Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three
Get insights from 68 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
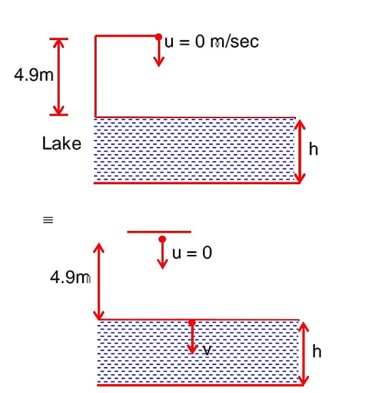
Total time (T) = 4 sec
Given u = 0 m/sec
a = g = 9.8 m/sec2
h = 4.9 m, t =?
t = 1 sec
'v' be the velocity with which ball hits the water v = u + at
= 0 + 9.8 * 1 = 9.8 m/sec
Time taken to reach the bottom of the lake from surface of the lake
= 4 – 1 = 3 sec
v = 9.8 m/sec
29.4 + 4.9 * 9 = 29.4 + 44.1
H = 73.5 m
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
NCERT Exemplar goes beyond the NCERT textbook as it contains questions based on the textbook concepts. While practicing the short answer type questions, long answer type questions, and multiple choice questions, students learn how to use these concepts for solving problems. It will help students improve their analytical thinking and problem-solving skills and develop a deeper understanding of concepts. It prepares students for CBSE Board exams and competitive exams like NEET and JEE.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
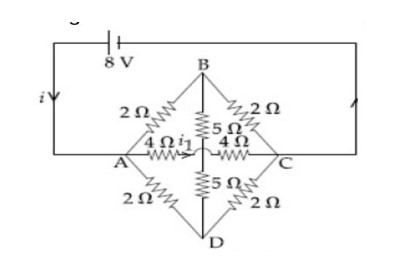
While applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) at junctions, the total current leaving is equal to the total current entering. For Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) in loops, the total of the voltage gains and drops around any closed loop is zero. To avoid mistakes, students must assign a direction to currents which can be positive for gains and negative for drops, and be consistent with the signs while solving the equations.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
When no current flows in the circuit, the total potential difference provided by a source is known as the Electromagnetic force (EMF). On the other hand, when current flows in the circuit, the actual voltage across the terminals of the cell is called the terminal voltage. The formula that depicts the relation is:
Where r is the internal resistance and I is the current.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
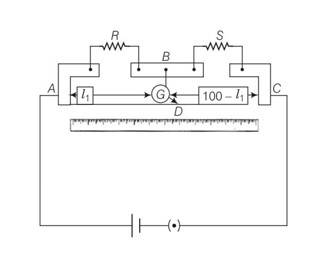
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (a, c)
Explanation- In case of meter bridge, the resistance wire AC is 100 cm long. Varying the position of tapping point B, bridge is balanced. If in balanced position of bridge AB = l, BC = (100 – l) so that Q/P= (100-l)/l. Also P/Q=R/S=>S= (100-l)/l R
When there is no deflection in galvanometer there is no current across the galvanometer, then points B and D are at same potential. That point at which galvanometer shows no deflection is called null point, then potential at B and neutral point D are same. When the jockey contacts a point on the meter wire to
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
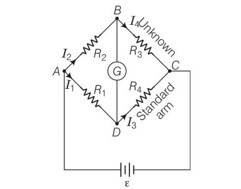
Answer – (b, c)
Explanation – According to the relation that p/q=r/s if galvanometer shows no deflection. In the above equation the value of R4 depends upon R1 and R2 . if the value of R1 and R2 will be feeble the value of R4 would be affected.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- according to the relation = also T
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers