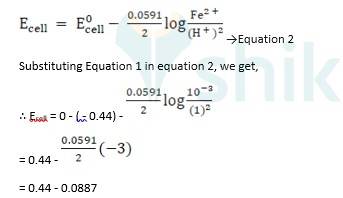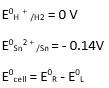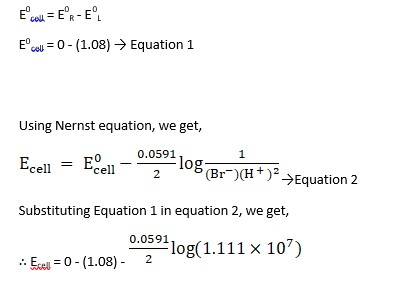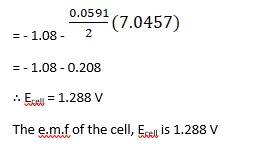Class 12th
Get insights from 11.8k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given - Zn → Zn2+ + 2e -, E0 = 0.76V (anode)
Ag2O + H2O + 2e - →2Ag + 2OH -, E0 = 0.344V (cathode), n = 2
ΔrG0 =?
Ecell0=?
Zn is oxidized and Ag2O is reduced.
Hence, the standard cell potential, Ecell0 is given as,
Ecell0 = ER0 - EL0
E0 cell = 0.344 + 0.76
∴ E0cell = 1.104 V
To calculate the standard Gibb's free energy? rG0, we use,
? rG0 = - nE0F → Equation 1
= - 2*96487*1.104 J
= - 213043.296 J
∴? rG0 = - 2.13*105 J
The standard cell potential, E0cell is 1.104 V and the standard Gibb's free energy? rG0 is - 2.13*105 J
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.6
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid due to extensive –H bonding with water due to the presence of –OH group) is a water-soluble vitamin in contrast to vitamin A, D, E and K which are fat soluble. Also, humans cannot synthesize it due to the lack of specific enzyme and it is rapidly absorbed from the intestine.
Because it is water-soluble, it is not stored in our body to a significant amount but is readily excreted in the urine.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Mg(s)|Mg 2+(0.001M)Cu2+(0.0001 M)|Cu(s) (ii) Fe(s)|Fe 2+(0.001M)H+ (1M)|H2 (g)(1bar)| Pt(s) (iii) Sn(s)|Sn2+(0.050 M)H+ (0.020 M)|H2 (g) (1 bar)|Pt(s) (iv) Pt(s)|Br – (0.010 M)|Br2 (l )H+ (0.030 M)| H2 (g) (1 bar)|Pt(s).
A 3.5 Ecell = ?
(i) Mg + Cu2+ → Mg2+ + Cu (n = 2)
E0 Cu2+ / Cu+ = 0.34V
E0 Mg 2+ / Mg = - 2.37 V
Ecell0 = ER0-EL0
Ecell0 = 0.34 - ( - 2.37) → Equation 1
Using Nernst equation, we get,
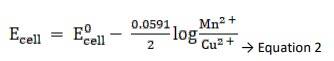
Substituting Equation 1 in equation 2, we get,
∴ Ecell = 0.34 - ( - 2.37) - 0.0591 / 2 log 10 -3/ 10-4
= 2.71 - 0.0591 / 2 log 10
= 2.71 - 0.02955
∴ Ecell = 2.68 V
The e.m.f of the cell, Ecell is 2.68 V
ii) Fe + 2H + →
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.5
Eggs contain protein and proteins are a polymer in amino acids. When an egg is boiled the protein present inside the egg is denatured (the process of loss of biological activity of protein like their ability of –H bonding when subjected to a physical change like a change in temperature, pH) and coagulated (the process of liquid changing to a solid or semi-solid state). Due to this, the water present in the egg is absorbed by the coagulated protein by –H bonding.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(1) Known - E0Cr3+/Cr = - 0.74 V
E0 cd2+ = - 0.40 V
? rG0 =? K =?
The galvanic cell of the given reaction is written as - Cr (s)|Cr3+ (aq)| Cd2+ (aq)|Cd (s)→ Reaction 1
Hence, the standard cell potential is given as, E0 = ER0 - EL0
= - 0.40 - (- 0.74)
∴ E0 = + 0.34 V
To calculate the standard Gibb's free energy? rG0, we use,
? rG0 = - nE0F → Equation 1
wherenF is the amount of charge passed and E0 is the standard reduction electrode potential. Substituting n = 6 (no. of e - involved in the reaction 1), F = 96487 C mol-1,
E0 = + 0.34 V in Equation 1, we get, l
? rG0 = - 6*0.34V*96487 C mol-1
= - 196833.48 CV mol-1
= - 196833.48 J mol-1
∴?
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.4
Amino acids are organic compounds containing amine (basic) and carboxyl (acidic) functional group with a specific side chain. Both acidic and basic group are present in the same molecule. In, aqueous solution carboxyl group can lose a proton (H+) and amino group can accept a proton (H+) giving rise to the dipolar ion called as zwitter ion. Zwitter ion is shown below:
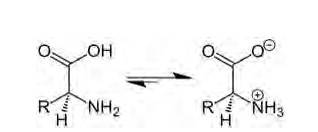
In this zwitter ion there is the presence of both positive as well as negative charge, so there is the development of strong electrostatic force of attraction between the molecules and the water. For this reason solubility of amino acids is higher. Due to strong e
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
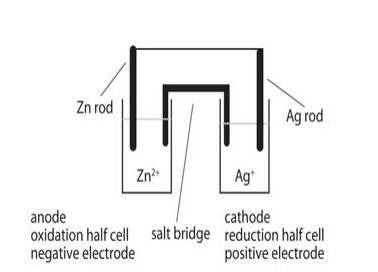
The galvanic cell corresponding to the given redox reaction can be represented as:
Zn|Zn2+ (aq)|Ag + (aq)|Ag
- 1) Zn electrode (anode) is negatively charged because, at this electrode, Zn is oxidized to Zn2+, causing electron accumulation at the
- 2) Electrons (ions) are the carriers of the current in the cell and in the external circuit, current flows from Ag (cathode) to Zn (anode) which is normally opposite to the electron flow which is from anode to cathode.
- 3) At anode:
Zn (s)⇒ Zn2 + (aq) + 2e– At cathode:
Ag + (aq) + e –⇒ Ag (s)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.3
D-glucose reacts with hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to form oxime due to the presence of the aldehyde functional group (-CHO). This is due to the cyclic structure of glucose which forms an open chain structure in an aqueous medium, which then reacts to give an oxime.
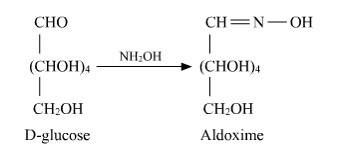
But in case of pentaacetate of D-glucose, it does not form open chain structure in an aqueous medium so it does not react with NH2OH.
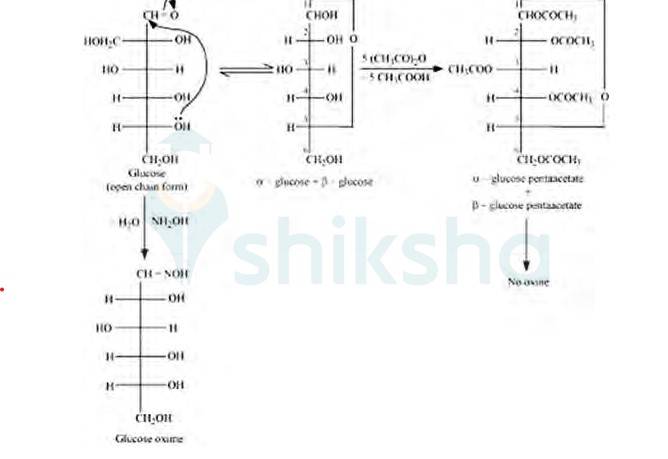
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
K + /K = –2.93V, Ag+ /Ag = 0.80V, Hg2+/Hg = 0.79V Mg2+/Mg = –2.37 V, Cr3+/Cr = – 0.74V
A 3.2 Reducing power of metals increase with the decrease of reduction potential. Hence, the increasing order of reducing power will be as,
Ag < Hg < Cr < Mg < K
When the reduction potential is lower, the element has more tendency to get oxidized and thus more will be reducing power. The metal that has more negative electrode potential will be the one with more reducing power. Thus, here potassium (K) has the highest reducing power among the given elements.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The order in which the given metals displace each other from the solution of their salts is given by,
Mg>Al> Zn> Fe> Cu
A metal of stronger reducing power displaces another metal of weaker reducing power from its solution of salt. The order of increasing the reducing power of given metals is Cu< Fe< Zn< Algiven metals displace each other from the solution of their salts is given by, Mg>Al> Zn> Fe> Cu. This is hence arranged in decreasing order of its reactivity
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers