- Gravitation Long Answer Type Questions
- JEE Mains Solutions 2022,29th july ,Physics, Second shift
- JEE Mains 2022
- JEE Mains Solutions 2022,25th june ,physics ,Second shift
- JEE Mains 2021
Gravitation Long Answer Type Questions
| 8.1 A star like the sun has several bodies moving around it at different distances. Consider that all of them are moving in circular orbits. Let r be the distance of the body from the centre of the star and let its linear velocity be v, angular velocity ω, kinetic energy K, gravitational potential energy U, total energy E and angular momentum l. As the radius r of the orbit increases, determine which of the above quantities increase and which ones decrease. |
| Explanation- when a body og mass m is revolving around a star of mass M. Linear velocity of the body v= so when r increases then v decreases. Angular velocity of the body w = 2 According to kepler’s law T2 r3 So T= kr3/2 So w= so when r increases , w decreases. Kinetic energy of the body K= 1/2mv2=1/2m( ) so when we increase r ,KE decreases. Gravitational potential energy of the body U=-GMm/r So when we increase r, PE becomes less negative Total energy of the body E= KE+PE= When r increases total energy becomes less negative . i.e increases. Angular momentum of the body L =mvr =mr m L= |
| 8.2 Six point masses of mass m each are at the vertices of a regular hexagon of side l. Calculate the force on any of the masses. |
| Explanation- consider a diagram having vertices A,B,C,D,E and F AC= AG+GC=2AG = 2lcos300= 2l = AD=AH+HJ+JD= lsin300+l+lsin300=2l Force on mass m at A due to mass m at B is f1= along AB Force on mass m at A due to mass m at C is f2= along AC Force on mass m at A due to mass m at D is F3= along AD Force on mass m at A due to mass m at E is F4= = along AE Force on mass m at A due to mass m at F is F5= along AF Resultant force due to F1 and F5 is F1= = along AD So net force along AD = F1+F2+F3= |
| 8.3 A satellite is to be placed in equatorial geostationary orbit around earth for communication. (a) Calculate height of such a satellite. (b) Find out the minimum number of satellites that are needed to cover entire earth so that at least one satellites is visible from any point on the equator. [M = 6 × 1024 kg, R = 6400 km, T = 24h, G = 6.67 × 10-11 SI units |
| Explanation- mass of earth M = 6 Radius of the earth , R = 6400km= 6.4 T=24h= 24 G = 6.67 10-11Nm2/kg2 (a) Time period T = = 2 = ( )1/3 ( )1/3-R So after solving we get h = 3.59 (b) If satellite is at height h from the earth’s surface
Cos = = cos81018’ = 81018’ =2(81018’)= 162036’ If n number of satellite needed to cover entire the earth then So n = 3600/2 = 2.31 So minimum 3 satellite are required to cover entire earth. |
| 8.4 Earth’s orbit is an ellipse with eccentricity 0.0167. Thus, earth’s distance from the sun and speed as it moves around the sun varies from day to day. This means that the length of the solar day is not constant through the year. Assume that earth’s spin axis is normal to its orbital plane and find out the length of the shortest and the longest day. A day should be taken from noon to noon. Does this explain variation of length of the day during the year? |
| Explanation-let m be the mass of the earth vp,va be the velocity of the earth at perigee and apogee respectively. Similarly wp and wa are angular velocities. At perigee , at apogee If a is the semimajor axis of the earth’s orbit then rp=a(1-e) and ra=a(1+e) = 0.00167
Let w be the angular speed which is geometric mean of wp and wa and corresponding to mean solar day. =1.0691 If w corresponds to 10 per day then wp = 1.0340 per day and wa= 0.9670 per day . since 3610=24, mean solar day we get 361.0340 which corresponds to 24h,8.14’’ and 360.9670 corresponds to 23h59min52’’. So this does not explain the actual variation of the length of the day during the year. |
Commonly asked questions
A star like the sun has several bodies moving around it at different distances. Consider that all of them are moving in circular orbits. Let r be the distance of the body from the centre of the star and let its linear velocity be v, angular velocity ω, kinetic energy K, gravitational potential energy U, total energy E and angular momentum l. As the radius r of the orbit increases, determine which of the above quantities increase and which ones decrease.
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- when a body og mass m is revolving around a star of mass M.
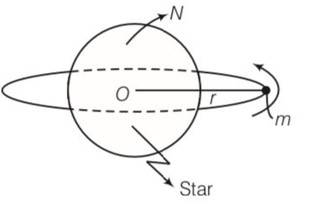
Linear velocity of the body v= so when r increases then v decreases.
Angular velocity of the body w = 2
According to kepler’s law T2 r3
So T= kr3/2
So w= so when r increases, w decreases.
Kinetic energy of the body K= 1/2mv2=1/2m ( ) so when we increase r, KE decreases.
Gravitational potential energy of the body
U=-GMm/r
So when we increase r, PE becomes less negative
Total energy of the body E= KE+PE=
When r increases total energy becomes less negative . i.e increases.
Angular momentum of the body L =mvr =mr m
L=
Six point masses of mass m each are at the vertices of a regular hexagon of side l. Calculate the force on any of the masses.
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- consider a diagram having vertices A,B,C,D,E and F
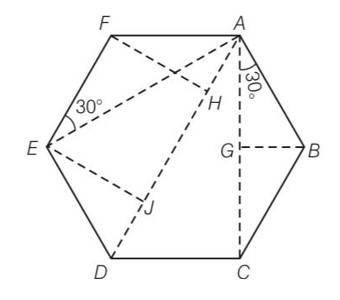
AC= AG+GC=2AG
= 2lcos300= 2l
=
AD=AH+HJ+JD= lsin300+l+lsin300=2l
Force on mass m at A due to mass m at B is f1= along AB
Force on mass m at A due to mass m at C is f2= along AC
Force on mass m at A due to mass m at D is F3= along AD
Force on mass m at A due to mass m at E is F4= = along AE
Force on mass m at A due to mass m at F is F5= along AF
Resultant force due to F1 and F5 is F1=
= along AD
So net force along AD = F1+F2+F3=
A satellite is to be placed in equatorial geostationary orbit around earth for communication.
(a) Calculate height of such a satellite.
(b) Find out the minimum number of satellites that are needed to cover entire earth so that at least one satellites is visible from any point on the equator.
[M = 6 × 1024 kg, R = 6400 km, T = 24h, G = 6.67 × 10-11 SI units
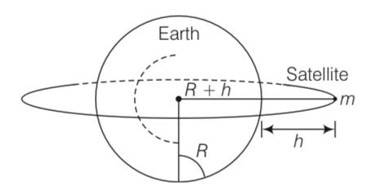
Explanation- mass of earth M = 6
Radius of the earth , R = 6400km= 6.4
T=24h= 24
G = 6.67 10-11Nm2/kg2
(a) Time period T =
= 2
= ( )1/3
( )1/3-R
So after solving we get h = 3.59
(b) If satellite is at height h from the earth’s surface
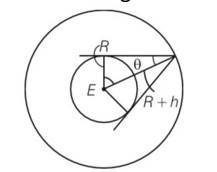
Cos = = cos81018’
= 81018’
=2(81018’)= 162036’
If n number of satellite needed to cover entire the earth then
So n = 3600/2 = 2.31
So minimum 3 satellite are required to cover entire earth.
Earth’s orbit is an ellipse with eccentricity 0.0167. Thus, earth’s distance from the sun and speed as it moves around the sun varies from day to day. This means that the length of the solar day is not constant through the year. Assume that earth’s spin axis is normal to its orbital plane and find out the length of the shortest and the longest day. A day should be taken from noon to noon. Does this explain variation of length of the day during the year?
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-let m be the mass of the earth vp, va be the velocity of the earth at perigee and apogee respectively. Similarly wp and wa are angular velocities.
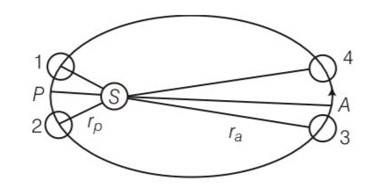
At perigee, at apogee
If a is the semimajor axis of the earth's orbit then rp=a (1-e) and ra=a (1+e)
= 0.00167
Let w be the angular speed which is geometric mean of wp and wa and corresponding to mean solar day.
=1.0691
If w corresponds to 10 per day then wp = 1.0340 per day and wa= 0.9670 per day . since 3610=24, mean solar day we get 361.0340 which corresponds to 24h,8.14' and 360.9670 corresponds to 23h59min52'. So this does not explain the actual variation of the length of the day during the year.
A satellite is in an elliptic orbit around the earth with aphelion of 6R and perihelion of 2 R where R= 6400 km is the radius of the earth. Find eccentricity of the orbit. Find the velocity of the satellite at apogee and perigee. What should be done if this satellite has to be transferred to a circular orbit of radius 6R ? [G = 6.67 × 10–11 SI units and M = 6 × 1024 kg].
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- rp= radius of perihelion =2R
Ra = radius of aphelion =6R
So ra=a(1+e)=6R
And rp= a(1-e)=2R
Solving above eqns
We get e = ½
By conservation of angular momentum angular momentum at perigee= angular momentum at apogee
So mvprp=mvara
Va/vp=1/3
Where m is mass of satellite .
By conservation of energy , energy at perigee =energy at apogee
-
So
Vp= =
Vp=6.85km/s , va=2.28km/s
So orbital velocity vc=
R=6R ,vc= 3.23km/s
Hence to transfer to a circular orbit at apogee , we have to boost the velocity by 3.23-2.28=0.95km/s.
Molecules in air in the atmosphere are attracted by gravitational force of the earth. Explain why all of them do not fall into the earth just like an apple falling from a tree.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-air molecules in the atmosphere are attracted vertically downward by the gravitational force of the earth just like an apple falling from the tree. Air molecules move randomly due to their thermal velocity and hence resultant motion of air molecules move randomly in vertical downward direction. But in case of apple it is heavier than air so it fall downwards only.
Give one example each of central force and non-central force.
Explanation- examples of central force – gravitational force and electrostatic force
Examples of non central force = nuclear force, magnetic force acting between two current carrying loops etc.
Draw areal velocity versus time graph for mars.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-
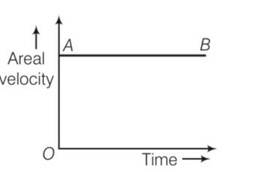
areal velocity of a planet revolving around the sun is constant with respect to time.
What is the direction of areal velocity of the earth around the sun?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-areal velocity of earth and sun
dA/dt=L/2m
where L is angular momentum
but we know L= r
dA/dt=1/2m (r )=1/2 (r )
so dA/dt direction will be perpendicular to the plane containing r and v
How is the gravitational force between two point masses affected when they are dipped in water keeping the separation between them the same?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Gravitational forces acting between two point masses m1 and m2, F= Gm1m2/r2 is independent of nature between them. So the gravitational force will remain unaffected when dipped in water.
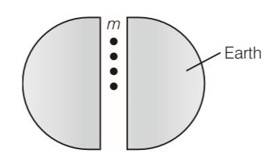
Is it possible for a body to have inertia but no weight?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Yes, a body can have inertia but no weight. When we taken body to the centre of earth its has some inertia but no weight .
We can shield a charge from electric fields by putting it inside a hollow conductor. Can we shield a body from the gravitational influence of nearby matter by putting it inside a hollow sphere or by some other means?
Explanation- A body can be shielded from the gravitational influence of nearby matter because gravitational force between two point mass bodies is independent of the intervening medium. we cannot shield a body from gravitational influence of nearby matter.
An astronaut inside a small spaceship orbiting around the earth cannot detect gravity. If the space station orbiting around the earth has a large size, can he hope to detect gravity?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Inside a small spaceship orbiting around the earth, the value of acceleration due to gravity can be calculated as constant and hence astronaut feels weightlessness.
If the space station orbiting around the earth has a large size such that variation in g matters in that case astronaut inside the spaceship will experience gravitational force and hence can detect gravity.
The gravitational force between a hollow spherical shell (of radius R and uniform density) and a point mass is F. Show the nature of F vs r graph where r is the distance of the point from the centre of the hollow spherical shell of uniform density.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- As density of the shell is constant
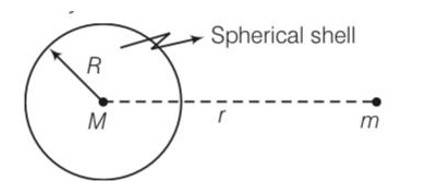
So mass of shell = density (volume)
=
If we consider shell is uniform so F=gravitational force =GMm/r2
F=0 for r
= GM/r2 for r>R
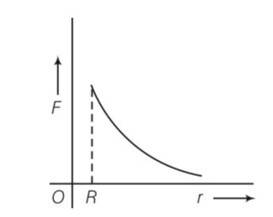
Variation of f verses r
Out of aphelion and perihelion, where is the speed of the earth more and why ?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Phelion is the location of the earth where it is the greatest distance from the sun and perihelion is the location of the earth where it is the nearest to the sun
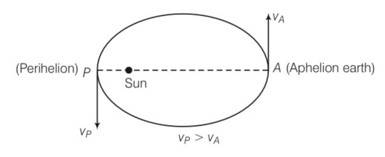
The areal velocity (1/2 rv) of the earth around the sun is constant . so speed of earth is more at perihelion.
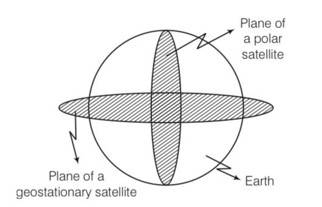
What is the angle between the equatorial plane and the orbital plane of (a) Polar satellite? (b) Geostationary satellite
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Angle between the equatorial plane and orbital plane of a polar satellite is 900 and angle between equatorial plane and orbital plane of a geostationary satellite is 00.
Mean solar day is the time interval between two successive noon when sun passes through zenith point (meridian). Sidereal day is the time interval between two successive transit of a distant star through the zenith point (meridian). By drawing appropriate diagram showing earth’s spin and orbital motion, show that mean solar day is four minutes longer than the sidereal day. In other words, distant stars would rise 4 minutes early every successive day. (Hint: you may assume circular orbit for the earth).
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-Every day the earth advances in the orbit by approximately 10. Then it will have to rotate by 3610 to have the sun at zenith point again. So 3610 corresponds to 24h
So 1o corresponds to 24/361= 0.066h=3.99 min =4min
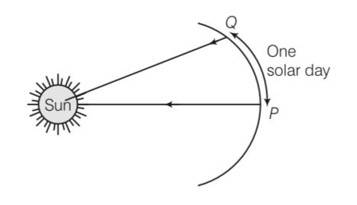
Hence distant stars would rise 4 min early every successive day.
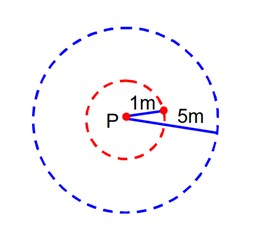
Two identical heavy spheres are separated by a distance 10 times their radius. Will an object placed at the midpoint of the line joining their centres be in stable equilibrium or unstable equilibrium? Give reason for your answer.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Let M be the mass and R be the radius of sphere . an object of mass m be placed at the mid point P of the line joining their centres
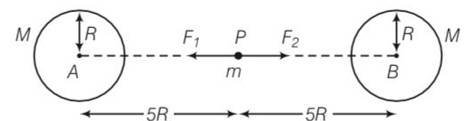
Force F1=F2=GMm/ (5R)2
If we displace it through x distance
New force towards sphere A, F1'= GMm/ (5R-x)2
Sphere B F2' = GMm/ (5R+x)2
As F1'>F2' therefore a resultant force (F1'-F2') acts on the objects towards sphere A therefore objects start to move towards A hence equilibrium is unstable.
Show the nature of the following graph for a satellite orbiting the earth.
(a) KE vs orbital radius R
(b) PE vs orbital radius R
(c) TE vs orbital radius R.
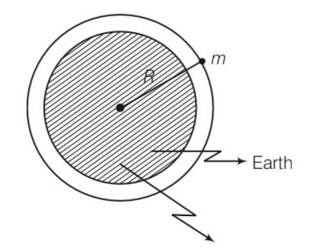
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Orbital speed of the satellite vo=
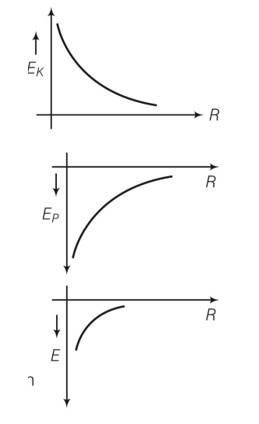
KE of the satellite of mass m, Ek = 1/2mvo2= Gmm/2R
So kinetic energy is inversely proportional to distance.
b)potential energy of a satellite Ep=-GMm/R
so it is also inversely proportional to R
c)total energy of the satellite E=Ek+Ep = = -
Shown are several curves (Fig. 8.2). Explain with reason, which ones amongst them can be possible trajectories traced by a projectile (neglect air friction).
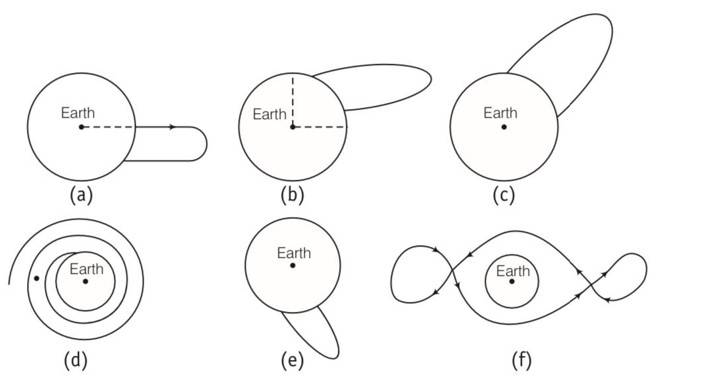
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-The trajectory of a particle under gravitational force of the earth will be in conic section with the centre of the earth as a focus. Only c meets this requirements
An object of mass m is raised from the surface of the earth to a height equal to the radius of the earth, that is, taken from a distance R to 2R from the centre of the earth. What is the gain in its potential energy?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-potential energy of the objects at the surface of the earth is =-
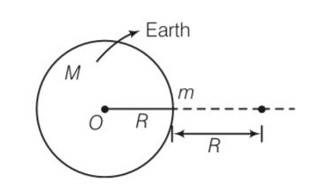
PE of the object at a height equal to radius of earth =
Gain in potential energy = - (- )=
= (GM=gR2)
A mass m is placed at P a distance h along the normal through the centre O of a thin circular ring of mass M and radius r. If the mass is removed further away such that OP becomes 2h, by what factor the force of gravitation will decrease, if h = r ?
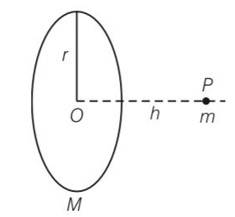
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Gravitational force at h height F =
When mass is displaced upto distance 2h then
F’=
=
When h = r then F=
So F =
F’=
F’ =
The earth is an approximate sphere. If the interior contained matter which is not of the same density everywhere, then on the surface of the earth, the acceleration due to gravity
(a) Will be directed towards the centre but not the same everywhere.
(b) Will have the same value everywhere but not directed towards the centre.
(c) Will be same everywhere in magnitude directed towards the centre.
(d) Cannot be zero at any point.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-d
Explanation- We treated that the mass of earth is at centre . in this case a=g=0 at centre but if earth is not uniform then value of g is different at different point.
As observed from earth, the sun appears to move in an approximate circular orbit. For the motion of another planet like mercury as observed from earth, this would
(a) Be similarly true.
(b) Not be true because the force between earth and mercury is not inverse square law
(c) Not be true because the major gravitational force on mercury is due to sun.
(d) Not be true because mercury is influenced by forces other than gravitational forces.
Answer-c
Explanation-The gravitational force between sun and earth follows inverse square law. Due to relative motion between earth and mercury, the orbit of mercury observed from the earth will not be approximately circular since the major gravitational force on mercury is due to the sun.
Different points in earth are at slightly different distances from the sun and hence experience different forces due to gravitation. For a rigid body, we know that if various forces act at various points in it, the resultant motion is as if a net force acts on the c.m. (centre of mass) causing translation and a net torque at the c.m. causing rotation around an axis through the c.m. For the earth-sun system (approximating the earth as a uniform density sphere)
(a) The torque is zero.
(b) The torque causes the earth to spin.
(c) The rigid body result is not applicable since the earth is not even approximately a rigid body.
(d) The torque causes the earth to move around the sun.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a
Explanation- As the earth is revolving around the sun in a circular motion due to gravitational attraction. The force of attraction will be of radial nature and angle between them is zero so torque is also zero.
Satellites orbiting the earth have finite life and sometimes debris of satellites fall to the earth. This is because,
(a) The solar cells and batteries in satellites run out.
(b) The laws of gravitation predict a trajectory spiralling inwards.
(c) Of viscous forces causing the speed of satellite and hence height to gradually decrease.
(d) Of collisions with other satellites.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-c
Explanation- As the total energy of the earth satellite bounded system is negative . due to the viscous force acting on the satellite, energy decreases continuously and radius also decreases.
Both earth and moon are subject to the gravitational force of the sun. As observed from the sun, the orbit of the moon
(a) Will be elliptical.
(b) Will not be strictly elliptical because the total gravitational force on it is not central.
(c) Is not elliptical but will necessarily be a closed curve.
(d) Deviates considerably from being elliptical due to influence of planets other than earth.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-b
Explanation- as observed from the sun two types of forces are acting on the moon one is due to gravitational attraction between the sun and the moon and the other is due to gravitational attraction between the earth and the moon hence total force is not normal.
In our solar system, the inter-planetary region has chunks of matter (much smaller in size compared to planets) called asteroids. They
(a) Will not move around the sun since they have very small masses compared to sun.
(b) Will move in an irregular way because of their small masses and will drift away into outer space.
(c) Will move around the sun in closed orbits but not obey Kepler’s laws.
(d) Will move in orbits like planets and obey Kepler’s laws.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-d
Explanation- asteroids are also being acted upon by central gravitational forces, hence they are moving in circular orbits like planets and obey Kepler's law.
Choose the wrong option.
(a) Inertial mass is a measure of difficulty of accelerating a body by an external force whereas the gravitational mass is relevant in determining the gravitational force on it by an external mass.
(b) That the gravitational mass and inertial mass are equal is an experimental result.
(c) That the acceleration due to gravity on earth is the same for all bodies is due to the equality of gravitational mass and inertial mass.
(d) Gravitational mass of a particle like proton can depend on the presence of neighbouring heavy objects but the inertial mass cannot.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-d
Explanation- gravitational mass of proton is equivalent to its inertial mass and independent of presence neighbouring heavy objects.
Particles of masses 2M, m and M are respectively at points A, B and C with AB = ½ (BC). m is much-much smaller than M and at time t = 0, they are all at rest (Fig. 8.1). At subsequent times before any collision takes place:
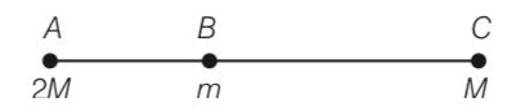
(a) m will remain at rest.
(b) m will move towards M.
(c) m will move towards 2M.
(d) m will have oscillatory motion.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-c
Explanation- force on B due to A = FBA=
force on B due to C = FBC=
BC = 2AB
FBC=
So it move towards BA
Which of the following options are correct?
(a) Acceleration due to gravity decreases with increasing altitude.
(b) Acceleration due to gravity increases with increasing depth (assume the earth to be a sphere of uniform density).
(c) Acceleration due to gravity increases with increasing latitude.
(d) Acceleration due to gravity is independent of the mass of the earth.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c, d
Explanation- acceleration due to gravity at altitude g’=
At depth d, g’=g (1-d/R)
In both cases value of g decreases
But in case of latitude the value of g increases when we increase
also we conclude from the formula that it is independent upon mass.
If the law of gravitation, instead of being inverse-square law, becomes an inverse-cube law-
(a) Planets will not have elliptic orbits.
(b) Circular orbits of planets is not possible.
(c) Projectile motion of a stone thrown by hand on the surface of the earth will be approximately parabolic.
(d) There will be no gravitational force inside a spherical shell of uniform density.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c
Explanation- as we know F=
V= orbital speed=
Time period of revolution of planet T = =
T2 ……….1
Hence orbit will be elliptical.
F= =g’m
It is clear from equation 1 that its path is parabola.
If the mass of sun were ten times smaller and gravitational constant G were ten times larger in magnitudes-
(a) Walking on ground would became more difficult.
(b) The acceleration due to gravity on earth will not change.
(c) Raindrops will fall much faster.
(d) Airplanes will have to travel much faster.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c, d
Explanation- G’=10G
Consider the diagram
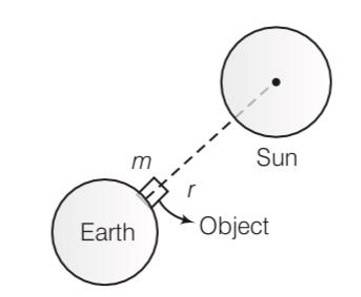
Force on the objects due to the earth =
= (10g)m= 10mg
Force on the objects due to the sun F=
As r>>R so F will be very small
So effect of sun will be neglected
Now g’=10g
Hence weight of person =10mg
So gravity pull on the person will increase, due to it walking on ground would be more difficult
Critical velocity Vc is proportional to g
So Vc
V’>g
Vc’>Vc hence rain will fall faster. To overcome the increased gravitational force of the earth the aeroplane will have to travel much faster.
If the sun and the planets carried huge amounts of opposite charges,
(a) All three of Kepler’s laws would still be valid.
(b) Only the third law will be valid.
(c) The second law will not change.
(d) The first law will still be valid.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c, d
Explanation-due to the huge amount of charges on the sun and the earth electrostatics force of attraction will be large. Gravitational force is also attractive in nature have both forces will be added and obeys kepler's law also.
There have been suggestions that the value of the gravitational constant G becomes smaller when considered over very large time period (in billions of years) in the future. If that happens, for our earth,
(a) Nothing will change.
(b) We will become hotter after billions of years.
(c) We will be going around but not strictly in closed orbits.
(d) After sufficiently long time we will leave the solar system.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-c, d
Explanation- Gravitation force F= where M is mass of sun and m is mass of earth.
When G decrease force will also decrease so according to this it will not in the fixed circular orbits around the sun. as when radius increases the force will decreases and soon earth leave the solar system.
Supposing Newton’s law of gravitation for gravitation forces F1 and F2 between two masses m1 and m2 at positions r1 and r2 read F1=-F2=- n where Mo is a constant of dimension of mass, r12 = r1 – r2 and n is a number. In such a case,
(a) The acceleration due to gravity on earth will be different for different objects.
(b) None of the three laws of Kepler will be valid.
(c) Only the third law will become invalid.
(d) For n negative, an object lighter than water will sink in water.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a,c,d
Explanation- F1=-F2=- n
r12=r1-r2
acceleration due to gravity ,g = F/mass=
as g is constant hence constant of proportionality will not be constant in kepler’s third law.
Hence kepler’s law will not be valid.
For negative n, g=
=
Mo>m1 or m2 so objects lighter than water will sink
Which of the following are true?
(a) A polar satellite goes around the earth’s pole in northsouth direction.
(b) A geostationary satellite goes around the earth in east-west direction.
(c) A geostationary satellite goes around the earth in west-east direction.
(d) A polar satellite goes around the earth in east-west direction
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c
Explanation- a geostationary satellite is having same sense of rotation as that of earth i.e west east direction.
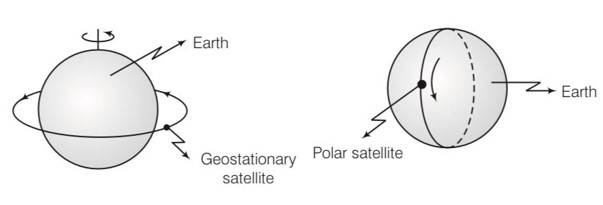
A polar satellite goes around earth's pole in north south direction.
The centre of mass of an extended body on the surface of the earth and its centre of gravity
(a) Are always at the same point for any size of the body.
(b) Are always at the same point only for spherical bodies.
(c) Can never be at the same point.
(d) Is close to each other for objects, say of sizes less than 100 m. (e) both can change if the object is taken deep inside the earth.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-d
Explanation- for small objects sizes less than 100 m centre of mass very close with the centre of gravity of the body. But when the size of object increases it weight changes and its CM and CG become far from each other.
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,29th july ,Physics, Second shift
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,29th july ,Physics, Second shift
Commonly asked questions
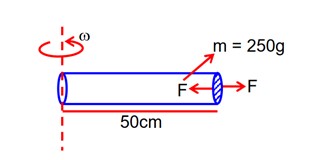
A tube of length 50 cm is filled completely with an incompressible liquid of mass 250g closed both ends. The tube is then rotated in horizontal plane about one of its ends with a uniform angular velocity If F be the force exertaed by the liquid at the other end then the value of x will be __________.
As, F =
Nearly 10% of the power of a 110 W light bulb is converted to visible radiation. The change in average intensities of visible radiation, at a distance of 1 m from the bulb to a distance of 5 m is a × 10‑2 W/m2. The value of ‘a’ will be________.
P = 10% of 110W = 11W
(Visible)
=84 × 10-2 = a × 10-2 = a = 84
A metal wire of length 0.5 m and cross-sectional area 10-4 m2 has breaking stress 5 × 108 Nm-2. A block of 10 kg is attached at one of the string and is rotating in a horizontal circle. The maximum linear velocity of block will be ________ ms-1.
A
Breaking stress,
F = 5 × 104N
T =
Vmax = 50m/s
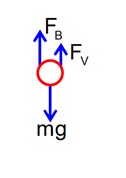
The velocity of a small ball of mass 0.3g and density 8 g/cc when dropped in a container filled with glycerine becomes constant after some time. If the density of glycerine is 1.3 g/cc, then the value of viscous force acting on the ball will be x × 10-4 N, value of x is________. [use g = 10 m/s2]
m = 0.3g density,
Fv + FB = mg.
=Fv = mg – FB = .3 × 10-3 × 10 – 1.3 ×
= 2.5 × 10-3N
= 25 × 10-4N
x = 25
A modulating signal 2sin (6.28 × 106)t is added to the carrier signal 4 sin(12.56 ×109)t for amplitude modulation. The combined signal is passed through a non-linear square law device. The output is then passes through a band pass filter. The bandwidth of the output signal of band pass filter will be_________ MHz.
Modulating signal 
Carrier signal 
The speed of a transverse wave passing through a string of length 60 cm and mass 10g is 60 ms-1. The area of cross-section of the wire is 2.0 mm2 and its Young’s modulus is 1.2 × 1011 Nm-2. The extension of the wire over its natural length due to its tension will be x × 10-5 m. The value of x is________.
m = 10g
A = 2mm2
Y = 1.2 × 1011N/m2
As,
=
So, x = 15

The metallic bob of simple pendulum has the relative density. 5 The time period of this pendulum is 10 s. If the metallic bob is immersed in water, then the new time period becomes The value of x will be_______.
geff = g –
=
=
So, x = 5
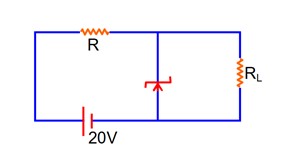
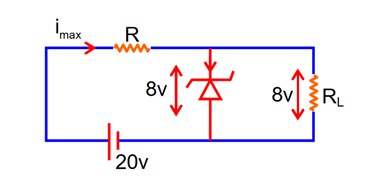
A 8 V Zener diode along with a series resistance R is connected across a 20V supply (as shown in the figure). If the maximum Zener current is 25 mA, then the minimum value of R will be_______ .
20 – imax R – 8 = 0
imax R = 12
At maxm zener current –
imaxR = 12v
25 × 10-3 R = 12
Two radioactive materials A and B have decay constants 25 and 16 respectively. If initially they have the same number of nuclei, then the ratio of the number of nuclei of B to that of A will be “e” after a time The value of a is__________.
At t = 0 Þ NA = NB = N0
after t =
->e =
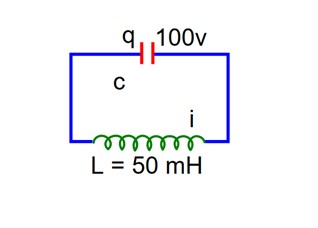
A capacitor of capacitance 500 is charged completely using a dc supply of 100 V. It is now connected to an inductor of inductance 50 mH to form an LC circuit. Then maximum current in LC circuit will be_______ A.
C = 500
In this LC – oscillation
q = q0 cos
=
So, imax =
= 10A
A projectile is launched at an angle ‘α’ with the horizontal with a velocity 20 ms-1. After 10 s, it inclination with horizontal is β. The value of tanβ will be: (g = 10ms-2).
We know that horizontal speed will remain constant
20 cos = v cos ……… (i)
Along y-axis
……. (ii)
In a carnot engine, the temperature of reservoir is 527°C and that of sink is 200 K. If the work done by the engine when it transfers heat from reservoir to sink is 12000 kJ, the quantity of heat absorbed by the engine from reservoir is___________× 106 J.
T2 = 200 k
w = 12000 kJ = 12 × 106 J
Q1 =?
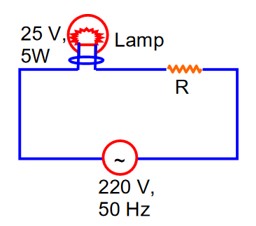
A 220 V, 50 Hz AC source is connected to a 25 V, 5 W lamp and an additional resistance R in series (as shown in figure)
to run the lamp at its peak brightness, then the value of R (in ohm) will be__________.
for lamp,
R = 975
In Young’s double slit experiment the two slits are 0.6mm distance apart. Interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance 80cm from the slits. The first dark fringe is observed on the screen directly opposite to one of the slits. The wavelength of light will be__________nm.
3d = 0.6mm
D = 80cm
= 800mm
Path difference is given by
BP – Andhra Pradesh = Dx
[for Dark fringe at P]
n = 0, for first dark fringe
first dark fringe is observed on the screen directly opposite to one of the slits]
A beam of monochromatic light is used to excite the electron in Li++ from the first orbit to the third orbit. The wavelength of monochromatic light found to be x × 10-10m. The value of x is_________.
[Given hc = 1242 eV nm]
We know
Energy on any orbit is given by,
[n1 = 1] (1)
For 3rd orbit
[n2 = 3]
E3 = 13.6ev
= 13.6 – (13.6 × 9)
= 114.15 × 1010m
A cell, shunted by a8 resistance, is balanced across a potentiometer wire of length 3m. The balancing length is 2m when cell is shunted by 4 resistance. The value of internal resistance of the cell will be__________ .
R shunt Resistance
Given
CD = 3m
CF = 2m
Current through potentiometer wire
I = (1)
A Area of potentiometer wire
Resistivity of the wire
L Length of the potentiometer wire
Case 1 When 8 shunt is bal aced at 3m length
VCD = VAB = E – I1r
=
(2)
Case 2 When 4 shunt is balanced at 2m length
=
=
(3)
r = 24 – 16
r = 8
The current density in a cylindrical wire of radius 4mm is 4 × 106Am-2. The current through the outer portion of the wire between radial distances and R is _________πA.
J (current density) = 4 × 106 Am-2
Area between radial distance
A =
I = AJ
=
= 3R2 × 106 πAmp
= 3 (4 × 10-3)2 × 106 πAmp
= 3 × 16 × 10-6 × 106π Amp
= 48πA
A capacitor of capacitance 50 pF is charged by 100 V source. It is then connected to another uncharged identical capacitor. Electrostatic energy loss in the process is _________nJ.
Q = CV
= 50 × 10-12 × 100
= 5 × 10-12 × 103
Q = 5 × 10-9C
Ui (Initial Energy)
=
=
Now capacitor is connected to an identical uncharged capacitor
kvL
q1 = q2
Initial change Q1 + Q2 = Q
Loss in energy = Ui = Ut
=
=
=
=
= 125 × 10-9
= 125 nJ
The height of a transmitting antenna at the top of a tower is 25m and that of receiving antenna is, 49m. The maximum distance between them, for satisfactory communication is LOS (Line-Of-Sight) is The value of K is___________.
(Assume radius of Earth is 64 × 10+5m) [Calculate upto nearest integer value]
Given, hT = 25m, R = 6400 km
hR = 49m
dm (Maximum distance for satisfactory communication)
dm =
dm =
=
=
=
k= 192
The area of cross-section of a large tank is 0.5 m2. It has a narrow opening near the bottom having area of cross-section 1 cm2. A load of 25 kg is applied on the water, coming out of the opening at the time when the height of water level in the tank is 40cm above the bottom, will be_________cms-1.
Bernoulli’s equation between (1) & (2)
A pendulum of length 2m consists of a wooden bob of mass 50g. A bullet of mass 75g is fired towards the stationary bob with a speed The bullet emerges out of the bob with a speed and the bob just completes the vertical circle. The value of is_________ms-1.
(if g = 10 m/s2).
Com
m1v + m2 × 0 = m1v1 + m2v2
75v =
JEE Mains 2022
JEE Mains 2022
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,25th june ,physics ,Second shift
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,25th june ,physics ,Second shift
Commonly asked questions
For where ‘a’ is a constant. If percentage error in measurement of ‘x’ and ‘y’ are 4% and 12% respectively, then the percentage error for ‘z’ will be…………%
A curved in a level road has aradius 75m. The maximum speed of a car turning this curved road can be 30 m/s without skidding.; If radius of curved road is changed to 48m and the coefficient of friction between the tyres and the road remains same, then maximum allowed speed would be…….m/s.
Now, R = 48 m (new Radius of curvature)
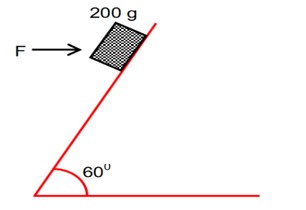
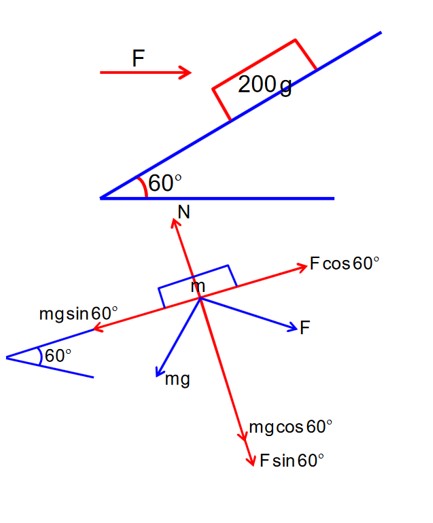
A block of mass 200g is kept stationary on a smooth inclined plane by applying a minimum horizontal force F N as shown in figure.
For equilibrium along the incline plane is given by,
F cos 60° = mg sin 60°
Moment of Inertia (M.I.) of four bodies having same mass ‘M’ and radius ‘2R’ are as follows:
I2 = M.I. of solid sphere about its diameter
I2 = M.I. of solid cylinder about its axis
I3 = M.I. of solid circular disc about its diameter
I4 = M.I. of thin circular ring about its diameter
if 2(I2 + I3) + I4 = x. I1 then the value of x will be…………
l1 = M. l of solid sphere about its diameter
l2 = M. I of solid cylinder about its axis
I3 = M. I of solid circular disc about its diameter
I4 = M. I of this circular ring about its diameter
x = 5
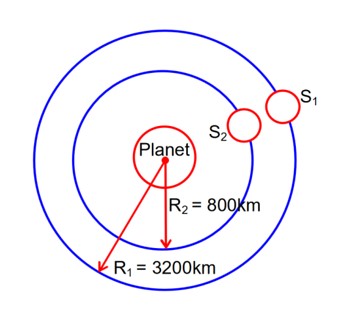
Two satellites S1 and S2 are revolving in circular orbits around a planet with radius R1 = 3200km and R2 = 800km respectively. The ratio of speed of satellite S1 to the speed of satellite S2 in their respective orbits would be where x =…………..
M1 ->Mass of satellite (1)
M2 -> Mass of satellite (2)
MP -> Mass of planet
Now NLM (2) on S1
Similarly v2 =
When a gas filled in a closed is heated by raising the temperature by , its pressure increases by 0.4%. The initial temperature of the gas is………..K.
For closed vessel
P a T [v = constant]
->P = kT
T = 250 K
27 identical drops are charged at 22V each. They combine to form a bigger drop. The potential of the bigger drop will be…………V.
Volume of 27 identical drops = volume of a bigger drop
R3 = 27r3
R = 3r
Given potential of a small drop = 22v
The length of a give cylindrical wire is increased to double of its original length. The percentage increase in the resistance of the wire will be……………..%.
volume of wire will remains constant
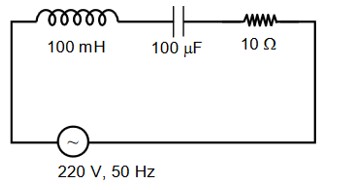
In a series LCR circuit, the inductance, capacitance and resistance are L = 100mH, C = and R = respectively. They are connected to an AC source of voltage 220V and frequency of 50 Hz. The approximate value of current in the circuit will be………..A.
JEE Mains 2021
JEE Mains 2021
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Eight Exam