Chemistry Solutions
Get insights from 89 questions on Chemistry Solutions, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry Solutions
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
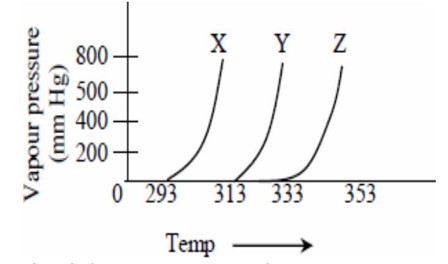
At a fixed temperature, having more vapour pressure as compared to . So, intermolecular interaction is lower as compared to .
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Vapour pressure over solvent is greater than that over solution.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
The above mixture will show positive deviation from Raoult's law.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
P (CO? ) = K? X (CO? )
X (CO? ) = P (CO? )/K? = 0.835 / (1.67 * 10³) = 0.5 * 10? ³
X (CO? ) = n (CO? )/ (n (CO? ) + n (H? O) ≈ n (CO? )/n (H? O) (since n (CO? ) << n (H? O)
n (H? O) in 0.9L = 900g/18gmol? ¹ = 50 mol
n (CO? ) = X (CO? ) * n (H? O) = 0.5 * 10? ³ * 50 = 25 * 10? ³ moles = 25 mmol
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
? = CRT
2.42 * 10? ³ = ( (1.46/M_polymer) / 0.1 ) * 0.083 * 300
M_polymer = (1.46 * 0.083 * 300) / (2.42 * 10? ³ * 0.1)
= 14.96 * 10? gm = 15 * 10? gm
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
ΔTb = 0.6 K
ΔTb = Kb * m = Kb * (wt. * 1000)/ (mol wt. * Wsolvent (gm)
0.6 = 5 * (3 * 1000)/ (mol wt. * 100)
∴ mol wt. = (15 * 10)/ (0.6) = 1500/6
= 250 g/mole
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers