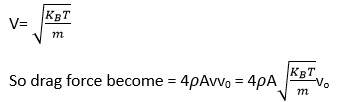Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Consider the diagram
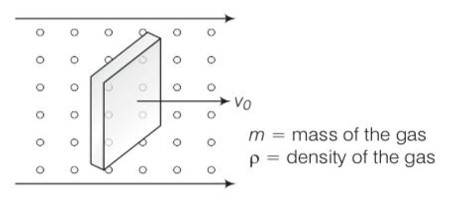
let n =number of molecules per unit volume
Vrms= rms speed of gas molecule
When block is moving with speed vo, relative speed of molecules w.r.t front face =v+vo
Coming head on, momentum transferred to block per collision =2m (v+vo)
Number of collisions in time = (v+vo)n A where A is the area of cross section.
So momentum transferred in time =m (v+vo)2nA this is from front surface
Similarly momentum transferred in time = m (v-vo)2nA ) this is from back surface
Drag force = mnA (v+vo)2- (v-vo)2)
= mnA (4wo)=4mnAvvo
= 4 vvo
So =mn/V=M/
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Given volume V = 1m3
area = 0.01mm2
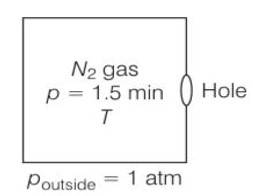
= 8.01 m2= m2
Temperature both inside and outside are equal
So initial pressure inside the box = 1.50atm
Final pressure inside the box= 0.1atm
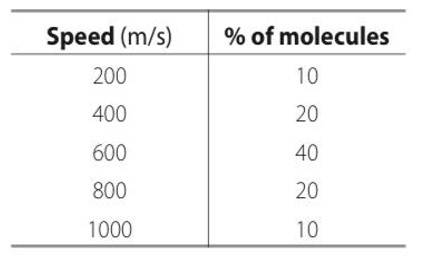
Assuming Vx= speed of nitrogen molecule in x direction
ni = number of molecules per unit volume in a time interval of
Let area of the wall, number of particles colliding in time
= i (vx )A , here we use ½ because particle moves both in positive and negative direction.
Vx2+ Vy2+ Vz2= Vrms2
Vx2= Vrms2/3 if all three velocities are equal.
½ mvrms2= 3/2KBT/m


New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Time require to avoid the collision T= l/v where l = mean free path =1/
Where n = N/V
n=number of aeroplanes/volume
= -3
T=
T= =
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar

New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) The moon has small gravitational force and hence, the escape velocity is small .
As the moon in the proximity of the earth as seen from the sun, the moonhas the same amount of heat per unit area as that of the earth.
The air molecules have large range of speeds . even though the rms speed of the air molcules is smaller than the escape velocity on the moon, a significant number of molecules have speed grater than the escape velocity.
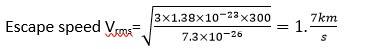
(b) As the molecules move higher their potential energy increases and hence kinetic energy decreases and hence temperature reduces. At g
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
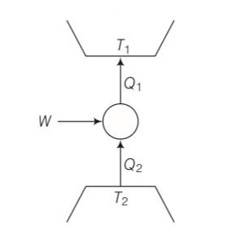
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (c) Q1= W+Q2
W=Q1-Q2>0
Q1>Q2>0
We can also write Q21
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
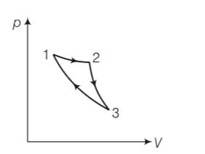
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) the given process is a cyclic process i.e returns to the original state 1
Hence change in internal energy dU =0
dQ= dU+dW=0+dW
hence total heat supplied is converted to work done by the gas which is not possible by second law of thermodynamics.
(c) When the gas expands adiabatically from 2 to 3 . it is not possible to return to the same state without being heat supplied hence 3 to 1 cannot be adiabatic.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
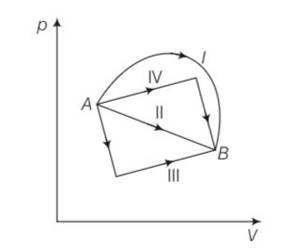
(b), (c) Change in internal energy for process A to B
dU=nCvdT=nCv (dT)=nCv (TB-TA)
work done from A to B = area under the PV curve which is maximum for path I
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (d) For isothermal dT= 0 so T=constant
For an ideal gas dU = change in internal energy = nCvdT=0
From first law of thermodynamics dQ= dU+dW
dQ= dW
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (b), (d) When the rod is hammered the external work is done on the rod which increases its temperature.
Heat is transferred to the gas in the small container by big reservoir at temperature T2
As the weight is added to the cylinder arrangement in the form of external pressure so it cannot reversed.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers