Hence binding energy= 918me’4/8
Dividing eqn
918 ( 4= =
= 3.64
Before the neutrino hypothesis, the beta decay process was thought to be the transition.
n —> p + e
If this was true, show that if the neutron was at rest, the proton and electron would emerge with fixed energies and calculate them. Experimentally, the electron energy was found to have a large range.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Pn=Pp+Pe
Pp+Pe=0
Pe=Pp=P
Ep= 1/2
Ee= 1/2
= 1/2
From conservation of energy
1/2= 1/2= mnc2
mpc2= 936MeV, mnc2=938MeV, mec2=0.51MeV
since the energy difference n and p is small
mpc2+
pc= mnc2-mpc2 = 938-936= 2MeV
Ep=( )1/2=
= 2.06MeV
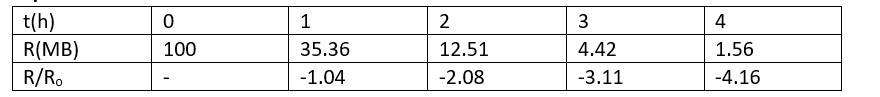
The activity R of a unknown radioactive nuclide is measurement at hourly intervals the result found are tabulated as follows.
Plot the graph of R verses t and calculate half life from the graph.
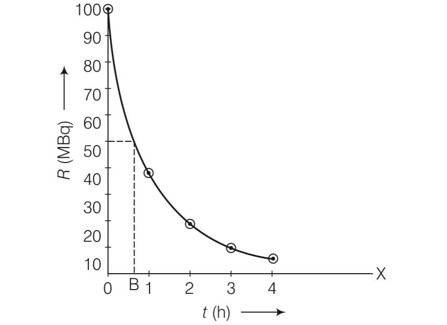
Plot the graph of In(R/Ro) verses t and obtain the value of half life from the graph.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-
Nuclei with magic no. of proton Z=2,8,20,28,50,52 and magic no. of neutrons N=2,8,20,28,50,82 and 126 are found to be stable. (i) Verify this by calculating the proton separation energy Sp for. 120Sn ( Z = 50 ) and 121Sb( Z = 51 ). The proton separation energy for a nuclide is the minimum energy required to separated the least tightly bound proton form a nucleus of that nuclide. It is given by Sp = ( Mz-1 , N + MH−Mz ,N )c2 𝑆𝑝 = ( 𝑀𝑧 - 1 , 𝑁 + 𝑀H – 𝑀Z , 𝑁 ) 𝑐 2 . given 119𝑆𝑛 = 118.9058 𝑢 , . 120𝑆𝑛 = 199.902199 , . 121𝑆𝑏 = 120.903824 𝑢 ,1𝐻 = 1.0078252 𝑢 (ii) what does the existence of magic number indicate?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- B.E = (Mp+MH-MN)c2
B.E= (118.9058+1.0078252-119.902199)c2
B.E=0.0114362 c2
B.E= (Mp+MH-MN)c2
B.E= (119.902199+1.0078252-120.902822)c2
B.E= 0.0059912c2
(ii) the existence of magic numbers indicates that the shell structure of nucleus is similar to the shell structure of an atom. This also explains peaks in binding energy curve.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Nuclei Objective Type Questions
Find below the solutions:
Commonly asked questions
Suppose we consider a large number of containers each containing initially 10000 atoms of a radioactive material with a half life of 1 year. After 1 year,
(a) All the containers will have 5000 atoms of the material
(b) All the containers will contain the same number of atoms of the material but that number will only be approximately 5000
(c) The containers will in general have different numbers of the atoms of the material but their average will be close to 5000
(d) None of the containers can have more than 5000 atoms
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer (c)
Explanation- it is a process in which metal decays spontaneously . so during a span of 1 year it will decay almost half of its original value so it will come close to 5000.
The gravitational force between a H atom and a another particle of mass m will be given newton’s law
F=GMm/r2 where r in km
(a) M=mproton+melectron
(b) M=mproton+melectron-
(c) M is not relate to the mass of the hydrogen atom
(d) M=mproton+melectron-(|V|)= magnitude of the potential energy of electron in H atom.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation- F=GMm/r2
M=effective mass of hydrogen atom=mass of electron +mass of proton -B2/c
B.E of hydrogen atom = 13.6eV
When a nucleus in an atom undergoes a radioactive decay, the electronic energy levels of the atom
(a) Do not change for any type of radioactivity
(b) Change for α and β-radioactivity but not for γ-radioactivity
(c) Change for α -radioactivity but not for others
(d) Change for β-radioactivity but not for others
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (b)
Explanation – because alpha and beta particle have some charge and mass so their energy level will change but in case of gamma particle it does not contain any charge.
Me and Ms denote the atomic masses of the parent and he daughter nuclei respectively in radioactive decay. The Q value for a beta-1 decay is Q1 and that for beta+ decay is Q2.if me denotes the mass of an electron, then which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Q1=(Mx-My)c2 and Q2=[Mx-My-2me]c2
(b) Q1=(Mx-My)c2 and Q2=[Mx-My]c2
(c) Q1=(Mx-My-2me)c2 and Q2=[Mx-My-2Ce]c2
(d) Q1=(Mx-My +2me)c2 and Q2=[Mx-My+2me]c2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer –a
Explanation- + decay represents
zXA z-1YA+1eo+v+Q2
Q2= [mn (zXA)-mn (z-1YA)-me]c2
= (Mx-My-2me)c2
- decay represents
zXA z+1YA+-1eo+v+ 1
1= [mn (zXA)-mn (z+1YA)-me]c2
= (Mx-My)c2
Tritium is an isotope of hydrogen whose nucleus triton contains 2 neutrons and 1 proton. Free neutrons decay into p + e + n . If one of the neutrons in Triton decays, it would transform into He3 nucleus. This does not happen. This is because
(a) Triton energy is less than that of a He3 nucleus
(b) The electron created in the beta decay process cannot remain in the nucleus
(c) Both the neutrons in triton have to decay simultaneously resulting in a nucleus with 3 protons, which is not a He3 nucleus.
(d) Free neutrons decay due to external perturbations which is absent in triton nucleus
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a)
Explanation – tritium contain 1 proton and 2 neutron but when it disintegrates and remove 1 beta particle it will now contain 2 proton and 1 neutron so it will change into 2He3 but its energy will be less from it.
Heavy stable nuclei have more neutrons than protons. This is because of the fact that .
(a) Neutrons are heavier than protons
(b) Electrostatic force between protons are repulsive
(c) Neutrons decay into protons through beta decay
(d) Nuclear forces between neutrons are weaker than that between protons
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (b)
Explanation – a nucleus contain more number of neutron than protons because the repulsive force is more if it contain more proton and become more unstable.
In a nuclear reactor, moderators slow down the neutrons which come out in a fission process. The moderator used have light nuclei. Heavy nuclei will not serve the purpose, because
(a) They will break up
(b) Elastic collision of neutrons with heavy nuclei will not slow them down
(c) The net weight of the reactor would be unbearably high
(d) Substances with heavy nuclei do not occur in liquid or gaseous state at room temperature
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (b)
Explanation- the moderator used have light nuclei . because when we use heavy nuclei then there will be collision of proton which does not slow down the process.
Fusion processes, like combining two deuterons to form a He nucleus are impossible at ordinary temperatures and pressure. The reasons for this can be traced to the fact
(a) Nuclear forces have short range
(b) Nuclei are positively charged
(c) The original nuclei must be completely ionized before fusion can take place
(d) The original nuclei must first break up before combining with each other
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a, b)
Explanation- fusion process are almost impossible at ordinary temperature because nuclei are positive charge and forces between them is of short range.
Samples of two radioactive nuclides A and B are taken. λAand λB are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
(a) Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA = λB
(b) Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA > λB
(c) Initial rate of decay of B is twice the initial rate of decay of A and λA > λB
(d) Initial rate of decay of B is same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λA < λB
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (b, d)
Explanation- this is only possible when rate of decay of 1 is almost double the rate of decay of other.so in this case initial decay of A must be twice of B. also Initial rate of decay of B is same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λA < λB
The variation of decay rate of two radioactive samples A and B with time is shown in figure.
Which of the following statements are true?
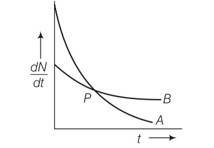
(a) Decay constant of A is greater thanB, hence A is always decays faster than B
(b) Decay constant of B is greater than that of A but its decay rate is smaller than that of A
(c) Decay constant of A is greater than that og B but it is does not always faster than B
(d) Decay constant of B is smaller than that of A but still decay rate becomes equal to that of A at later instant
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (c, d)
Explanation- in given figure the slope of curve A is greater than slope B. so decay in A is faster than B . also wavelength of A is grater than B.
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter Thirteen NCERT Exemplar
The following are the important formulas of Chapter Thirteen, Physics NCERT Exemplar Nuclei:
Mass-Energy Equivalence
Nuclear Radius Formula
Nuclear Density
Binding Energy (B.E.)
Binding Energy per Nucleon
Radioactive Decay Law
Activity (Rate of Decay)
Half-Life
Mean Life
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,26th july , physics, second shift
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,26th july , physics, second shift
Commonly asked questions
Two projectiles are thrown with same initial velocity making an angle of and with the horizontal respectively. The ration of their respectively ranges will be:
In a Vernier Calipers, 10 divisions of Vernier scale is equal to the 9 divisions of main scale. Then both jaws of Vernier calipers touch each other, the zero of the Vernier scale is shifted to the left of zero of the main scale and 4th Vernier scale division exactly coincides with the main scale reading. One main scale division is equal to 1mm. While measuring diameter of a spherical body, the body is held between two jaws. It is now observed that zero of the Vernier scale lies between 30 and 31 divisions of main scale reading and 6th Vernier scale division exactly coincides with the main scale reading. The diameter of the spherical body will be:
1 MSD = 1mm
9 MSD = 10 VSD
1VSD = 0.9 MSD = 0.9 mm
Least count = 1 MSD – 1 VSD
= 0.1 mm = 0.01 cm
Zero Error = (10 – 4) × 0.1 = 0.6 mm
Reading = MSR + VSR – Zero error
= 3 cm + 6 × 0.01 – (0.06)
= 3.12 cm 3.10 cm
A ball of mass 0.15 kg hits the wall with its initial speed of 12 ms-1and bounces back without changing its initial speed. If the force applied by the wall on the ball during the contact is 100 N, calculate the time during of the contact of ball with the wall.
A body mass 8kg and another of mass 2kg are moving with equal kinetic energy. Thee ratio of their respective momenta will be:
Two uniformly charged spherical conductors A and B of radii 5mm and 10mm are separated by a distance of 2cm. If the spheres are connected by a conducting wire, then in equilibrium condition, the ratio of the magnitudes of the electric fields at the surface of the sphere A and B will be:
The oscillating magnetic field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given by The amplitude of electric field will be:
Speed of wave V =
Light travels in two media M1 and M2 with speeds 1.5 × 108 ms1 and 2.0 × 108 ms1 respectively. The critical angle between them is:
A body is projected vertically upward from the surface of earth with a velocity equal to one third of escape velocity. The maximum height attained by the body will be:
Using conservation of Mechanical Energy
The maximum and minimum voltage of an amplitude modulated signal are 60V and 20V respectively. The percentage modulation index will be:
Percentage modulation =
Percentage modulation =
= 50%
A nucleus of mass M at rest splits into two parts having masses and The ratio of de Broglie wavelength of two parts will be:
P1 = P2 as Fnet = 0
An ice cube of dimensions 60cm × 50cm × 20cm is placed in an insulation box of wall thickness 1cm. The box keeping the ice cube at 898
of temperature is brought to a room of temperature The rate of melting of ice is approximately:
(Latent heat of fusion of ice is 3.4 × 105 J kg1 and thermal conducting of insulation wall is 0.05 )
= 1.04 M2
A gas has n degrees of freedom. The ratio of specific heat of gas at constant volume to the specific heat of gas at constant pressure will be:
A transverse wave s represented by y = The value of wavelength (in cm) for which the wave velocity becomes equal to the maximum particle velocity. Will be:
Maximum particle velocity =
Wave velocity =
A battery of 6V is connected to the circuit as shown below. The current I drawn from the battery is:
The circuit is balanced whetstone bridge.
A source of potential difference V is connected to the combination of two identical capacitors as shown in the figure. When key ‘K’ is closed, the total energy stored across the combination is E1. Now key ‘K’ is opened and dielectric of dielectric constant 5 is introduced between the plates of the capacitors. The total energy stored across the combination is now E2. The ratio E1/E2 will be:
I > When switch is closed
Ceq = 2C
Energy E1 =
E1 = CV2
II > When switch is opened
Two concentric circular loops of radii r1 = 30cm and r2 = 50cm are placed in X – Y plane as shown in the figure. A current I = 7A is flowing through them in the direction as shown in figure. The net magnetic momentum of this system of two circular loops is approximately:
A velocity selector consists of electric field and magnetic field with B = 12 mT. The value of E required for and electron of energy 728 eV moving along the positive x-axis to pass undeflected is:
(Given. Mass of electron = 9.1 × 1031kg)
V = 16 × 106 m/s
For Lorentz force to be zero
eE = eVB
= 192 × 103 V/m
Two masses M1 and M2 are tied together at the two ends of a light inextensible string that passes over a frictionless pulley. When the mass M2 is twice that of M1. The acceleration of the system is a1. When the mass M2 is thrice that of M1 the acceleration of the system is a2. The ratio will be:
Mass numbers of two nuclei are in the ratio of 4 : 3. Their nuclear densities will be in the ratio of
Density is independent of mass number
The area of cross section of the rope used to lift a load by a crane is 2.5 × 10-4m2. The maximum lifting capacity of the crane is 10 metric tons. To increase the lifting capacity of the crane to 25 metric tons, the required area of cross section of the rope should be:
Breading stress =
If The magnitude of component of vector along vector will be________m.
Component of along =
= 2
The radius of gyration of a cylindrical rod about an axis of rotation perpendicular to its length and passing through the centre will be________m.
Given, the length of the rod is
In the given figure, the face AC of the equilateral prism is immersed in a liquid of refractive index ‘n’. For incident angle at the side AC, the refracteel light beam just grazes along face AC. The refractive index of the liquid
The value of x is_______.
(Given refractive index of glass = 1.5)
1.5 × sin 60 = R × sin 90
x = 27
Two lighter nuclei combine to form a comparatively heavier nucleus by the relation given below:
The binding energies per nucleon for are 1.1 Me V and 7.6
Me V respectively. The energy released in this process is________ Me V.
Energy released = Binding energy of product – Binding energy of reacts :
= 26 MeV
A uniformly heavy rod of mass 20kg, cross sectional area 0.4 m2 an length 20m is hanging from a fixe support. Neglecting the lateral contraction. The elongation in the rod due to its own weight is x × 10-9m. The value of x i________.
The typical transfer characteristics of a transistor in CE configuration is shown in figure. A load resistor of is connected in the collector branch of the circuit used. The input resistance of the transistor is The voltage gain of the transistor is________.
Voltage gain =
= 200
Three point charges of magnitude are located at the vertices A, B, C of a right angled triangle whose sides are AB = 3cm, BC = and CA = 3 and point A is the right angle corner. Charge at point A experiences __________ N of electrostatic force due to the other two charges.
= 15 N
= 8N
= 17 N
In a coil of resistance the magnetic flux due to an external magnetic field varies with time as The value of total heat produced in the coil, till the flux becomes zero, will be_______J.
t = 3 sec
Heat =
A potentiometer wire of length 300 cm is connected in series with a resistance 780 and a standard cell of emf 4V. A constant current flows through potentiometer wire. The length of the null point for cell of emf 20 mV is found to be 60 cm. The resistance of the potentiometer wire is ________ .
Potential Difference across AB = l × R =
Potential Difference across AC =
As per given figures, two spring constants k and 2k are connected to mass m. If period of oscillation in figure (a) is 3s, then the period of oscillation in figure (b) will be The value of x is________.
In figure a
27th July 2022 first shift
Commonly asked questions
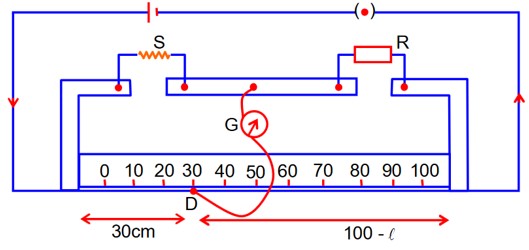
In a meter bridge experiment, for measuring unknown resistance ‘S’, the null point is obtained at a distance 30cm from the left side as shown at point D. If R is 5.6 , then the value of unknown resistance ‘S’ will be ___________
= 2.4k = 2400
The one division of main scale of Vernier calipers reads 1mm and 10 divisions of Vernier scale is equal to the 9 divisions on main scale, When the two jaws of the instrument touch each other, the zero of the Vernier lies to the right of zero of the main scale and its fourth division coincides with a main scale division. When a spherical bob is tightly placed between the two jaws, the zero of the Vernier scale lies in between 4.1 cm and 4.2cm and 6th Vernier division coincides with a main scale division. The diameter of the bob will be ________× 10-2 cm.
1 msD = 1mm
10 vsD = 9msD
1vsD = 0.9 MsD
L.C. = 1MSD – 1VSD = 1 – 0.9 = 0.1 mm
Zero error = 4LC = 0.4 mm
Reading = MSR + VSR + correction
= 4.1 cm + 6 * .01 cm + (-0.04 cm) = (4.1 + 0.06 – 0.04) cm
= 4.12 cm = 412 * 10-2 cm
Two beams of light having intensities I and 4I interfere to produce a fringe pattern on a screen. The phase difference between the two beams are p/2 and p/3 at points A and B respectively. The difference between the resultant intensities at the two points is xI. The value of x will be________.
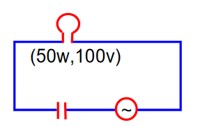
To light, a 50 W, 100 V lamp is connected, in series with a capacitor of a capacitance with 200V, 50Hz AC source. The value of x will be________.
A 1 m long copper wire carries a current of 1 A. If the cross section of the wire is 2.0mm2 and the resistivity of copper is 1.7 × 10-8 the force experienced by moving electron in the wire is _______× 10-23N.
i = 1 A
A = 2mm2
=
= 136 × 10-23 N
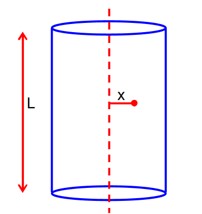
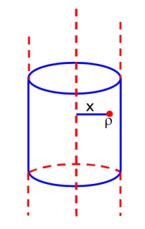
A long cylindrical volume contains a uniformly distributed charge of density The electric field inside the cylindrical volume at a distance from its axis is_________Vm-1.
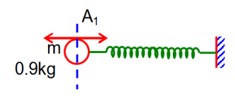
A mass 0.9kg, attached to a horizontal spring, executes SMH with an amplitude A1. When this mass passes through its mean position, then a smaller mass of 124 g is placed over it both masses move together with amplitude A2. If the ratio then the value of a will be______.
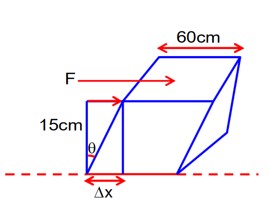
A square aluminium (shear modulus is 25 × 109 Nm-2) slab of side 60 cm and thickness 15 cm is subjected to a shearing force (on its narrow face) of 18.0 × 104 N. The lower edge is riveted to the floor. The displacement of the upper edge is ________
Shear modulus = 25 × 109 N/m2
A pulley of radius 1.5m is rotated about its axis by a force F = (12t – 3t2)N applied tangentially (while t is measured in seconds). If moment of inertia of the pulley about its axis of rotation is 4.5 kg m2, the number of rotation made by the pulley before its direction of motion is reversed, will be The value of K is ________.
r = 1.5 m
F = 12t – 3t2 N
l = 4.5 kgm2
No. of rev =
A ball of mass m is thrown vertically upwards. Another ball of mass 2 is thrown at an angle q with vertical. Both the balls stay in air for the same period of time. The ratio of the heights attained by the two balls respectively is The value of x is _______.
- (i)
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Thirteen Exam