Maths
Get insights from 6.5k questions on Maths, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Maths
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have, f(x) =
{
At
So we have three disjoint internal i.e.,
When,
So, f(x) is increasing.
When
So, f(x) is decreasing.
When
f(x) =
So, f(x) is increasing.
f(x) is increasing for x(∞,1) and [1, ∞] and decreasing for x[1, 1].
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have, f(x)=
So,
Now,
And, as cos x lies in [1, 1].
So, (i) for increasing, f(x) ≥ 0.
cosx ≥ 0.
x lies in Ist and IVth quadrant.
i.e., f(x) is increasing for and
(ii) for decreasing, f(x) ≤ 0.
cosx ≤ 0.
x lies in IInd and IIIrd quadrant.
i.e., f(x) is decreasing for .
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have
Slope of the normal at any point is
The equation of the normal at a given point is given by,
Now, the perpendicular distance of the normal from the origin is
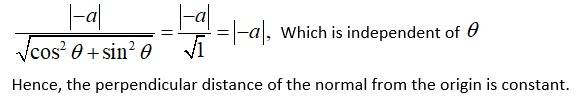
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Equation of the curve is
Now, the slope of the normal at point is
Equation of the normal at is
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let 'b' and 'x' be the fixed base and equal side of isosceales triangle.
Then, cm/s (Ø decreasing).

New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have, f(x)
f(x) =
f(x) =
=
= =
At extreme points, f(x) = 0.
At x = e, f"(e) =
x = e is a point of maximum.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) Consider
Now, is approximately equal to and is given by,
Hence, the approximate value of is
=0.677
(b)
(b) Consider
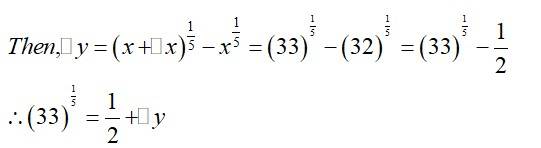
Now, is approximately equal to and is given by,
Hence, the approximate value of
is
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have,
At f(x) = 0.
2x – 1 = 0
=
Option (B) is
Hence maximum value of f(x) = at x = 1 and x = 0.
Option (c) is correct.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have,
At f(x) = 0.
x = 1 and x = -1.
At
At x = -1,
The maximum value of f(x)
Hence, option (D) is correct.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
The equation of the given curve is
x2 = 2y.
Let p (x, y) be a point on the curve.
The distance of p (x, y) from (0, 5) is say S is given by
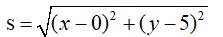
Let z = s2 = x2 + y2 + 25 – 10y = 2y + y2 -10y + 25
z = y2 – 8y + 25
So,
At
At y = 4,
y = 4, is point of minimum distance.
So, x2 = 2y->x2 = 2 * 4-> x2 = 8
Hence, the point of the nearest distance are and
Option (A) is correct.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
