Surface Chemistry
Get insights from 216 questions on Surface Chemistry, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Surface Chemistry
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.32
Uses of Emulsions-
It is used in making of medicines,
Cleansing action of soaps is based on this emulsion
Digestion of fats in intestine takes place by the process of
Antiseptics and disinfectant added to water form emulsion for
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.31
Electrophoresis: The movement of colloidal particles under an applied electric potential is called When an electric potential is applied to two platinum electrodes dipping in colloidal solutions the colloidal particle move towards the Oppositely charged electrodes.
Coagulation: The process of settling of colloidal particles is called coagulation. When the charge is removed from colloidal solution somehow, then particle start coagulation and settling due to the force of
Dialysis: It is a process of removing a dissolved substance from AC colloidal solution by means of diffusion through a suitable the animal membrane or parchment paper
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.30
The catalytic reaction that depends upon the pore structures of the catalysts and the size of reactant and product molecules is called shape selective catalysis. Zeolites are good shape- selective catalysts.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.29
Catalysis by zeolites is dependent on shape. Because zeolites are shape-selective catalysts. They are alumino silicates which are microporous in nature. It has Honeycomb structure. That makes them shape selective. In zeolites, some si atoms are replaced by Al to form Al-O-Si network.
Reactants are very sensitive to the pore size of zeolites. Zeolites are used in petrochemical industry. Ex- ZSM-5 used to convert alcohol into gasoline.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.28
Activity - It is the ability of the catalyst to accelerate the Reaction. It mostly depends upon the Chemisorption strength.
Selectivity - It is an ability to direct reaction to yield of a particular product i.e., One catalyst cannot be a catalyst for other reactions.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.27
Oxidation of sulphur dioxide into sulphur trioxide in the presence of
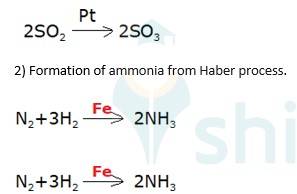
(3) Oxidation of ammonia into nitric acid in presence of platinum gauze in Ostwald's process
→ 4NH3 (g)+ 5O2 (g) Pt (s) 4NO +6H2O
(4) Hydrogenation of vegetable oils in presence of Nickel as catalyst
Vegetable oil (l)+H2 (g) Ni → Vegetable ghee (s)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.26
Soap is sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids (long chain). Represented as RCOO–Na+. When dissolved in Water it dissociates in the RCOO– and Na+. In first ion there are two parts R and COO–. R is hydrophobic tail and COO– Hydrophilic head. RCOO– ions present at the surface with COO– group inside and R group outside.
Increasing concentration to critical micelle concentration anions are pulled inside the bulk and Form a spherical shape of hydrocarbon chain pointing towards the centre and COO– pointing outside this are called as micelle.
Cleansing action of soap: Soap molecules form micelle around oil droplets. So
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.25
Emulsifiers form an interfacial film between the suspended particles and medium. It provide coating to every drop of suspended particle and prevent it from coagulating. And it remain suspended in medium. Ex- Proteins, gums, alcohols, Lampblack etc.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.25
Emulsions –The system which has Liquid as both dispersed phase and dispersion medium. There are two types of emulsions
Oil in Water-Ex-Milk
Water in oil-Ex-Butter.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.23
(i) In this case Tyndall effect is observed i.e. scattering of light by the colloidal particles takes place and the path of light become visible.
(ii) The coagulation takes place in this case positive charge particles of Fe (OH)2 gets attached with Cl-. And of FeCl3 is obtained.
(iii) In this case coagulation will take place. After passing electric current through colloidal solution particle will get attracted towards oppositely charged and lose their charge and coagulate.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
