Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- vx=2t for 0
= 2 (2-t) for 1
=0 for t>2s
Vy= t for 0
= 1 for t>1s
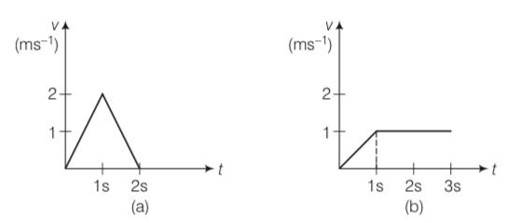
Fx= max= mdvx/dt= 1 (2)
Fy = may= mdvy/dt
= 1 (1) for 0
F= Fx? +Fy?
= 2? +?
=-2?
=0
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- as angle is 45
On smooth inclined plane acceleration will be a = gsin
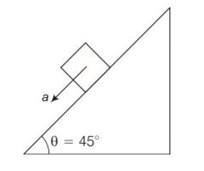
So acceleration will become a= g/
Using equation of motion s =ut +1/2at2
S=
On rough inclined plane a = g (sin )
= g (sin )=
So s=ut +1/2at2
S= 0+ 2
Comparing two above distance
2=
So after solving we get
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) Boyle's law | (e) p ∝ at constant n and T |
(ii) Charle's law | (d) V ∝ T at constant n and p |
(iii) Dalton's law | (b) ptotal = p1 + p2 + p3……… at constant T, V |
(iv) Avogadro law | (a) V ∝ n at constant T and p |
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) Pressure vs temperature (a) graph at constant molar volume. | (c) Isochores |
(ii) Pressure vs volume graph at constant temperature. | (a) Isotherms |
(iii) Volume vs temperature graph at constant pressure. | (d) Isobars |
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
1. At low pressure, the curve of real gas coincides with that of ideal gas, this shows that the deviation of behaviour of real gas with respect to ideal gas is small or negligible.
2. At high pressure, the curve of real gas is far apart from ideal gas, this shows that the deviation of behaviour of real gas with respect to ideal gas is large.
3. The pressure p1 and volume V1 are the point where real gas behaves as an ideal gas.

New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
1. According to Boyle's law,
Pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to volume of gas at constant temperature. So, the volume decreases with increase in pressure at constant temperature.
2. According to Charles's law,
Volume of a gas is directly proportional to temperature when the pressure is constant. So, the volume of gas increases with increase in temperature.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The increase in temperature increases the kinetic energy of the molecules which decreases the intermolecular forces operating between its particles and hence, the viscosity of a liquid decreases. So, the viscosity of a liquid decreases if its temperature is increased.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Hexane is a nonpolar molecule which has london force between the molecules, which is a weak force.
Water and glycerine have O atoms which is an electronegative atom that forms H bonding between the molecules along with dipole-dipole interaction.
Glycerine has three O atoms, so it forms more H bonding and hence, has stronger intermolecular forces.
So the increasing order of intermolecular forces is Hexane < Water < Glycerin. Stronger the intermolecular forces, the greater is the viscosity, so the increasing order of their viscosities is:
Hexane < Water < Glycerin
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The two phenomena that can be explained on the basis of surface tension are:
1. Spherical shape of rain droplets.
2. Capillary action due to which the liquid in capillary rises and falls.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar

Unit of 'P' = N m-2
Unit of 'a' = N m-2 X (m3)2 / (mol)2
= N-m4 mol-2
Unit of 'a' when pressure is in atm, and volume in dm3
Unit of 'P' = atm
Unit of 'a' = atm X (dm3)2 / (mol)2
= atm-dm6 mol-2
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers



