Alcohol Phenol And Ethers
Get insights from 261 questions on Alcohol Phenol And Ethers, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Alcohol Phenol And Ethers
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.9 Phenol on mixing with chloroform and NaOH at 340K followed by Acidic hydrolysis, salicyl aldehyde is formed. When carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is used at the place of chloroform salicylic acid is This type of reaction is known as Reimer - Tiemann reaction.
2. The sodium phenoxide reacts with CO2 under pressure 4-7 atm at a 400K temperature to form sodium salicylate, which on acidification yields salicylic acid. This type of reaction is known as Kolbe's
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.8
Resonating structures of o-nitrophenoxide ions that are formed by the loss of a proton from o-nitrophenol are as follows:
Resonating structures of p-nitrophenoxide ions that are formed by the loss of a proton from p- nitrophenol are as follows:
Resonating structures of phenoxide ions that are formed by the loss of a proton from phenol are as follows:
It is clearly evident from the above structures that due to —R-effect of— NO2NO2 group, o-and p-nitrophenoxide ions are more stable than phenoxide ions. Consequently, o- and p- nitrophenols are more acidic than phenols.
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) (i) Primary alcohols do no react appreciably with Lucas' reagent (HCl –ZnCl2) at room temperature.
(ii) Tertiary alcohol reacts immediately with Lucas 'reagent.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.5 In this reaction, when propene reacts with the given reagent then the double bond of propene breaks down with charges on them. So, H+ gets placed on the carbon which already has two hydrogen atom and OH- gets substituted on center carbon because it has the more positive charge which attracts OH-. Thus we get propene-2-or as a
2. In this reaction, when Methyl ( 2-oxocyclohexyl) ethanoate reacts with the given reagent then the double bond between the oxygen atom and cyclohexyl gets breaks down, such that O has a negative charge and that particular carbon will have a positive charge on it. So, to neutralize it, H+ gets substitut
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.4 In the Grignard reagent reaction, the first step of the reaction is the nucleophilic addition of Grignard reagent to the carbonyl group to form an adduct, Hydrolysis of adduct results in the formation of alcohol.
Here, is the general reaction with Grignard reagent below:-
From here, it is clear that HCHO gives CH2OH groups, so R of Grignard reagent is the remaining part of given alcohols. Thus, select the suitable Grignard reagent by substituting the value of R. Now we can see the reaction given below:-
Methanal reacts with iso-propyl magnesium bromide, in presence of dry ether gives an additional compound. And this additional compou
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.3 (i) 3-chloroethyl-2-isopropylpentan-1-ol
(ii) 2,5-Dimethylhexane-1,3-diol
(iv) 3-Bromocyclohexanol
(v) Hex-1-en-3-ol
(vi) 2-Bromo-3-methylbut-2-en-1-ol
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
11.2 Allylic alcohol is an organic compound which has the structural formula CH2 = CHCH2OH. In other words, in these alcohols, the-OH group is attached to sp2 hybridized carbon next to the carbon-carbon double bond, that is to an allylic carbon. Therefore, in the above examples, the following are the allylic alcohols.
(ii) H2C = CH – CH2OH and
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
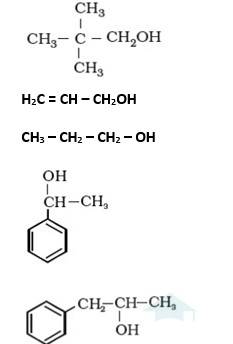
It is primary alcohol because carbon which carries the –OH group is only attached to one alkene group.
It is primary alcohol because the carbon which carries the –OH group is only attached to one propyl group.
It is secondary alcohol because the carbon which carries the –OH group is joined directly to methyl and benzene.
It is secondary alcohol because the carbon which carries the –OH group is joined directly to two different alkyl groups.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
