physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.15 The speed of the ball, u = 40 m/s
Ceiling height, h = 25m
Since the ball is thrown, it will follow the path of a projectile. For projectile motion, the maximum height for a body projected at an angle is given by
h= , sin2 = (25 ,
Horizontal range is given by,=
R = = ((40 ) )/9.81 = 150.38m
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
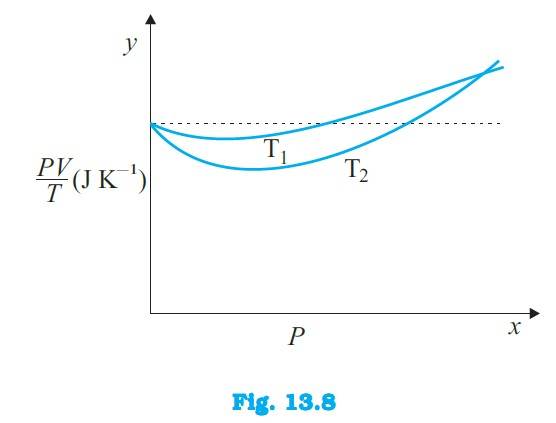
13.3 (a) The dotted plot in the graph signifies the ideal behaviour of the gas, i.e. = R, (where is the number of moles and R is the universal gas constant) is a constant quantity. It is not dependent on the pressure of the gas. The curve of the gas at temperature is closer to the dotted plot than the curve of the gas at temperature
(b) A real gas approaches the behaviour of an ideal gas when its temperature increases. Therefore > is true for the given plot.
(c) The value of the ratio , where the two curves meet, is R. This is because the ideal gas e
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.14
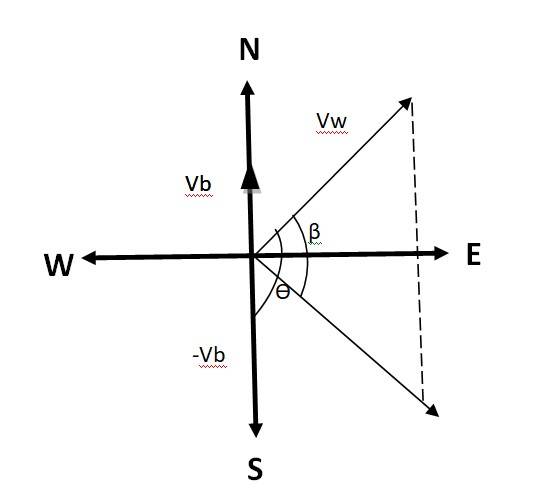
The velocity of the boat = 51 km/h, the velocity of the wind = 72 km/h
Flag is fluttering in N-E direction, so the direction is N-E.
When the ship begins to sail towards North, the flag will flutter along the direction of relative velocity of the wind w.r.t. the boat.
The angle between & - = 90
tan = = =
tan-1( ) = 45.099
Angle with respect to East direction = 45.099 - 45 = 0.099
Hence the flag will flutter almost due East.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.13 Swimming speed = 4 km/h, Width of the river = 1.0 km
Time required to cross the river = = h= 15 min
Speed of the river = 3 km/h
Distance covered by the river in 15 min = 3 = 750 m
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
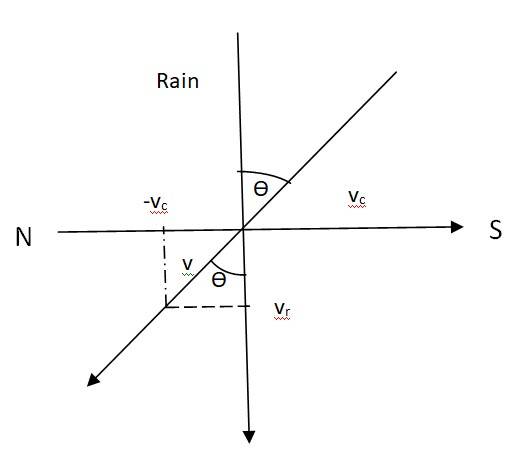
4.12 Let Vc = Velocity of the cyclist
Vr = Velocity of the rain
If V is the relative velocity, the woman must hold her umbrella in the direction of V.
V = Vr + (-Vc) = 30 + (-10) = 20 m/s
Tan = = , = 18
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.2 The ideal gas equation relating to pressure (P), volume (V) and absolute temperature (T) is given by the relation
PV = nRT, where
R is the universal gas constant = 8.314 J /mol/K
N = number of moles = 1 (given)
T = standard temperature = 273 K
P = standard pressure = 1 atm = 1.013 N/
Therefore V = = = 0.02240 = 22.4 litres
Hence the molar volume of a gas at STP is 22.4 litres.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.11
(a) Total distance travelled = 23 km, Total time taken = 28 min
Average speed = = km/min = 49.29 km/h
(b) Average velocity = = km/min = 21.43 km/h
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.10
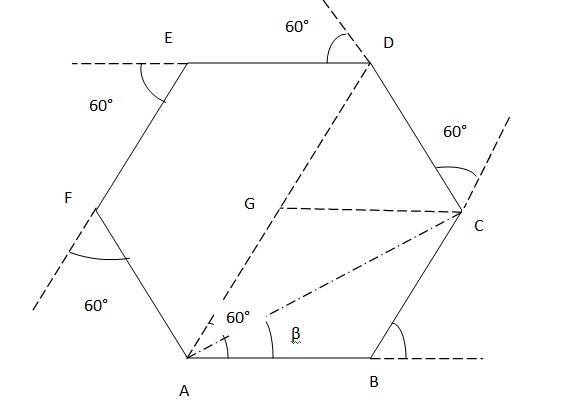
Since the motorist taking the 60° turn after every 500m, It will form a perfect hexagon of side 500m after 6 turns.
Suppose the motorist starts from point A. From A, turns 60° to reach B (first turn), then to C and so on.
1. At third turn, The magnitude of displacement = DG + GA = 500m + 500m = 1000m Total path length = AB + BC + CD = 500m +500m +500m = 1500 m
2. At sixth turn, When the motorist takes the 6th turn, he is at starting point A. Therefore,
The magnitude of displacement = 0Total path length = AB + BC + CD + DE + EF + FA = 500m + 500m
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.9
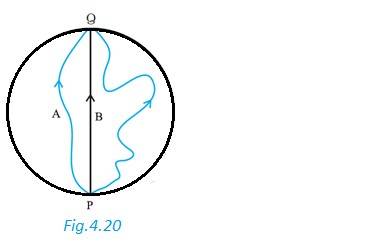
(a) Since the cyclist came back to his starting point O, so the displacement is Zero
(b) Average velocity = = 0
(c) Average speed =
Distance travelled = OP + PQ + QO
= 1 + (1/4) 3.57 km
Average speed = 3.57 / 10 km/min = 21.43 km/h
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
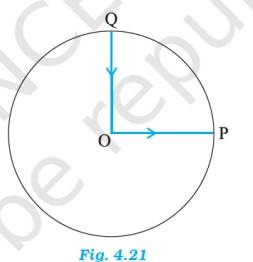
4.8 The radius of the ground = 200 m, the distance PQ = diameter of the ground = 400 m
The displacement all 3 girls = 400 m
This magnitude is equal to the path skated by girl B
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers