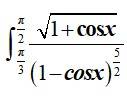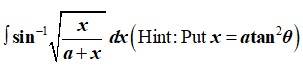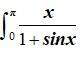Class 12th
Get insights from 12k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
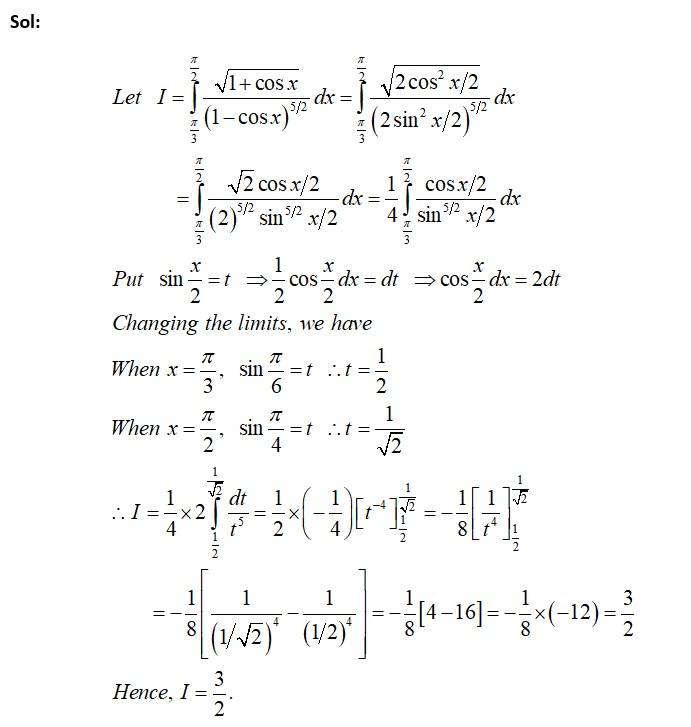
Sol:
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
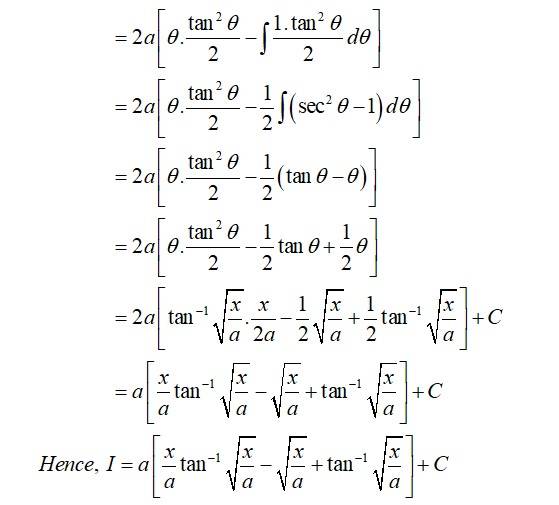
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
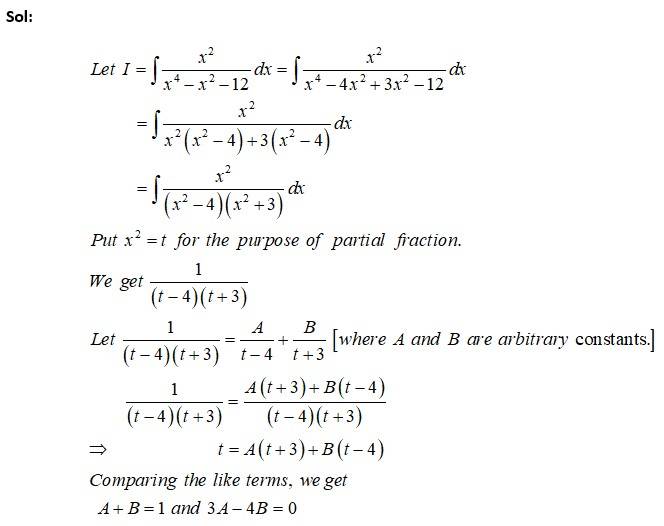
Sol:
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
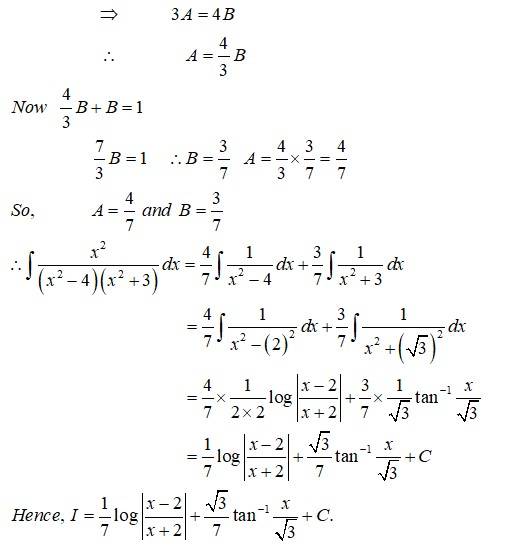
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
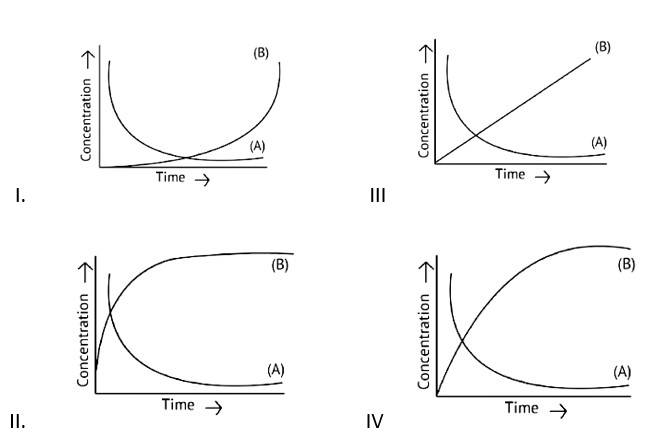
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option B
If A→B then the concentration of both reactants and the products vary exponentially with time. But, in option B graph the reactant concentration decreases exponentially and the product concentration increases.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option C
Let's start with what a pseudo-first-order response is.
Although the pseudo-first-order reaction looks to be an order, it belongs to another order. It's a second-order reaction because it involves two reactants.
Let's have a look at a reaction.
CH3Br + OH→CH3OH + Br-
So, the rate law for the reaction is
Rate = k [OH] [CH3Br]
Rate = k [OH- ] [CH3Br] = k (constant) [CH3Br] = K' [CH3Br]
Only the concentration of CH3Br will change during the reaction, and the rate will be determined by the reaction's modifications.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers