physics ncert solutions class 11th
Get insights from 951 questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert solutions class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.25
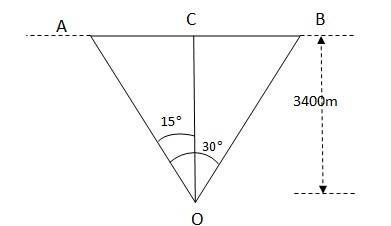
Height of the aircraft from the ground = 3400m
Let A and B be the positions of the aircraft, making an angle of AOB = 30 . The perpendicular OC and OC is the height of the aircraft. Angles AOC = angle BOC = 15
In AOC, AC = OC
= 3400 = 911.03m
AB = AC + CB = 2AC = 1822m
The distance of AB is covered in 10s, so the speed of the aircraft = 1822/10 m/s = 182.2 m/s
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.24
(a) Despite being a scalar quantity, energy is not conserved in elastic collisions. False
(b) Despite being a scalar quantity, the temperature can take negative values. False
(c) The total path length is a scalar quantity. Yet it has the dimension of length. False
(d) A scalar quantity such as gravitational potential can vary from one point to another point in space. False
(e) The value of a scalar does not vary for observers with different orientation of axis. True
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.23
(a) For any arbitrary motion of a particle average velocity cannot be expressed by this equation. False
(b) The arbitrary motion of the particle can be represented by this equation, True
(c) For arbitrary motion of the particle, the acceleration may also be non uniform. False
(d) The motion of the particle is arbitrary, acceleration of the particle may also be non-uniform, so can not represent the motion of the particle in space. False
(e) The arbitrary motion of the particle can be represented by the given equation. True
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.14 Let the atomic mass of a substance be = M and the density of the substance be =
Avogadro's number, N = 6.023
Volume of N number of molecules = ……. (i)
Volume of one mole of a substance = …… (ii)
Equating (i) and (ii), we get

New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.13 According to law of atmospheres, we have
n2 = n1 exp [ -mg (h2 – h1)/ kBT] ….(i)
where is the number of density at height and is the number of density at height
mg is the weight of the particle suspended in the gas column
Density of the medium =
Density of the suspended particle =
Mass of one suspended particle = m'
Mass of medium displaced = m
Volume of the suspended particle = V
According to Archimedes's principle for a particle suspended in a liquid column, the effective weight of the suspended particle is given as:
Weight of the medium displaced – weight of the suspended particle = mg – m'g
= mg- V = mg –
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.12 Rate of diffusion of hydrogen, = 28.7 cm3 s–1
Rate of diffusion of another gas, = 7.2 cm3 s–1
According to Graham's law of diffusion, we have:
= , where = molecular mass of hydrogen = 2.02 g and is the molecular mass of the unknown gas
= 2.02= 32.09 = Molecular mass of Oxygen
Hence, the unknown gas is Oxygen.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.11 Length of the narrow bore, L = 1 m = 100 cm
Length of the mercury thread, l = 76 cm
Length of the air column between mercury and the closed end, = 15 cm
Since the bore is held vertically in air with the open end at the bottom, the mercury length that occupies the air space is 100 – (76 + 15) = 9 cm
Hence, total length of the air column = 15 + 9 = 24 cm
Let h cm of mercury flow out as a result of atmospheric pressure.
Length of the air column in the bore = 24 + h cm
Length of the mercury column = 76 – h cm
Initial pressure, = 76 cm of mercury
Initial volume, = 15
Final pressure, = 76 – (76 – h) = h cm
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.10 Pressure inside the cylinder containing nitrogen, P = 2.0 atm = 2 Pa
Temperature inside the cylinder, T = 17
Radius of nitrogen molecule, r = 1.0 Å = 1 m
Diameter of nitrogen molecule, d = 2 m
Molecular mass of nitrogen molecule, M = 28 u = 28 g (assume) = 28 kg
The root means square speed of nitrogen is given by the relation
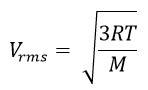
R is the universal gas constant = 8.314 J/mole/K
Hence
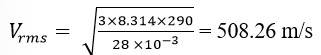
The mean free path is given by
where k = Boltzmann constant = 1.38 kg-
= 1.11 m
Collision frequency = = = 4.57 /s
Collision time, T = =S= 3.93 s
T
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.9 Temperature of the helium atom, = – 20 °C = 253 K and temperature of argon atom be =
Atomic mass of helium, = 4.0 u
Atomic mass of Argon, = 39.9 u
Let be the rms speed of Argon and be the rms speed of Helium
From the relation of we get
rms speed of Argon,
rms speed of Helium,
Since both the speeds are equal, we get
= or = or = = = 2523.675 K = 2.523 K
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.8 (a) According to Avogadro's law, the three vessels will contain an equal number of the respective molecules. This number is equal to Avogadro's number, N = 6.023
(b) The root mean square speed ( of a gas of mass m and temperature T is given by the relation . Where k is Boltzmann constant. For the given gases, k and T are constants. Hence depends only on the mass of the atoms ![]()
Therefore, the root mean square speed of the molecules in the three cases is not the same. Among Neon, Chlorine and Uranium hexafluoride, the mass of the neon is the smallest, so Neon will have the highest root mean square sp
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
