physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
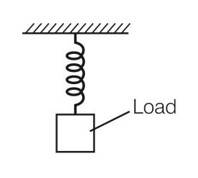
(c) Consider the diagram where a spring is stretched by applying a load to its free end. Clearly the length and shape of the spring changes. The change in length corresponds to longitudinal strain and change in shape corresponds to shearing strain.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) Y young's modulus is inversely proportional to temperature, so if we increase temperature , young's modulus decreases.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) breaking stress = breaking force/area of cross section
Breaking force will not depend upon length.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) No frictional force exists in case of ideal fluid. Hence tangential forces are zero.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As ivory ball is more elastic than wet clay ball. So ivory ball tries to regain its original shape quickly, hence more energy and momentum transferred to ivory than clay ball. So ivory ball rises high
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Length of steel cable l=9.1m
Radius r= 5mm=
Tension in the cable F =800N
Young's modulus of steel Y= 2
So
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-d
Explanation- for small objects sizes less than 100 m centre of mass very close with the centre of gravity of the body. But when the size of object increases it weight changes and its CM and CG become far from each other.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c
Explanation- a geostationary satellite is having same sense of rotation as that of earth i.e west east direction.
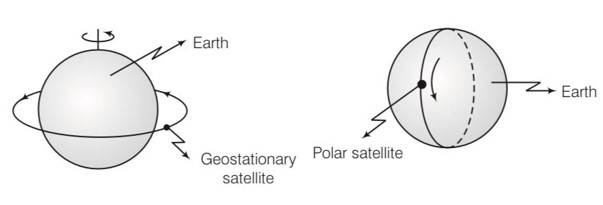
A polar satellite goes around earth's pole in north south direction.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a,c,d
Explanation- F1=-F2=- n
r12=r1-r2
acceleration due to gravity ,g = F/mass=
as g is constant hence constant of proportionality will not be constant in kepler's third law.
Hence kepler's law will not be valid.
For negative n, g=
=
Mo>m1 or m2 so objects lighter than water will sink
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-c, d
Explanation- Gravitation force F= where M is mass of sun and m is mass of earth.
When G decrease force will also decrease so according to this it will not in the fixed circular orbits around the sun. as when radius increases the force will decreases and soon earth leave the solar system.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
