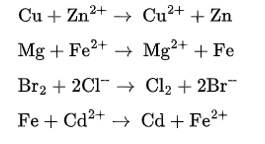Redox Reactions
Get insights from 110 questions on Redox Reactions, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Redox Reactions
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In MnO42–, Mn is in the highest oxidation state that is +7 hence here manganese cannot undergo oxidation that is why disproportionate is not possible whereas in MnO42- manganese is in +6 oxidation state which can be oxidized as well as reduced.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The given reaction is as below-
Cl2 (g) +2OH-- (aq)→ClO-- (aq)+ Cl-- (aq) + H2O (l)
In the given reaction, oxidation number of Cl increases from 0 (in Cl2) to +1 (in ClO-) and decreases to -1 (in Cl-). Therefore, Cl2 is both oxidized to ClO- and reduced to Cl-. Since Cl- ion cannot act as an oxidizing agent (because it cannot decrease its O.N. lower than -1), hence, Cl2 bleaches substances due to oxidizing action of hypochlorite, ClO ion.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
We can Measure the electrode potential of the given species by connecting the redox couple of the given species with standard hydrogen electrode. If it is positive, the electrode of the given species acts as reductant and if it is negative, it acts as an oxidant. Find the electrode potentials of the other given species in the same way, compare the values and determine their comparative strength as an reductant or oxidant. Example Measurement of standard electrode potential of electrode E? Zn2+/Zn using SHE as a reference electrode.
Types of Redox Reactions
The diffe
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
We can calculate the oxidation states by - ]
NaClO4 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +7
Suppose oxidation number of chlorine is x then, 1 + x + 4 * (−2) = 0
∴ x - 7 = 0
x = +7
We can calculate, the oxidation states, as given below-
NaClO3 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +5
? NaClO Oxidation no. of chlorine = +1
? KClO2 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +3
? Cl2O7 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +7
ClO3 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +6
Cl2O Oxidation no. of chlorine = +1
NaCl Oxidation no. of chlor
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Redox couple are given as
Cu2+/Cu and Zn2+/Zn
Mg2+/Mg and Fe2+ /Fe
Br2/Br- and Cl2 / Cl-
Fe2+ /Fe and Cd2+/Cd
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Disproportionate is defined as the reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states So, to occur such type of redox reaction, the element should exist in at least three oxidation states. So that element present in the intermediate state and it can change to both higher and lower oxidation state during disproportionate reaction. Fluorine is the most electronegative element and a strong oxidizing agent and is the smallest in size of all the halogens. It does not show a positive oxidat
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
On the basis of standard reduction potential suggested in the reactivity series (ii) reaction can take place as Mg has more negative value of E? cell. Hence, Mg will be oxidized by losing electron and iron will be reduced by gaining electron.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The given reaction is a redox change.
2Na (s)+H2 (g)→2NaH (s)
The half reaction is:
2Na (s)→2Na+ (g)+2e-
The other half reaction is:
H2 (g)+2e-→2H- (g)
This splitting of the reaction into two half-reactions automatically reveals here that sodium is oxidized, and hydrogen is reduced. Any substance which loses electron is oxidized and gains electron is reduced hence is the case of sodium and hydrogen atoms respectively. Hence, the complete reaction is a redox change.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The potential associated with each electrode is known as electrode potential. If the concentration of each species taking part in the electrode reaction is unity (if any gas appears in the electrode reaction, it is confined to 1 atmospheric pressure) and further there action is carried out at 298K, then the potential of each electrode is said to be the Standard Electrode Potential. By convention, the standard electrode potential (E? ) of hydrogen electrode is 0.00 volts. The electrode potential value for each electrode process is a measure of the relative tendency of the active species in the process to remainin the oxidised/reduced fo
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Two methods are used to balance chemical equations for redox processes. One of these methods is based on the change in the oxidation number of reducing agent and the oxidising agent (i.e. oxidation number method) and the other method is based on splitting the redox reaction into two half reactions — one involving oxidation and the other involving reduction (half reaction method). Both these methods are in use and the choice of their use rests with the individual using them.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers