Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three
Get insights from 68 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Metallic strips have negligible resistance and need not to be counted in the length l1, of the null point of potentiometer. That's why the thick metallic strips are used in potentiometer. It is for the convenience of experimenter as he measures only their lengths along the straight segments each of lengths 1 m.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- In a Wheatstone bridge the main advantage of null point method is that the resistance of galvanometer does not affect the balance point, there is no need to determine current in resistances and the internal resistance of a galvanometer. It is convenient and easy method for observer.
The R unknown can calculated applying Kirchhoff's rules to the circuit. We would need additional accurate measurement of all the currents in resistances and galvanometer and internal resistance of the galvanometer.
The necessary and sufficient condition for balanced Wheatst
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- relaxation time =mean free path/rms velocity of electron
Also = = relaxation time is inversely proportional to velocities
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – In the circuit when an electron approaches a junction, in addition to the uniform E that faces it normally (which keep the drift velocity fixed), as drift velocity (vd) is directly proportional to Electric field (E). That's why there are accumulation of charges on the surface of wires at the junction.
These produce additional electric fields. These fields alter the direction of momentum. Thus, the motion of a charge across junction is not momentum conserving
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
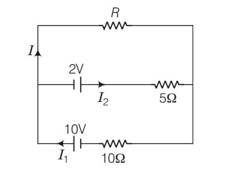
Explanation- applying kirchhoff's junction rule I1 = I+I2
Applying kirchhoff's rule in outer loop containing 10V cell
10= IR+10I1……………. (1)
Applying kirchhoff's rule in outer loop containing 2V cell
2= 5I2-RI= 5 (I1-I)-RI
4= 10I1-10I-RI………… (2)
From 1 and 2
6=3RI+10I
2=I (R+10/3)
V= I (R+Reff)
After comparing V=2V, Reff= 10/3 ohm
Since effective internal resistance Reff of two cells 10/3 ohm, being the parallel combination 5 ohm and 10 ohm . the equivalent circuit is
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- according to ohm's law V= IR
I= 6/6 = 1A
I= AneVd or Vd= i/neA
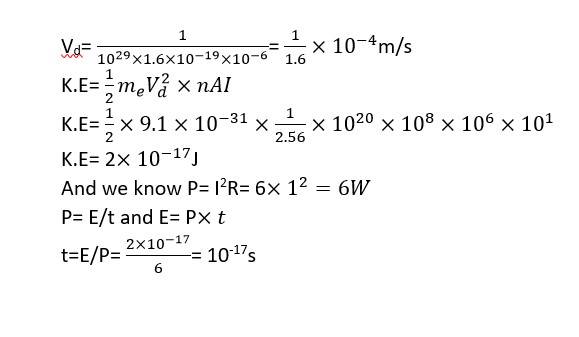
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
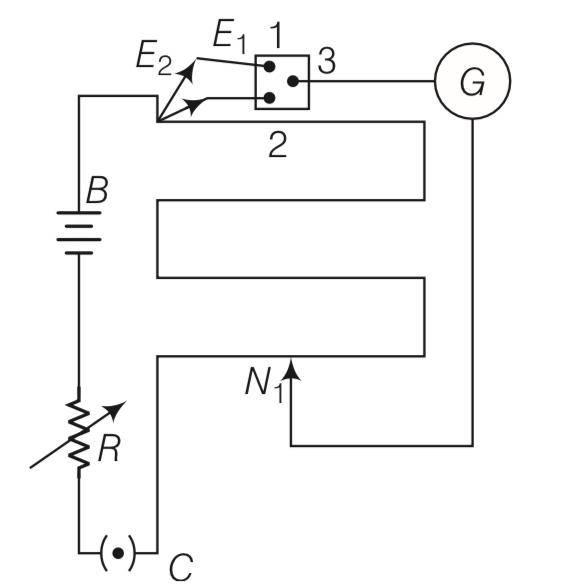
Explanation – let R' be the resistance of potentiometer wire.
Effective resistance of potentiomter and variable resistor r=50ohm is 500+R'
Effective voltage across potentiometer = 10V
The current through main circuit I= =
Potential difference across wire of potentiometer
IR'=
Since with 50 ohm resistor, null point is not obtained it is possible when
10R'
2R'<400 or R'<200 ohm
Similarly with 10 ohm resistor, null point is obtained its is only possible when
2R'>40
R'>40
7.5R'<80+8R'
R'>160
160
Any R' between 160 ohm and 200 ohm will achieve.
Since the null point on the last 4th segment of
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – power consumption in a day i.e in 5 = 10 units
Power consumption per hour = 2 units
Power consumption = 2 units =2KW= 2000J/s
Also power =V I
2000W= 220V l or l= 9A approx.
R=
Power consumption in first current carrying wire
P= I2R
l2= 1.7 10-8 j/s = 4J/s approx.
Loss due to joule heating in first wire = 100=0.2%
Power loss in Al wire =1.6 4= 6.4J/s
Fractional loss due to joule heating in second wire = 100= 0.32%
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers