
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three Electrochemistry offers step-by-step solutions for this crucial chapter. The exemplar includes the solutions to the numerical and advanced conceptual problems. There are various types of questions, including Multiple Choice Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Matching Type, Assertion and Reason Type, and Long Answer Type questions. These questions cover the key topics of the chapter, like electrode potentials, galvanic and electrolytic cells, Nernst equation, electrochemical cells, electrolysis, electrode potentials, and conductance of electrolytic solutions.
The students will be able to find a free Electrochemistry NCERT PDF on this page. The PDF is well-structured, and all the solutions are created by the subject matter experts. Students can rely on these solutions for their CBSE board exam preparation and JEE and NEET preparations. The students should download the PDF to read it at any time without the requirement of any internet connectivity.
To get the topic-wise revision PDF and solved questions of Chemistry NCERT Class 12, students should also check NCERT Class 12 Chemistry.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter Three Electrochemistry
- Electrochemistry Class 12 Short Answer Type Questions
- Chemistry Class 12 Electrochemistry Long Answer Type Questions
- Class 12 Electrochemistry Matching Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Electrochemistry Class 12 Assertion and Reason Type
- Electrochemistry NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Objective Type Questions
- Common Mistakes and Tips for NCERT Chemistry Exemplar Chapter Three
- JEE Mains Solutions 2022,28th june , Chemistry ,Second shift
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter Three Electrochemistry
There are various academic and practical benefits of downloading this PDF for students. First, it provides offline accessibility; once the student downloads it, they do not require an internet connection to access the solutions. Hence, they can have uninterrupted study while traveling, at some remote location, or anywhere with poor or no internet connection. The PDF has solutions to all the questions of the NCERT Exemplar book, including the MCQs, long answers, short answers, and other questions.
The Class 12 NCERT Exemplar Electrochemistry PDF serves as a valuable revision tool for students, allowing them to create digital notes, highlight key points, and quickly revisit difficult concepts, thereby making their revisions more effective and efficient. They can also get a printout of the PDF if they want to study on paper and underline the important solutions and concepts. The students should also refer to the NCERT solutions Chapter Two Electrochemistry.
Related Links Below
| NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry | NCERT Solutions |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry | NCERT Notes |
Commonly asked questions
In the given reaction,
X + Y + 3Z XYZ3
If one mole of each of X and Y with 0.05 mol of Z gives compound XYZ3. (Given: Atomic masses of X, Y and Z are 10, 20 and 30 amu, respectively.) The yield of XYZ3 is_____________g.
x + y + 3z = xyz3
1 mole 1 mole 0.05 mole
here z is limiting reagent.
mole z gives 1 mole xyz3
mass of xyz3 = n × molecular mass
=
= 0.5 × 4 = 2g
An element M crystallises in a body centred cubic unit cell with a cell edge of 300 pm. The density of the element is 6.0g cm-3. The number of atoms in 180g of the element is_________× 1023 (Nearest integer)
B.C.C structure
a = 300 pm = 300 × 10-12 m
d = 6g/cm3
z = 2
= 3.69 × 6.022 × 1023
= 22.22 × 1023
the nearest integer = 22
The number of paramagnetic species among the following is
B2, Li2, C2, , , and .
Paramagnetic
Diamagnetic
Paramagnetic
Paramagnetic
Paramagnetic molecules are
150g of acetic acid was contaminated with 10.2g ascorbic acid to lower down its freezing point by (x × 10-1)°C. The value of x is _________. (Nearest integer)
(Given Kf = 3.9 K kg mol-1; molar mass of ascorbic acid = 176 g mol-1]
3.9 × 0.386
Ans = 15
Ka for butyric acid (C3H7COOH) is 2 × 10-5. The pH of 0.2 M solution of butyric acid is ____________× 10-1 (Nearest integer)
[Given log2 = 0.30]
Ka for C3H7COOH = 2 × 10-5
=5 – 0.3 = 4.7
pH of 0.2 (M) solution =
![]()
For the given first order reaction
A ® B
The half life of the reaction is 0.3010 min. The ration of the initial concentration of reactant to the concentration of reactant at time 2.0 min will be equal to________________. (Nearest integer)
t1/2 = 0.301 min
t = 2 min
Ans. 100
The number of interhalogens from the following having square pyramidal structure is:
CIF3, IF7, BrF5, BrF3, I2Cl6, IF5, ClF, ClF5
® T-shaped (sp3d)
IF7 ® Pentagonal bipyramidal (sp3d3)
BrF5 ® Square pyramidal (sp3d2)
BrF3 ® T-Shaped (sp3d)
I2Cl6 ® Triangular bipyramidal (sp3d)
Square Pyramidal (sp3d2)
ClF ® (sp3)
ClF5 ® Square Pyramidal (sp3d2)
Br5, IF5 & ClF5 ® Square Pyramidal
The disproportionation of in acidic medium resultant in the formation of two manganese compounds A and B. If the oxidation state of Mn is B is smaller than that of A, then the spin-only magnetic moment value of B in BM is___________.
(Nearest integer)
Oxidation state of Mn in B < A
B is MnO2
![]() Oxidation state of Mn = +4
Oxidation state of Mn = +4
![]() unpaired electron = 3
unpaired electron = 3
Spin only magnetic moment
Total number of relatively more stable isomer(s) possible for octahedral complex will be________________.
More stable isomers = 3 (trans isomers)
On complete combustion of 0.492g of an organic compound containing C, H and O, 0.7938 g of CO2 and 0.4428 g of H2O was produced. The % composition of oxygen in the compounds is____________.
% of C in organic compound
=
=
= 100 – 54 = 46%
Electrochemistry Class 12 Short Answer Type Questions
The SA questions need concise answers. It assesses a student's conceptual clarity of the chapter. It normally requires students to provide numerical applications, precise explanations, or reasoning behind electrochemical principles. Practicing short-answer-type questions helps students boost their problem-solving abilities and sharpen their critical thinking skills. The topics include the calculation of cell potentials, electrochemical cell notations, the Nernst equation, Faraday’s laws, and conductance.
Below Are SA Solutions
Ans: No, the difference in potentials of the electrodes is measured. A reference electrode is to be taken while measuring the electrode potential of the electrode.
Q: Can EᶱCell or ΔrG for cell reactions to ever be equal to zero?
Ans: E? Cell can never be zero. For a feasible reaction, E? Cell should be positive or ΔrG should be negative, and at the stage of equilibrium, both of these parameters are zero.
Commonly asked questions
Why is alternating current used for measuring the resistance of an electrolytic solution?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Alternating current is used to stop electrolysis so that the concentration of the ions in the solution remains constant.
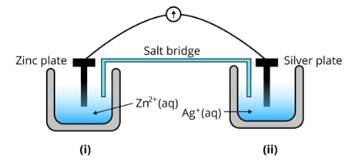
Depict the galvanic cell in which the cell reaction is
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Galvanic cell consists of two electrodes in which anode and cathode are present as electrodes. The anode is present on the left side at which oxidation occurs. The cathode is present on the right side at which reduction occurs and in the middle, there is a salt bridge which is depicted by parallel lines. Therefore, the galvanic cell is Cu|Cu2+ |Ag+ |Ag.
What is electrode potential?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The potential difference between the metal and its solution is termed electrode potential.
In an aqueous solution how does the specific conductivity of electrolytes change with the addition of water?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Conductivity due to the total number of ions present in the solution is termed as specific conductivity. An increase in the number of ions per unit volume increases. In addition to water, the number of ions per unit volume decreases therefore conductivity decreases.
Which reference electrode is used to measure the electrode potential of other electrodes?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is used as a reference electrode and its electrode potential is assumed to be zero. The electrode potential of other electrodes is measured concerning standard hydrogen electrodes.
Consider a cell given below
Cu|Cu2+||Cl−|Cl2,pt
Write the reactions that occur at anode and cathode
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The given cell reaction consists of two half cell reactions represented below as follows;
At anode: Cu→Cu2++ 2e−
At cathode: Cl2 + 2e− →2Cl−
Here oxidation of copper and reduction of chlorine is taking place
Aqueous copper sulfate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolyzed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells. Will the mass of copper and silver deposited on the cathode be the same or different? Explain your answer
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: According to Faraday’s second law of electrolysis, the amount of different substances liberated keeping the electricity flow same through the electrolytic solution is directly proportional to the equivalent weight.
=
E1and E2 have different values. Therefore, the mass of copper and silver deposited will be different
Value of standard electrode potential for the oxidation of Cl− ions is more positive than that of water, even then in the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride, why is Cl− oxidized at anode instead of water?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In the electrolysis process of sodium chloride, oxidation of water at anode requires more potential. So Cl− is oxidized at anode instead of water.
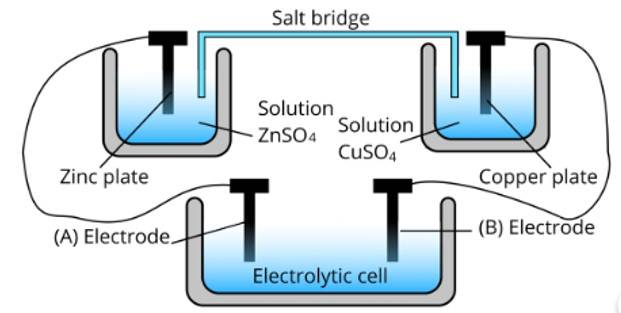
Consider the following diagram in which an electrochemical cell is coupled to an electrolytic cell. What will be the polarity of electrodes ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the electrolytic cell?
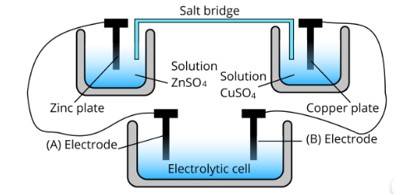
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The cell represented above shows an electrochemical cell in which two different electrodes are present and the cell at the bottom represents the electrolytic cell.
In this zinc is losing electrons moving towards electrode A and copper is accepting an electron from electrode B. Therefore, the polarity of electrode A is positive and electrode B is negative.
A galvanic cell has an electrical potential of1.1V. If an opposing potential of 1.1V is applied to this cell, what will happen to the cell reaction and current flowing through the cell?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: When the opposing potential becomes equal to the electrical potential there is no current flowing in the cell and the cell reaction stops and there is no chemical reaction in the cell
How will the pH of brine (aq.NaCl solution) be affected when it is electrolyzed?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Electrolysis of brine solution is as follows
NaCl (aq)→Na+ (aq)+Cl− (aq)
At the cathode, the reaction goes this way,
H2O (l) + e−→12H2 (g)+OH− (aq)
At the anode, the reaction goes this way,
Cl− (aq)→12Cl2 (g) + e−
The pH of the solution will increase as sodium hydroxide is being formed.
Unlike dry cells, the mercury cell has a constant cell potential throughout its useful life. Why?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The number of ions present in the cell decides the life-time of any cell. In mercury cells, ions are not involved so the mercury cell has a constant cell potential throughout its useful life.
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λ�of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Stronger electrolytes undergo cent percent dissociation. Electrolyte B will be the stronger electrolyte since the concentration of ions remains the same upon dilution.
When acidulated water (dil.H2SO4 solution) is electrolyzed, will the pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: pH of the substance depends on the concentration of hydronium ions present. Here the concentration of hydronium ions remains constant so pH remains constant.
The electrolysis reaction is as follows;
At anode: 2H2O (l)→O2 (g)+ 4H+ + 4e−
At cathode:4H+ + 4e− →2H2
Write the Nernst equation for the cell reaction in the Daniel cell. How will the Ecell be affected when the concentration of Zn2+ ions are increased?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The reactions taking place in the Daniel cell is as follows;
Zn+ + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu
The number of electrons involved in two. The Nernst equation is as follows;
Ecell = E cell - log
From the above equation, we conclude that increasing the concentration of Zn2+, Ecell will decrease.
What advantage do the fuel cells have over primary and secondary batteries?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Primary batteries contain a limited amount of reactants and once consumed are discharged. Secondary batteries take a long time to recharge. Fuel cells run continuously as long as reactants are supplied to them and products are consumed
Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharged. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the battery is discharged?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The cell reaction of a lead storage battery is as follows;
Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4→2H2SO4 + 2H2O
The density of electrolytes changes because water is formed and sulphuric acid is consumed as a product during discharge of the battery
Why on dilution the Λm of CH3COOH increase drastically, while that of CH3COONa increases gradually?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Acetic acid is a weak electrolyte and the number of ions on dilution increases due to an increase in the degree of dissociation. In the case of strong electrolytes the number of ions remains the same but interionic attraction decreases.
Chemistry Class 12 Electrochemistry Long Answer Type Questions
It requires detailed explanations of questions. Students need to have an in-depth understanding of concepts. They normally include derivations, multi-step numerical problems, comparative analyses, or detailed working of concentration cells. Students need to integrate the conceptual knowledge with practical applications. Practicing LA questions, prepares students for the descriptive answers in CBSE Board exams.
LA Questions
| Consider Fig. 3.2 and answer the following questions. (i) Cell ‘A’ has Ecell =2V and Cell ‘B’ has Ecell =1.1Vwhich of the two cells ‘A’ or ‘B’ will act as an electrolytic cell. Which electrode reactions will occur in this cell? |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: Cell ‘B’ will act as an electrolytic cell because to less value of Ecell The reactions occurring in the cell are as follows; At anode: Zn2+ + 2e− → Zn At cathode: Cu(s) → Cu2+ + 2e− |
| (ii) If cell ‘A’ has Ecell =0.5V and cell ‘B’ has Ecell =1.1V .Then what will be the reactions at anode and cathode? |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans:Cell ‘B’ has a higher emf so it acts as a galvanic cell. The reactions are as follows; At anode: Zn → Zn2+ + 2e− At cathode: Cu2+ + 2e− → Cu |
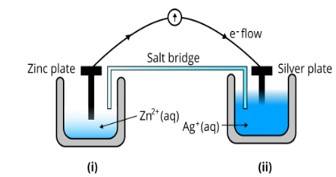
| Consider Fig. 3.2 and answer the questions (i) to (vi) given below (i) Redraw the diagram to show the direction of electron flow. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: The diagram is as follows; |
| (ii) Is silver plate the anode or cathode? |
| Ans: Agis cathode where the reduction process is taking place where Ag+ takes electrons and deposits them at the cathode |
| (iii) What will happen if the salt bridge is removed? |
| Ans: Potential is zero when the salt bridge is suddenly removed. |
| (iv) When will the cell stop functioning? |
| Ans: Cell will stop functioning at discharging position when the cell potential is zero |
| (v) How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected when the cell functions? |
| Ans: The concentration of Zn2+ ions will increase and the concentration of Ag+ ions will decrease due to conversion in oxidized and reduced forms. |
| (vi) How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected after the cell becomes ‘dead? |
| Ans: When the cell is dead, the potential is zero and at equilibrium condition. Thus, the concentration of Zn2+ and Ag+ will not change. |
Commonly asked questions
What is the relationship between Gibbs free energy of the cell reaction in a galvanic cell and the emf of the cell? When will the maximum work be obtained from a galvanic cell?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The relation between Gibbs free energy and the emf of the cell is as follows;
ΔG=−nFEcell
E cell s the cell potential
is the standard emf of the cell
Maximum work obtained from the galvanic cell is nFE .
Class 12 Electrochemistry Matching Type Questions
It requires students to match two related sets of information, such as electrolytes and their conductivity, conductors and their properties, and electrodes and their standard potentials. These types of questions help students improve memory recall.
Matching Type Solutions Below
Match the terms given in Column I with the units given in Column II.
| Column I |
Column II |
| (i)Λm |
(a)Scm−1 |
| (ii)Ecell |
(b)m−1 |
| (iii) k |
(c)Scm2mol-1 |
| (iv)G∗ |
(d)V |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i)The unit of Λm is Scm2mol−1
(ii) The unit of Ecell is m−1
(iii) The unit of k is Scm−1
(iv)The unit of G∗ is m−1
Hence, the answer is:
(i)-c ; (ii)-d ; (iii)-a ; (iv)-b
Match the terms given in Column I with the units given in Column II.
| Column I |
Column II |
| (i) Λm |
(a)intensive property |
| (ii) Ecell |
(b)depends on the number of ions/volume |
| (iii) k |
(c)extensive property |
| (iv) ΔrGcell |
increases with dilution |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i)On dilution, the number of ions per unit volume increases so the molar conductivity increases with dilution.
(ii) E cell is an intensive property as it is not dependent on the amount or mass of the substance.
(iii) k is conductivity or be precise specific conductivity which depends on the number of ions
(iv) ΔrGcell is an extensive property as it depends on the amount of substance or number of particles in the solution.
Hence, the answer is:
(i)-d ; (ii)a ; (iii)-b ; (iv)-c
Commonly asked questions
Match the terms given in Column I with the units given in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i)Lead storage battery |
(a)Maximum efficiency |
|
(ii)Mercury cell |
(b)prevented by galvanization |
|
(iii)Fuel cell |
(c)gives steady potential |
|
(iv)Rusting |
(d)Pbis the anode,PbO2 is cathode |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) The cell reaction of a lead storage battery is as follows;
Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4→2H2SO4 + 2H2O
At cathode:PbO2 (s)+SO42− (aq)+2e−→2PbSO4 (s) + 2H2O (l)
At anode:Pb (s)+SO42− (aq)→PbSO4 (s)+2e−
Therefore Pb is the anode and PbO2 is cathode
(ii)Mercury cell doesn’t contain ions so it gives steady potential.
(iii)Fuel cells have maximum efficiency as they produce energy due to the combustion reaction of fuel.
(iv)Rusting is prevented by galvanization.
Hence, the answer is:
(i)-d ; (ii)-c ; (iii)-a ; (iv)-b
Match the terms given in Column I with the units given in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i)k |
(a)I x T |
|
(ii)Λm |
(b) |
|
(iii) |
(c) |
|
(iv) |
(d) |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i)Conductivity k is defined as k =
(ii)Molar conductivity is given by Λm =
(iii)Degree of dissociation is given by ? =
(iv)Charge is the product of current and time = I
Hence, the answer is:
(i)-d; (ii)-c; (iii)-b; (iv)-a
Match the items of column I and column II
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i)Lechlanche cell |
(a)cell reaction |
|
(ii)Ni−Cd |
(b) does not involve any ion in solution and is used in hearing aids. |
|
(iii)Fuel cell |
(c)rechargeable |
|
(iv)Mercury cell |
(d)reaction at anode |
|
(e) converts energy of combustion into electrical energy |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i)The reaction occurring at Lechlanche cells are
At anode: Zn→Zn2+ + 2e−
At cathode: MnO2 + NH4+ + e−→MnO (OH)+NH3
(ii)Ni−Cd is rechargeable. So it has a longer lifetime.
(iii) Energy in the fuel cell is due to the combustion process. It converts combustion energy into electrical energy 2H2 + O2→2H2O
(iv) Mercury cells don’t involve any solution and are used in hearing aids.
Hence, the answer is:
(i)-d; (ii)-c; (iii)-a, e; (iv)-b
Match the items of Column I and Column II based on data given below:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i)F2 |
(a)metal is the strongest reducing agent |
|
(ii)Li |
(b)metal ion which is the weakest oxidizing agent |
|
(iii)Au 3+ |
(c)non-metal which is the best oxidizing agent |
|
(iv)Br − |
(d)unreactive metal |
|
(v)Au |
(e)anion that can be oxidized by Au 3+ |
|
(vi)Li+ |
(f)anion which is the weakest reducing agent |
|
(vii)F− |
(g)metal which is an oxidising agent |
E F2/F=2.87V E Li/Li= 3.5V EAu3+/Au = 1.4V E Br2/Br- = 1.09V
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) F2 is a non-metal which is the best oxidizing agent since the standard reduction potential of F2 is 2.87V.
(ii)Liis a metal and the strongest reducing agent because the standard reduction potential of Li is −3.05V.
(iii)Au3+ is a metal ion which is an oxidizing agent as standard reduction potential of Au3+ is 1.40V.
(iv) Br−is an anion that can be oxidized by Au3+ as standard reduction potential of Au3+ is 1.40V which is more than that of Br− which is E Br2/Br−0=1.09V.
(v)Auis an unreactive metal
(vi)Li+ is a metal ion having the least value of standard reduction potential of 3.05V. Hence it is the weakest oxidizing agent
(vii)F−is an anion that is the weakest reducing agent as it has less oxidation potential.
Hence, the answer is:
(i)-c; (ii)-a; (iii)-g; (iv)-e; (v)-d; (vi)-b; (vii)-f
NCERT Exemplar Electrochemistry Class 12 Assertion and Reason Type
These types of questions challenge students to logically analyze the cause-effect relationships in electrochemical phenomena. The students are provided with a statement and an explanation and must find out whether the reason is true and whether it correctly explains the assertion. Practicing the Assertion and Reason type questions also helps in scoring high in the entrance exams as they deepen the conceptual understanding of the students and boost their reasoning skills.
Assertion and Reason Type Questions
Reason: E Cu2+/Cu is negative.
Ans: Correct Option: (iii)
(i)The electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu is negative. The electrode potential of 2H+/H2 is 0.00V. Therefore, the assertion is correct and the reason is incorrect and the reason is not a correct explanation of assertion. Therefore, this option is incorrect
(ii) E Cu2+/Cu is not negative so the reason is incorrect. Therefore, this option is incorrect
(iii) The electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu is negative. The electrode potential of 2H+/H2 is 0.00V. Therefore, the assertion is correct and the reason is incorrect. Therefore, this option is correct
(iv) Assertion is true and the reason is false therefore this option is incorrect
(v)Assertion is true therefore this option is incorrect.
Assertion: Ecell should have a positive value for the cell to function
Reason: Ecathode < Eannode
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iii)
(i)A chemical reaction is spontaneous when the Gibbs free energy is negative. This is possible when Ecell is positive. Ecathode < Eannode .Therefore, the assertion is correct and the reason is incorrect and the reason is not a correct explanation of assertion. Therefore, this option is incorrect
(ii) Ecathode < Eannode reaction is spontaneous when the Gibbs free energy is negative. This is possible when Ecell is positive. Ecathode < Eannode . Therefore, the assertion is correct and the reason is incorrect. Therefore, this option is correct
(iv) Assertion is true and the reason is false therefore this option is incorrect
(v) Assertion is true therefore this option is incorrect.
Commonly asked questions
Assertion: Conductivity of all electrolytes decreases on dilution
Reason: On dilution the number of ions per unit volume decreases.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct Option: (i)
Ans: (i) Conductivity is due to the movement of ions. The number of ions present per unit volume decides the conductivity. It decreases on dilution. The number of ions per unit volume decreases on dilution. So, the assertion is correct, the reason is correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. Therefore, this option is correct
(ii) Assertion is correct, the reason is correct and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion. Therefore, this option is incorrect
(iii) Assertion and true both are correct therefore this option is incorrect
(iv) Assertion is true and the reason is false therefore this option is incorrect
(v) Assertion is true therefore this option is incorrect.
Assertion: Λm Weak electrolytes show a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with the dilution of solution
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (i)
(i) Molar conductivity of weak electrolytes increases on dilution. In addition to solution the degree of dissociation increases leading to an increase in the number of ions produced. Therefore, Λm shows a sharp increase.
Therefore, the assertion is correct, the reason is correct and the reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(ii) Assertion is correct, the reason is correct and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion. Therefore, this option is incorrect
(iii)Assertion and true both are correct therefore this option is incorrect
(iv) Assertion is true and the reason is false therefore this option is incorrect
(v)Assertion is true therefore this option is incorrect.
Assertion: Mercury cell does not give steady potential.
Reason: In the cell reaction, ions are not involved in the solution.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (i)
(i)Mercury cells give a steady potential. The reason is that the ions are not involved in this reaction. The assertion is incorrect and the reason is correct so this option is incorrect
Assertion: Electrolysis of NaCl solution gives chlorine at anode instead of ?2 .
Reason: Formation of oxygen at anode requires overvoltage
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (i)
(i) Electrolysis of sodium chloride is represented by the following equations
H+ (aq)+ e−→12H2 (g)
At the anode, the reaction goes this way,
Cl− (aq)→12Cl2 (g) + e− E cell =1.36V
2H2O (aq)→O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq)+ 4e− E cell =1.23V
The reaction with the lower value Ecell is preferred but the formation of oxygen requires overpotential
Therefore, the assertion is correct, the reason is correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion. Therefore, this option is correct
Assertion: For measuring the resistance of an ionic solution an AC source is used.
Reason: Concentration of ionic solution will change if DC source is used
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (i)
The resistance of an ionic solution is measured by alternating current. The concentration of DC changes with electrolysis. Therefore, the assertion is correct, the reason is correct and the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion.
Assertion: Current stops flowing when E cell =0.
Reason: Equilibrium of the cell reaction is attained
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (i)
(i)At the equilibrium stage E cell = 0 and current stops flowing in the cell. Therefore, the assertion is correct, the reason is correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion. Therefore, this option is correct
(ii) Assertion is correct, the reason is correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion. Therefore, this option is incorrect
Assertion: Copper sulfate can be stored in a zinc vessel.
Reason: Zinc is less reactive than copper
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iv)
(i) Copper sulfate can’t be stored in zinc vessels due to less reactive nature than zinc due to the negative standard reduction value of zinc.
So both assertion and reason are false. Therefore, this option is incorrect.
Assertion: EAg+/Ag increases with increase in the concentration of Ag+ ions.
Reason: EAg+/Ag has a positive value
This is a Assertion and Reason Type as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (ii)
(i) The Nernst equation can be written as follows
Ecell = E cell – log
Ecell = E cell + 0.059 logAg+
Here we observe that EAg+/Ag increases with increase in the concentration of Ag+ ions. It has a positive value.
Here both assertion and reason are correct .The reason is not a correct explanation of assertion. So this option is incorrect
(ii) The Nernst equation can be written as follows
Ecell = E cell – log
Ecell = Ecell + 0.059 Ag+
Here we observe that EAg+/Ag increases with increase in the concentration of Ag+ ions. It has a positive value.
Here both assertion and reason are correct. The correct explanation of assertion is not the reason given. So, this option is correct
Electrochemistry NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Objective Type Questions
It mostly includes multiple-choice questions (MCQs), which are important for competitive exam preparation. It assesses the numerical aptitude, conceptual clarity, and theoretical knowledge. These are also useful for quick revision and self-assessment. The topics include the electrode potential, conductance, electrolysis, and electrode potential.
MCQs Below
Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode?
(i) Pt (s)|H2 (g,0.1 bar) | H+ (aq.,1 M) ||Cu2+(aq.,1M) | Cu
(ii) Pt(s) |H2 (g, 1 bar) |H+ (aq.,1 M) || Cu2+ (aq.,2 M) |Cu
(iii) Pt(s) | H2 (g, 1 bar) |H+ (aq.,1 M) ||Cu2+ (aq.,1 M) | Cu
(iv) Pt(s) |H2 (g, 1 bar) |H+ (aq.,0.1 M) || Cu2+ (aq.,1 M)| Cu
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iii)
(i) For measurement of electrode potential standard conditions must be met which is 1 bar pressure and 1M concentration which is not here so this option is incorrect.
(ii) For measurement of electrodes potential standard conditions must be met which is 1 bar pressure and 1M concentration which is not here so this option is incorrect.
(iii) When copper electrode is connected to SHE it acts as cathode and its standard electrode potential can be measured as follows
E E R- E L
For calculationn of standard potential of a given cell it should be coupled with SHE and standard conditions such as 1 bar pressure and 1M concentration and the concentrations of oxidised and reduced forms is one so this option is correct.
(iv) For measurement of electrode potential standard conditions must be met which is 1 bar pressure and 1M concentration which is not here so this option is incorrect.
Electrode potential for Mg electrode varies according to the equation
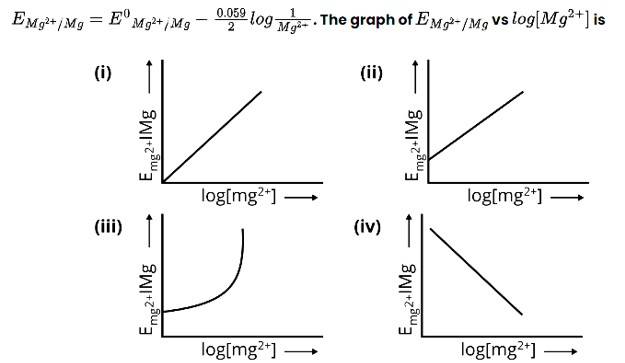
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Commonly asked questions
Using the data given below find out the strongest reducing agent
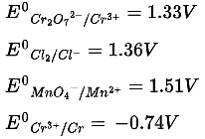
(i) Cl–
(ii) Cr
(iii) Cr3+
(iv) Mn2+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (ii)
According to the electrochemical series and standard reduction potential of metal, the higher the negative value of standard reduction potential stronger will be the reducing agent
In the given options, the standard reduction potential of chromium has the highest value so it is the strongest reducing agent.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(i) ECell and ∆rG of cell reaction both are extensive properties.
(ii) ECell and ∆rG of cell reaction both are intensive properties.
(iii) ECell is an intensive property while ∆rG of cell reaction is an extensive property.
(iv) ECell is an extensive property while ∆rG of cell reaction is an intensive property.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iii)
(i) The properties which don’t depend on the mass of species are termed intensive properties. ECell is an intensive property that doesn’t depend on the mass of the species.? rG is an extensive property as it depends on the mass of the species. Therefore, this option is incorrect
(ii) ECell is an intensive property but? rG is an extensive property so this option is incorrect
(iii) The properties which don’t depend on the mass of species are termed intensive properties ECell is an intensive property that doesn’t depend on the mass of the species.? rG is an extensive property as it depends on the mass of the species. Therefore, this option is correct
(iv) ECell is an intensive property but? rG is an extensive property so this option is incorrect.
The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called ___________.
(i) Cell potential
(ii) Cell emf
(iii) Potential difference
(iv) Cell voltage
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iii)
The difference between electrode potential potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is termed as cell emf. It is the energy provided by a cell per coulomb of charge passing through it. It is the maximum potential difference between the electrodes of a cell.
Which of the following statements is not correct about an inert electrode in a cell?
(i) It does not participate in the cell reaction.
(ii) It provides a surface either for oxidation or for reduction reaction.
(iii) It provides a surface for conduction of electrons.
(iv) It provides a surface for redox reaction.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iv)
(i) Inert electrodes like graphite are a source of electrons in a reaction. It doesn't participate in a chemical reaction. Therefore, this option is incorrect
(ii) Inert electrode chemically doesn't participate in the reaction but it provides a surface either for oxidation and reduction reaction. Therefore, this option is incorrect
(iii) Inert electrodes provide surface for conduction of electrons so this option is incorrect.
(iv) Inert electrodes cease transfer of electrons for oxidation or reduction but not for redox reaction. Therefore, this option is correct.
An electrochemical cell can behave like an electrolytic cell when ____________.
(i) Ecell = 0
(ii) Ecell > Eext
(iii) Eext > Ecell
(iv) Ecell = Eext
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iii)
On the application of external potential, an increased reaction starts till the opposing voltage becomes 1.1V.
However, further increase in the external potential leads the reaction to start in an opposite direction functioning as an electrolytic cell which is a device that uses electrical energy for carrying out electrochemical reactions.
Which of the statements about solutions of electrolytes is not correct?
(i) Conductivity of solution depends upon the size of ions.
(ii) Conductivity depends upon the viscosity of the solution.
(iii) Conductivity does not depend upon the solvation of ions present in the solution.
(iv) Conductivity of solution increases with temperature
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iii)
(i) Conductivity of solution depends upon the size of ions as more is the size of ion, mobility decreases, and conductivity decreases so this option is incorrect.
(ii) Viscosity is the measure of the resistance of a liquid to flow. Greater will be the viscosity of solvent, less will be the flow of electrons and lesser will be the conductivity. Therefore, this option is incorrect.
(iii) Conductivity depends on the solvation of ions in the solution. Greater is the solvation, lesser will be the conductivity of the solution. Therefore, this option is correct.
(iv) On increasing temperature the moving ions acquire higher kinetic energy and move with higher speeds thus increasing conductivity. Therefore, this option is incorrect
Use the data given in Q.8 and find out which of the following is the strongest oxidizing agent.
(i) Cl–
(ii) Mn2+
(iii) MnO4–
(iv) Cr3+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iii)
According to the electrochemical series higher the positive value of standard reduction potential of metal ion, the higher is the oxidizing power
Therefore, MnO4− is the strongest oxidizing agent.
Using the data given in Q.8 find out in which option the order of reducing power is correct.
(i) Cr3+ < Cl– < Mn2+ < Cr
(ii) Mn2+ < Cl– < Cr3+ < Cr
(iii) Cr3+ < Cl– < Cr2O72– < MnO4 –
(iv) Mn2+ < Cr3+ < Cl– < Cr
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iii)
According to the electrochemical series, the lower the reduction potential higher is the reducing power.
Therefore, the order of reducing power is Mn2+ < Cl– < Cr3+ < Cr
Use the data given in Q.8 and find out the most stable ion in its reduced form.
(i) Cl–
(ii) Cr3+
(iii) Cr
(iv) Mn2+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iv)
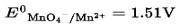
Use the data of Q.8 and find out the most stable oxidised species.
(i) Cr3+
(ii) MnO4–
(iii) Cr2O72–
(iv) Mn2+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (i)
According to the given table, ![]() has the most negative value among the given species. So
has the most negative value among the given species. So
Cr3+ is the most stable oxidized species.
The quantity of charge required to obtain one mole of aluminium from Al2O3 is ___________.
(i) 1F
(ii) 6F
(iii) 3F
(iv) 2F
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct Option: (iii)
Ans: Given: One mole of aluminium
Calculate the number of electrons required to convert Al2O3 to Al
It is the charge required to obtain one mole of aluminium from Al2O3
The dissociation of aluminium oxide is as follows;
Al2O3→2Al3++3O2−
Al3++3e−→Al
Therefore 3Fcharge is required to obtain one mole of aluminum from Al2O3.
The cell constant of a conductivity cell _____________.
(i) Changes with the change of electrolyte.
(ii) Changes with the change of concentration of electrolyte.
(iii) Changes with the temperature of the electrolyte.
(iv) Remains constant for a cell.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iv)
The cell constant is described as the ratio of the length of the object and the area of cross-section. It can be written as follow
G=
As l and A remains constant for an object it can be inferred that the cell constant for a conductivity cell remains constant for a cell.
While charging the lead storage battery ______________.
(i) PbSO4 anode is reduced to Pb.
(ii) PbSO4 cathode is reduced to Pb.
(iii) PbSO4 cathode is oxidised to Pb.
(iv) PbSO4 anode is oxidised to PbO2 .
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (i)
In the lead storage battery, a reverse reaction occurs and lead sulfate is formed at the anode, and at the cathode, it is converted into lead and lead oxide respectively. The reaction is as follows
At the cathode, the reaction goes this way,
PbSO4 (s)+2e−→Pb (s)+SO42− (aq), Reduction process
At the anode, the reaction goes this way,
PbSO4 (s)+2H2O→PbO2 (s)+SO42−+2H+ +2e, oxidation process
The overall reaction is as follows;
2PbSO4 (s)+2H2O→Pb (s)+PbO2 (s)+4H+ (aq)+2SO42− (aq)
Therefore, at anode lead sulfate is reduced to lead.
Λ0m(NH4OH) is equal to ______________.
(i) Λ0m(NH4OH) + Λ0m(NH4Cl) - Λ0(HCl)
(ii) Λ0m(NH4Cl)+ Λ0m(NaOH) – Λ0 (NaCl)
(iii) Λ0m(NH4Cl)+ Λ0m (NaCl) – Λ0(NaOH)
(iv) Λ0m(NaOH) + Λ0m (NaCl) –Λ0(NH4Cl)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (ii)
Given: Salt ammonium hydroxide
Apply Kohlrausch Law
Kohlrausch law of states that limiting molar conductivity of any salt species is equal to the sum of the limiting molar conductivity of cations and anions of the electrolyte
Λ0m (NaOH) = Λ0m (NH4+) + Λ0m (OH-) + Λ0m (Na+) + Λ0m (OH-) - Λ0m (Na+)- Λ0m (Cl-)
Λ0m (NH4OH) = Λ0m (NH4OH) + Λ0m (NaOH) – Λ0 (NaCl)
In the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride solution which of the half cell reaction will occur at anode?
(i) Na+ (aq) + e– → Na (s); EᶱCell = –2.71V
(ii) 2H2O (l) → O2 (g) + 4H + (aq) + 4e– ; EᶱCell = 1.23V
(iii) H + (aq) + e– → H2 (g); EᶱCell = 0.00 V
(iv) Cl– (aq) → Cl2 (g) + e– ; EᶱCell = 1.36 V
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (iv)
The electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride is as follows
NaCl→Na+ + Cl−
H2O→H+ + OH−
At the cathode, the reaction goes this way,
H2O + e− → H2 + OH−
At the anode, the reaction goes this way,
Cl− (aq)→ Cl2 (g)+ e− E? Cell =1.36V
2H2O (g)→O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e− E? Cell =1.23V
At the anode, the reaction with a lower E? value will be preferred and oxidation of oxygen is a slow process and requires high voltage so the first reaction will take place.
The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu2+/ Cu indicates that ____________.
(i) This redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H+/H2 couple.
(ii) This redox couple is a stronger oxidizing agent than H+/H2
(iii) Cu can displace H2 from acid.
(iv) Cu cannot displace H2 from acid
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: (ii, iv)
The lesser the E? value of the redox couple higher is the reducing power
For Cu2+ + 2e−→Cu; E? =0.34V
For 2H+ + 2e−→H2 E? =0.00V
Since the second redox couple has less standard reduction potential than the first so it can be concluded that the redox couple is a stronger oxidizing agent than H+/H2 and copper cannot displace H2 from acid.
EᶱCell for some half-cell reactions are given below. On the basis of these mark the correct answer
(a) ; EᶱCell =0.00V
(b) ; EᶱCell =1.23V
(c) ; EᶱCell =1.96V
(i) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, hydrogen will be reduced at the cathode.
(ii) In concentrated sulphuric acid solution, water will be oxidized at the anode.
(iii) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, water will be oxidized at the anode.
(iv) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, SO42− ion will be oxidized to tetrathionate ion at the anode
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, iii)
In the electrolysis of sulphuric acid, the following reactions occur
2SO42− (aq)→S2O82− (aq) + 2e− E? Cell =1.96V
2H2O (l)→O2 (g)+4H+ (aq) + 4e− E? Cell =1.23V
The reaction will lower the value of E? Cell is preferred at anode so the second reaction is feasible.
H+ + e− → H2 E? Cell = 0.00V
At the cathode, reduction of water occurs. Therefore, in dilute sulphuric acid solution, hydrogen will be reduced at the cathode.
EᶱCell =1.1 V for Daniel's cell. Which of the following expressions are the correct description of the state of equilibrium in this cell?
(i) 1= Kc
(ii)
(iii)
(iv) 1.1
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (ii, iii)
At equilibrium, ?G = -2.303 RT
-nFE = -2.303 RT
E =
For Daniel cell, n=2
E =
At equilibrium, E = 1.1V
1.1V =
(i) Since this option is incorrect
(ii) As derived 1.1V =
(iii) As derived so this option is correct
(iv) As ,so this option is incorrect
Conductivity of an electrolytic solution depends on ____________.
(i) Nature of electrolyte.
(ii) Concentration of electrolyte.
(iii) Power of AC source.
(iv) Distance between the electrode
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, ii)
Conductivity is due to the movement of ions in the solution. The conductivity of ions depends on the following factors:
(i) nature of electrolyte added
(ii) size of ion produced
(iii) concentration of electrolyte
(iv) nature of the solvent
(v) temperature
Distance between electrodes does not affect the conductivity of an electrolytic solution.
Λ0m(H2O) is equal to _______________.
(i) Λ0m(HCL) + Λ0m(NaOH) - Λ0 m (NaCl)
(ii) Λ0m(HNO3)+ Λ0m(NaNO3) – Λ0 m (NaoH)
(iii) Λ0m(HNO3)+ Λ0m (NaoH) – Λ0 m (NaNO3)
(iv) Λ0m(NH4OH) + Λ0m (HCL) –Λ0 m (NH4Cl)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, iii)
Kohlrausch law of states that limiting molar conductivity of any salt species is equal to the sum of the limiting molar conductivity of cations and anions of the electrolyte
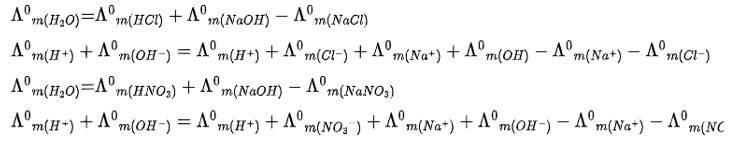
What will happen during the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of CuSO4 by using platinum electrodes?
(i) Copper will deposit at the cathode.
(ii) Copper will deposit at the anode.
(iii) Oxygen will be released at anode.
(iv) Copper will dissolve at the anode
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, iii)
Electrolysis of copper sulfate solution is as follows
CuSO4 ? Cu2+ + SO42−
H2O? H+ + OH−
At the cathode, the reaction goes this way,
Cu2+ + 2e− → Cu; E? Cell = 0.34V
H2O− → H2 E? Cell = 0.00V
At the anode, the reaction goes this way,
2SO42- + 2e−→S2O82− E? Cell =1.96V
2H2O→O2 + 4H+ + 4e− E? Cell =1.23V
The reaction will lower the value of E? Cell is preferred at anode so the second reaction is feasible.
What will happen during the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of CuSO4 in the presence of Cuelectrodes?
(i) Copper will deposit at the cathode.
(ii) Copper will dissolve at the anode.
(iii) Oxygen will be released at anode.
(iv) Copper will deposit at the anode
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, ii)
In the electrolysis process of CuSO4 the following reactions occur at the half cell which is as follows:
At the cathode, the reaction goes this way,
Cu2++2e−→Cu (s)
At the anode, the reaction goes this way,
Cu (s)→Cu2++2e−
Here copper will be deposited at the cathode and copper will dissolve at the anode.
Conductivity k , is equal to ____________.
(i) ,
(ii)
(iii) Λm
(iv)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, ii)
Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance and conductivity is the reciprocal of resistivity. It can be written as follows
k =
R=
=
k =
k =
k = G*
k =
G* is cell constant.
Molar conductivity of ionic solution depends on ___________.
(i) Temperature.
(ii) Distance between electrodes.
(iii) Concentration of electrolytes in solution.
(iv) Surface area of electrodes.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (i, iii)
The conductivity in an ionic solution is due to the ions in the solution. It depends on the following factors;
(a)Temperature: On an increase in temperature, the molar conductivity of ionic solutions increases.
(b)Concentration of Electrolytes: An increase in the concentration of electrolytes decreases the molar conductivity as the number of ions per unit volume decreases.
Therefore, options (i, iii) are correct
For the given cell, Mg|Mg2+||Cu2+| Cu
(i) Mg is cathode
(ii) Cu is anode
(iii) The cell reaction is
(iv) Cu is an oxidizing agent
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct Option: Option (ii, iii)
In the given representation of the cell, the left side represents the oxidation half cell and the right side of the cell represents the reduction half cell
The electrode at which oxidation occurs is called anode and oxidation of magnesium occurs at anode so magnesium is the anode.
Similarly, the electrode at which the reduction occurs is called the cathode, and the reduction of copper occurs at the cathode.
The cell reaction is as follows
Mg + Cu2+→Mg2++ Cu
Common Mistakes and Tips for NCERT Chemistry Exemplar Chapter Three
See below the common mistakes in Chapter Three Electrochemistry:
- Students get confused between the Galvanic and Electrolytic Cells. They sometimes mix up the anode and cathode toles in these two cells.
- They also use incorrect units by forgetting to convert concentrations into standard units while using the Nernst Equation. In problems involving conductivity or the Nernst equation, they forget that temperature affects the outcome.
- In Cell Notation, many students incorrectly place the anode and cathode or miswrite the standard cell notation.
- They often ignore the significance of the salt bridge.
- Students also use incorrect electrode potential signs.
- The students confuse the molar conductance (Λm) with specific conductance (κ).
These are the tips students can follow to avoid the common mistakes in Electrochemistry:
- First, understand and then memorize the key formulas, such as Kohlrausch’s law, Nernst equation, and formulas for conductance thoroughly. While practicing these, make sure to apply the correct conditions and units.
- In cell reactions, use a systematic approach by first identifying the cell type and then seeing which half-cell is oxidized and which is reduced.
- Cell notations should be practiced correctly and they should be written in the following order: Anode | Anode solution || Cathode solution | Cathode.
- Try to understand the physical meaning behind the concepts, which is the 'why' behind the electrode potential, salt bridge function and ionic conductance.
- While solving the numerical problems, pay close attention to the units, such as in conductance and electrode potential problems.
- Revise the Electrochemical Series regularly.
- Students should solve the NCERT exemplar questions for more confidence and understanding of concepts while appearing in the exams.
Also read:
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,28th june , Chemistry ,Second shift
Commonly asked questions
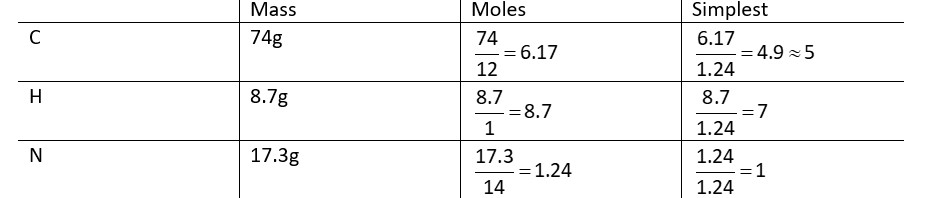
Compound A contains 8.7% Hydrogen, 74% Carbon and 17.3% Nitrogen. The molecular formula of the compound is,
Given : Atomic masses of C,H and N are 12, 1 and 14 amu respectively. The molar mass of the compound A is 162 g mol-1.
Empirical formula is C5H7N
Empirical mass = 81
Molecular mass = 162
So, molecular formula is C10H14N2
Consider the following statements:
(A) The principal quantum number ‘n’ is a positive integer with values of ‘n’ = 1, 2, 3,….
(B) The azimuthal quantum number for a given ‘n’ (principal quantum number) can have values as
(C) Magnetic orbital quantum number for a particular (azimuthal quantum number) has values.
(D) are two possible orientations of electron spin.
(E) For there will be a total of 9 orbitals
Values of principal quantum number, n = 1, 2, 3, .
Values of azimuthal quantum number,
Number of values of magnetic quantum number are
Values of spin quantum number are
Number of orbitals for particular value of
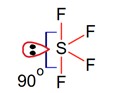
In the structure of SF4, the lone pair of electrons on S is in.
Geometry of SF4 is trigonal bipyramidal, in which there is one lonepair which occupy equatorial position as,
There are two lone pair – bond pair repulsions at 90°
A student needs to prepare a buffer solution of propanoic acid and its sodium salt with pH 4. The ratio of required to make buffer is_________.
Given :
pH of acidic buffer is given by,
pH = pKa + log10
or,
or,
Match List – I with List – II:
List – I List – II
(a) Negatively charged sol (I) Fe2O3. xH2O
(b) Macromolecular colloid (II) CdS sol
(c) Positively charged sol (III) Starch
(d) Cheese (IV) a gel
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
Metallic suphides i.e CdS are negatively charged colloidal solution.
Starch colloid is macro molecular colloidal solution.
Fe2O3. xH2O sol is positively charged colloidal solution.
Cheese is an example of gel.
Match List – I with List – II:
List – I (Oxide) List – II (Nature)
(A) Cl2O7 (I) Amphoteric
(B) Na2O (II) Basic
(C) Al2O3 (III) Neutral
(D) N2O (IV) Acidic
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
· Cl2O7 being non-metallic oxide is acidic in nature.
· Na2O being metallic oxide is basic in nature.
· Al2O3 is an amphoteric oxide
· N2O is neutral oxide
In the metallurgical extraction of copper, following reaction is used:
FeO + SiO2 ® FeSiO3
FeO and FeSiO3
FeO and FeSiO3 respectively are.
In extraction of copper from copper pyrite (CuFeS2).
FeS converted to FeO as;
Then FeO is removed as slag by given reaction
FeO + SiO2 ®
Hydrogen has three isotopes : protium (1H), deuterium (2H or D) and tritium (3H or T). They have nearly same chemical properties but different physical properties. They differ in
Isotopes are the atom of same element with different atomic mass.
Among the following, basic oxide is:
CaO – Basic Oxide
SO3 & SiO2 – Acidic oxides
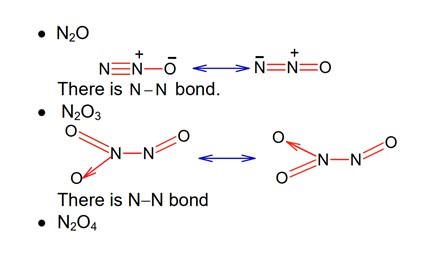
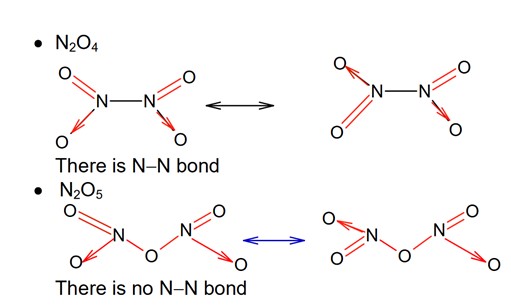
Among the given oxides of nitrogen ; N2O, N2O3, N2O4 and N2O5, the number of compound / (s) having N – N bond is:
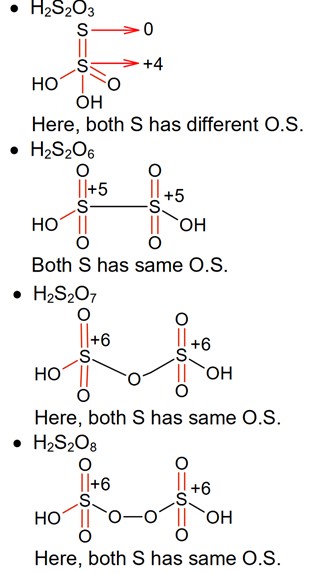
Which of the following oxoacids of sulphur contains “S” in two different oxidation states?
Correct statement about photo –chemical smog is:
Photochemical smog occurs in warm, dry and sunny climate. The main components of photochemical smog result from the action of sunlight on unsaturated hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides produced by automobiles and factories. Photochemical smog has high concentration of oxidising agents so called as oxidizing smog.
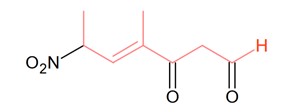
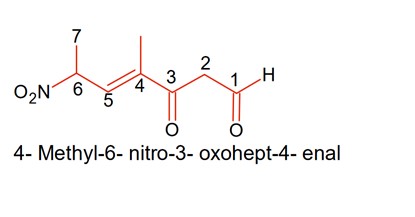
The correct IUPAC name of the following compound is:
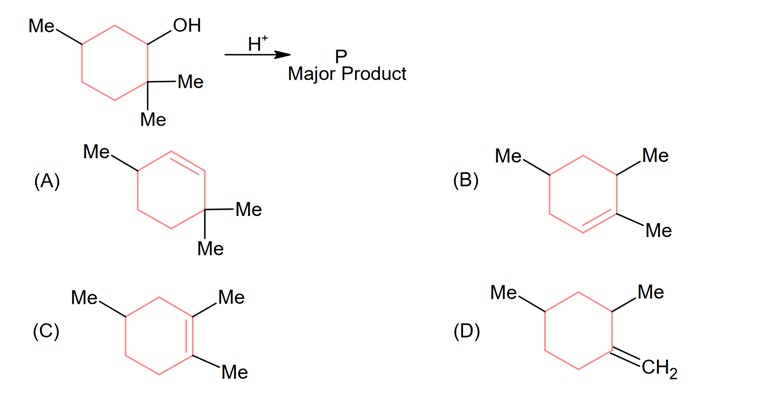
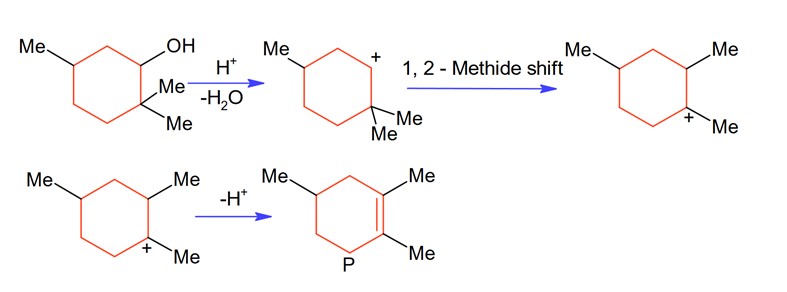
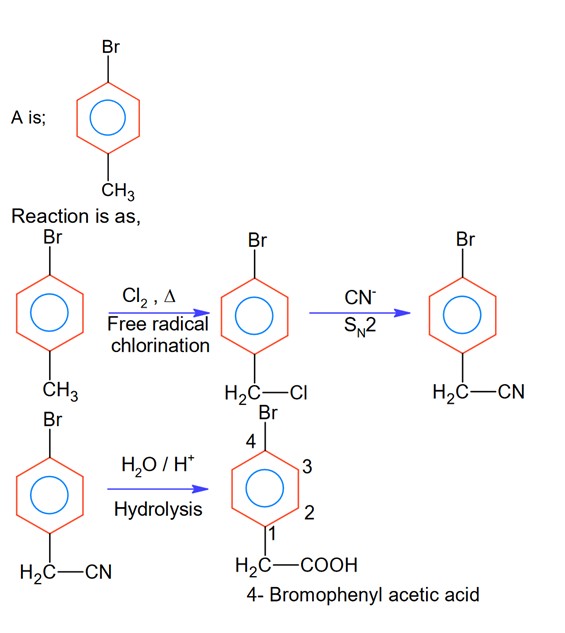
The major product of the given reaction is (where, Me is – CH3)
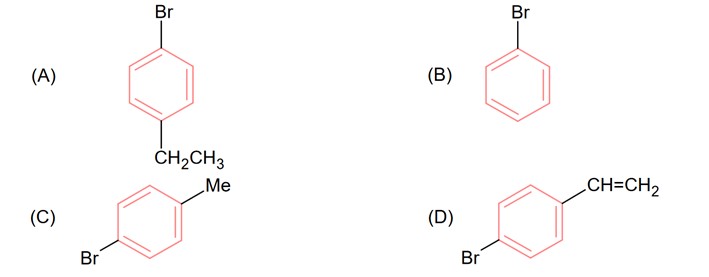
A 4-Bromophenyl acetic acid.
In the above reaction ‘A’ is
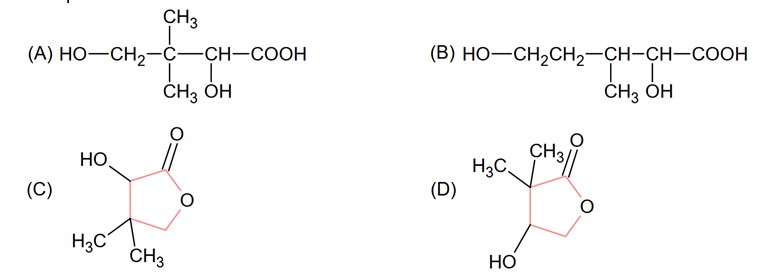
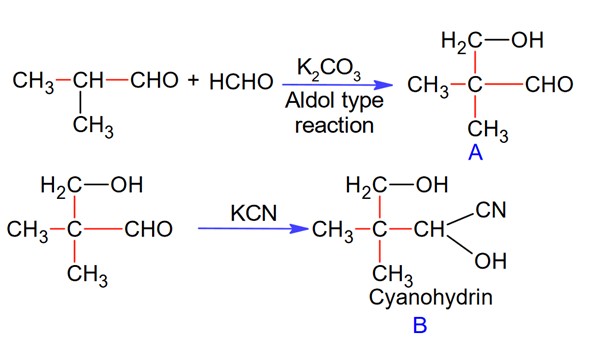
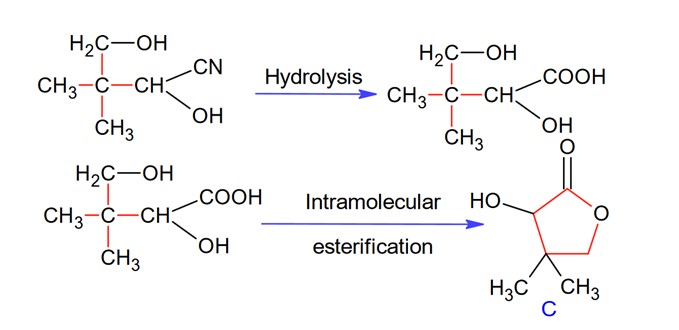
Isobutyraldehyde on reaction with formaldehyde and K2CO3 given compound ‘A’. Compound ‘A’ reacts with KCN and yields compound ‘B’, which on hydrolysis gives a stable compound ‘C’. The compound ‘C’ is
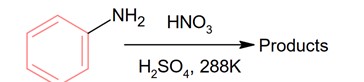
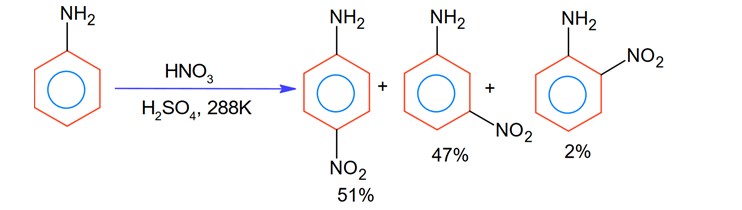
With respect to the following reaction, consider the given statements:
(A) o-Nitroaniline and p-nitoraniline are the predominant products.
(B) p-Nitroaniline and m-nitroaniline are the predominant products.
(C) HNO3 acts as an acid.
(D) H2SO4 acts as an acid.
Choose the correct option.
During nitration using HNO3 and H2SO4, H2SO4 act as an acid while HNO3 act as a base.
Given below are two statements, one is Assertion (A) and other Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Natural rubber is a linear polymer of isoprene called cis-polyisoprene with elastic properties.
Reason (R): The cis-polyisoprene molecules consist of various chains held together by strong polar interactions with coiled structure.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct one from the options given below:
Natural rubber is a linear polymer of isoprene called cis-polyisoprene and has elastic properties.
Ci-polyisoprene molecule consists of various chains held together by weak vander Waals interactions and has a coiled structure.
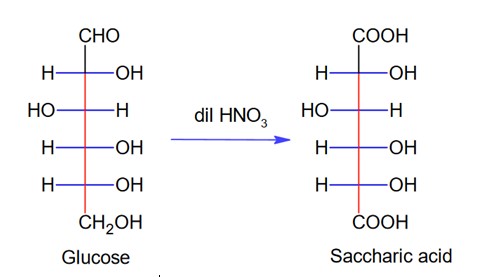
When sugar ‘X’ is boiled with dilute H2SO4 in alcoholic solution, two isomers ‘A’ and ‘B’ are formed. ‘A’ on oxidation with HNO3 yields saccharic acid where as ‘B’ is laevorotatory. The compound ‘X’ is:
Compound X is sucrose as,
Here, glucose is A which on oxidation with HNO3 gives saccharic acid as
B is b-D fructose which is laevarotatory.
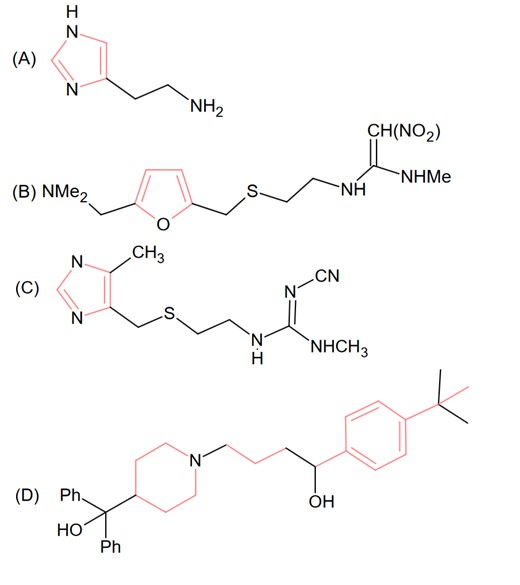
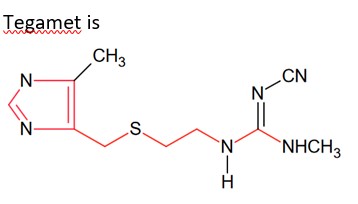
The drug tegamet is:
100g of an ideal gas is kept in a cylinder of 146 L volume at 27°C under 1.5 bar pressure. The molar mass of the gas is _________g mol-1. (Nearest integer)
(Given : R = 0.083 L bar K-1 mol-1)
Using : PV = nRT
1.5 × 416 = n × 0.083 × 300
n = 25mol =
25 =
So, molar mass, M = 4 g/mol.
For combustion of one mole of magnesium in an open container at 300 K and1 bar pressure, the magnitude of change in internal energy for the reaction is__________ kJ. (Nearest integer)
For combustion of Mg:
Mg (s) +
Here,
Now using
-601.7 =
So; magnitude of is 600 kJ (the nearest integer).
For the given reactions
Sn2 + 2e- ® Sn
Sn4 + 4e- ® Sn
The electrode potentials are ; = -0.140V and The magnitude of standard electrode potential for Sn4+ / Sn2+ i.e. is ___________ × 10-2 V. (Nearest integer)
Here,
= 16 × 10-2 V
2.5g protein containing only glycine (C2H5NO2) is dissolved in water to make 500 mL of solution. TH osmotic pressure of this solution at 300 K is found to be 5.03 × 10-3 bar. The total number of glycine units present in the protein is___________.
(Given : R = 0.083 L bar K-1 mol-1)
Molar mass of protein, M = 24751 g/mol
Molar mass of glycine = 75 g/mol
So; number of glycine units =
A radioactive element has a half life of 200 days. The percentage of original activity remaining after 83 days is___________. (Nearest integer)
(Given : antilog 0.125 = 1.333, antilog 0.693 = 4.93)
83 =
0.125 =
= 1.333
Activating remaining =
= 75%
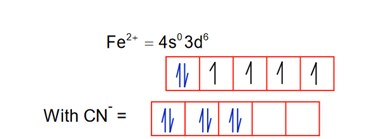
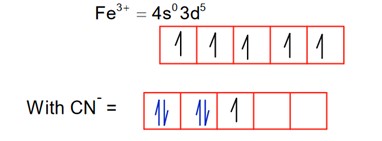
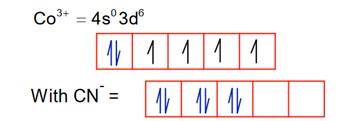
Among the given complexes, number of paramagnetic complexes in__________.
CN is a strong field ligand, so pairing occurs.
1.
So; it is diamagnetic
2.
So; it is paramagnetic.
3.
Ti3+ = 4s03d1
It is paramagnetic
4.
It is diamagnetic
5.
Hence, are paramagnetic.
(a) CoCl3 .4NH3, (b) CoCl3 .5NH3, (c) CoCl3. 6NH3 and (d) CoCl(NO3)2. 5NH3.
Number of complex(es) which will exist in cis-trans form is /are__________.
(a) will show cis- trans isomerism as;
(b) will not show cis- trans isomerism.
(c) will not show cis- trans isomerism.
(d) will not show cis-trans isomerism.
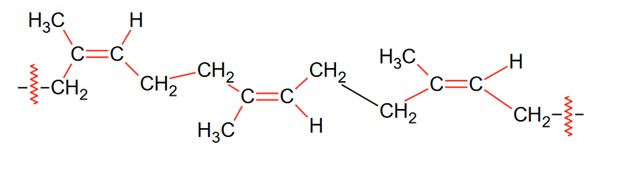
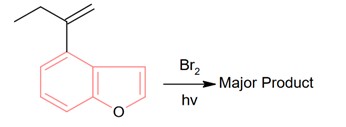
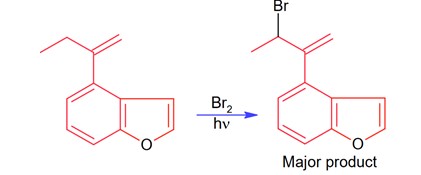
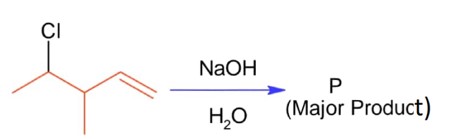
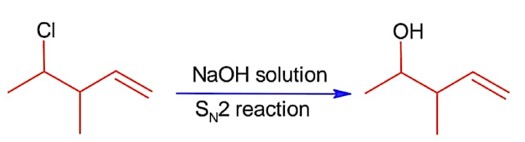
The major product of the following reaction contains _____________ bromine atom(s).
Bromination through free radical mechanism occurs at allylic carbon.
The complete combustion of 0.492g of an organic compound containing ‘C’, ‘H’ and ‘O’ given 0.793g of CO2 and 0.442g H2O. The percentage of oxygen composition in the organic compound is __________. (nearest integer)
Moles of C = moles of CO2
=
Mass of C =
= 0.261g
Moles of H = 2 ×
Mass of H =
Total mass of compound = 0.492g (given)
So; mass of O = (0.492 – 0.216 – 0.049) g
= 0.227g
% of O =
= 46.14%
the nearest integer = 46
0.01 M KMnO4 solution was added to 20.0mL of 0.05 M Mohr’s salt through a burette. The initial reading of 50mL burette is zero. The volume of KMnO4 solution left in the burette after the end point is__________ mL. (nearest integer)
n-factor of KMnO4 in acidic medium = 5
n-factor of Mohr's salt = 1
meq of KMnO4 = meq of Mohr's salt
0.01 * 5 * V = 0.05 * 1 * 20
Volume of KMnO4 used, V = 20 mL
So; Volume of KMnO4 left in burette = 50 -20mL
= 30 mL
At 300K, a sample of 3.0g of gas A occupies the same volume as 0.2g of hydrogen at 200K at the same pressure. The molar mass of gas A is _________g mol-1, (nearest integer) Assume that the behavior of gases as ideal. (Given: The molar mass of hydrogen (H2) gas is 2.0g mol-1.)
A Company dissolves ‘x’ amount of CO2 at 298K in 1 litre of water to prepare soda water X = _________________ × 10-3 g. (nearest integer)
According to Henry’s law
As
Mass of CO2 gas =
= 1222 × 10-3 gm
PCl5 dissociates as
PCl5(g) PCl3 (g) + Cl2(g)
5 moles of PCl5 placed in a 200 litre vessel which contains 2 moles of N2 and is maintained at 600K. The equilibrium pressure is 2.46 atm. The equilibrium constant Kp for the dissociation of PCl5 is ____________ × 10-3g. (nearest integer).
(Given R = 0.082 L atm K-1 mol-1; Assume ideal gas behavior)
Eq.(5 – x) mole x molex mole
Total number of moles at equilibrium
= 1107 × 103 atm
The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.01 MKCl solution at 298K is . If is 0.152 × 10-3 cm-1, then the cell constant of the conductivity cell _________ × 10-3 cm-1.
= 0.152 × 10-3 × 1750
= 266 × 10-3 cm-1
When 200mL of 0.2 M acetic acid is shaken with 0.6g of wood charcoal, the final concentration of acetic acid after adsorption is 0.1M. The mass of acetic acid adsorbed per gram of carbon is ______________ g.
Number of moles of CH3COOH Adsorbed on 0.6 gm wood charcoal.
= 20 × 10-3 moles
Mass of CH3COOH absorbed = 20 × 10-3 × 60 = 1.2 gm
Mass of CH3COOH adsorbed per gram =
(a) Baryte (b) Galena (c) Zinc blende and (d) Copper pyrites. How many of these minerals are sulphide based?
Baryte – BaSO4 [Sulphate based ore]
Galena – PbS
Zinc blende – ZnS
Copper pyrite – CuFeS2
Manganese (VI) has ability to disproportionate in acidic solution. The difference in oxidation states of two ions it forms in acidic solution is ____________.
In acidic solution
Difference in oxidation state of Mn is product
= 7 – 4 = 3
0.2g of an organic compound was subjected to estimation of nitrogen by Dumas method in which volume of N2 evolved (at STP) was found to be 22.400 mL. The percentage of nitrogen in the compound is __________. [nearest integer]
(Given : Molar mass of N2 is 28g mol-1, Molar volume of N2 at STP : 22.4L)
Number of moles of gas =
Mass of nitrogen =
% of N in organic compound =
In alanylglycylleucylalanylvaline, the number of peptide linkages is____________.
Ala – Gly – Leu-Ala- Val
Two amino acid units are connected by peptide linkage. So number of peptide linkage = 4.
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three Exam

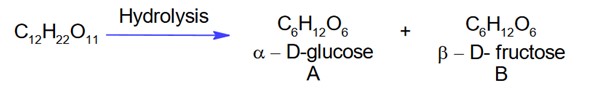

 ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff
ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff