Physics
Get insights from 5.6k questions on Physics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) R= 20cm, = 1.5, f= = =40cm so lens acts as convex lens.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) According to VIBGYOR, among all given sources of light, the blue light have the smallest wavelength. According to Cauchy relationship, smaller the wavelength higher the refractive index and consequently smaller the critical angle. So, corresponding to blue colour, the critical angle is least which facilitates total internal reflection for the beam of blue light. The beam of green light would also undergo total internal reflection.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) A passenger in an aeroplane may see a primary and a secondary rainbow like concentric circles.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) When an object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed of 5 m/s, the image away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) Since v ∝ λ, the light of red colour is of the highest wavelength and therefore of the highest speed. Therefore, after travelling through the slab, the red colour emerge first.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) since deviation = (1.5-1)50= 2.50
But so
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
1/f=1/v-1/u
-u+V=D
U=-(D-v)
Putting
On solving v2-Dv+Dt=0
So v=
When the objects distance is
The image forms at
Similarly when the objects distance is
The image forms at
The distance between the poles for these two objects distance is
If u = D/2+d/2 then the image is at v=D/2-d/2
The magnification m1=
If u =D-d/2then v= D+d/2
The magnification m2=
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
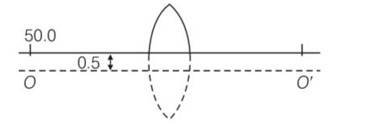
If there was no cut, then the object would have been at a height of 0.5 cm from the principal axis OO'.
Applying lens formula, we have
1/v-1/u=1/f Z
=
V= 50cm
Magnification m = v/u= 50/-50=-1
So coordinates of image are (50cm, -1cm)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- p=100W
1= 1nm
2= 500nm
Also n1and n2 represent number of photon of x-rays and visible light emitted from the two sources per sec
E/t=P=n1hc/ 1=n2hc/ 2
So n1/ 1 = n2/ 2
So n1/n2= 1/500
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
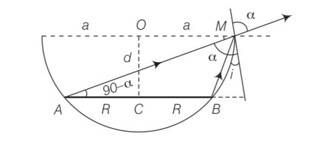
Refering to the figure, AM is the direction of incidence ray before liquid is filled. After liquid is filled in, BM is the direction of the incident ray. Refracted ray in both cases is same as that along AM
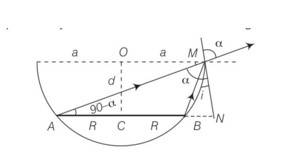
N= 900, OM= a, CB = NB= a-R, AN= a+R
Sint=Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers