Electrochemistry
Get insights from 145 questions on Electrochemistry, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Electrochemistry
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, iii)
The conductivity in an ionic solution is due to the ions in the solution. It depends on the following factors;
(a)Temperature: On an increase in temperature, the molar conductivity of ionic solutions increases.
(b)Concentration of Electrolytes: An increase in the concentration of electrolytes decreases the molar conductivity as the number of ions per unit volume decreases.
Therefore, options (i, iii) are correct
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, ii)
Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance and conductivity is the reciprocal of resistivity. It can be written as follows
k =
R=
=
k =
k =
k = G*
k =
G* is cell constant.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, ii)
In the electrolysis process of CuSO4 the following reactions occur at the half cell which is as follows:
At the cathode, the reaction goes this way,
Cu2++2e−→Cu (s)
At the anode, the reaction goes this way,
Cu (s)→Cu2++2e−
Here copper will be deposited at the cathode and copper will dissolve at the anode.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, iii)
Electrolysis of copper sulfate solution is as follows
CuSO4 ? Cu2+ + SO42−
H2O? H+ + OH−
At the cathode, the reaction goes this way,
Cu2+ + 2e− → Cu; E? Cell = 0.34V
H2O− → H2 E? Cell = 0.00V
At the anode, the reaction goes this way,
2SO42- + 2e−→S2O82− E? Cell =1.96V
2H2O→O2 + 4H+ + 4e− E? Cell =1.23V
The reaction will lower the value of E? Cell is preferred at anode so the second reaction is feasible.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, iii)
Kohlrausch law of states that limiting molar conductivity of any salt species is equal to the sum of the limiting molar conductivity of cations and anions of the electrolyte
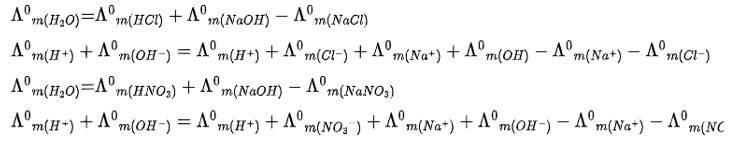
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, ii)
Conductivity is due to the movement of ions in the solution. The conductivity of ions depends on the following factors:
(i) nature of electrolyte added
(ii) size of ion produced
(iii) concentration of electrolyte
(iv) nature of the solvent
(v) temperature
Distance between electrodes does not affect the conductivity of an electrolytic solution.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (ii, iii)
At equilibrium, ?G = -2.303 RT
-nFE = -2.303 RT
E =
For Daniel cell, n=2
E =
At equilibrium, E = 1.1V
1.1V =
(i) Since this option is incorrect
(ii) As derived 1.1V =
(iii) As derived so this option is correct
(iv) As ,so this option is incorrect
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, iii)
In the electrolysis of sulphuric acid, the following reactions occur
2SO42− (aq)→S2O82− (aq) + 2e− E? Cell =1.96V
2H2O (l)→O2 (g)+4H+ (aq) + 4e− E? Cell =1.23V
The reaction will lower the value of E? Cell is preferred at anode so the second reaction is feasible.
H+ + e− → H2 E? Cell = 0.00V
At the cathode, reduction of water occurs. Therefore, in dilute sulphuric acid solution, hydrogen will be reduced at the cathode.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (ii, iv)
The lesser the E? value of the redox couple higher is the reducing power
For Cu2+ + 2e−→Cu; E? =0.34V
For 2H+ + 2e−→H2 E? =0.00V
Since the second redox couple has less standard reduction potential than the first so it can be concluded that the redox couple is a stronger oxidizing agent than H+/H2 and copper cannot displace H2 from acid.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iv)
The electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride is as follows
NaCl→Na+ + Cl−
H2O→H+ + OH−
At the cathode, the reaction goes this way,
H2O + e− → H2 + OH−
At the anode, the reaction goes this way,
Cl− (aq)→ Cl2 (g)+ e− E? Cell =1.36V
2H2O (g)→O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e− E? Cell =1.23V
At the anode, the reaction with a lower E? value will be preferred and oxidation of oxygen is a slow process and requires high voltage so the first reaction will take place.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
