Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) When number of molecules breaks then number of moles would become double.
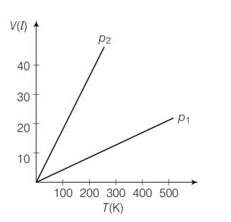
P where n is the number of moles and T is temperature of ideal gas
As gases breaks number of moles becomes twcice of initial so n2 =2n1
= 20
p2=20p1
so 20 times
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Pressure is inversely proportional to slope
So
So p1 > p2
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
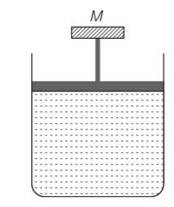
(c) The pressure inside the gas will be
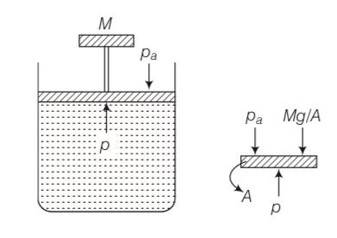
P= pa+Mg/A
A= area of piston
Pa= atmospheric pressure
Mg = weight of piston
When temperature is increases
pV=nRT so volume increases at constant pressure.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Boyle's law is applicable when temperature is constant
PV=nRT=constant
PV= constant
So pressure is inversely proportional to volume.
So process is called isothermal process.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
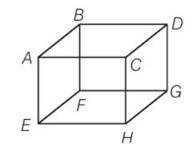
(d) In an ideal gas when a molecules collides elastically with a wall, the momentum transferred to each molecule will be twice the magnitude of its normal momentum. For the face EFGH, it transfer only half of that.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) As the motion of the vessel as a whole does not affect the relative motion of the gas molecules with respect to the walls of the vessel, hence pressure of the gas inside the vessel, as conserved by us, on the ground remains the same.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
According to kinetic interpretation of temperature, absolute temperature of a given sample of a gas is proportional to total translational kinetic energy of its molecule.
Hence any change in absolute temperature of a gas will contribute to corresponding change in translational KE and vice versa.
N= number of moles
m=molar mass of the gas
when the container stops its total kinetic energy transferred to the gas molecules in the form of translational KE, thereby increasing the absolute temperature.
KE of molecules due to velocity KE=
Increase in translational KE =n T
Accordin
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
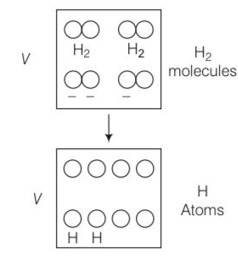
Volume occupied by 1 mole = 1mole of the gas at NTP= 22400mL=22400cc
So number of molecules in 1cc of hydrogen=
H2 is a diatomic gas, having a total of 5 degrees of freedom
So total degrees possesed by all the molecules
= 5
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Number of helium = 5
T=7oC=7+273=280K
(a) hence number of atoms = number of moles Avogadro's number
= atoms
(b) now average kinetic energy per molecule = 3/2 KBT
= total internal energy
= number of atoms
=
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When air is pumped, more molecules are pumped and boyle's law is staed for situation where number of molecules remains constant . in this case as the number of air molecules keep increases, hence mass change. Boyle's law is only applicable in situations, where number of gas molecule of remains fixed.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers