Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
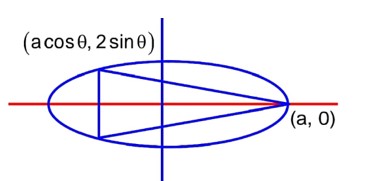
Equation of tangent at P (x, y) is Y =
It passes through (3, 3), c = 3
Length of latus rectum = 3
New answer posted
5 months agoNew answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
To represent in detail NCERT ideas of organic chemistry basics (Class 11, Chapter Organic Chemistry - some basic principles and methodologies), you can use a variety of superb online resources. Sites such as Khan Academy provide entire notes, video recorded lectures and solved examples which deconstructs hard topics such as nomenclature, isomerism, reaction mechanisms and the effect of electron displacement. Physics Wallah and Aakash also have detailed revision videos as part of the NCERT syllabus which goes into details about these base concepts. Going through the platforms will give you deeper insights than the textbook.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers