Class 12th
Get insights from 11.8k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.15
Hydrolysis is the process of using water to break down a molecule into two parts. It is usually a type of decomposition reaction where one reactant is water, where water is used to break chemical bonds in the other reactant. It can be considered as reverse of a condensation reaction.
The general formula of a hydrolysis reaction is:
XY + H2O → XH + YOH
(i) On hydrolysis with dilute acids, sucrose yields an equimolecular mixture of α –D glucose and β–D- fructose.
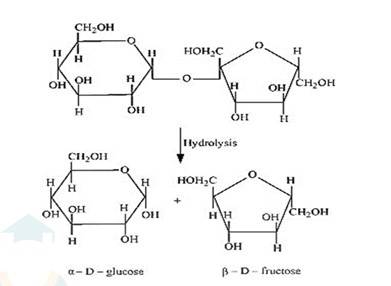
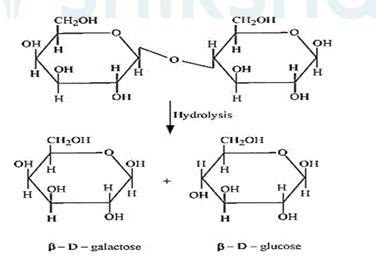
(ii) The hydrolysis of lactose gives β–D-galactose and β–D-glucose as final products.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Equivalent weight is Ag, EAg = 180/1 = 180
Equivalent weight is Cu, ECu = 63.5 / 2 = 31.75
Equivalent weight is Zn, EZn= 65/2 = 32.5
Using Faraday's second law of electrolysis, to find the mass of Cu and Zn, we use Equation 1,
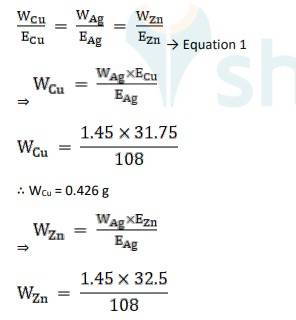
∴ WZn = 0.436 g
To find the time of current flow, using Faraday's first law of electrolysis we get,
M = Z *I *t ⇒ Equation 2
? Z = Equivalent Weight / 96487, Equation 2 becomes,
M = 108 / 96487 X 1.5 X t
t = 1.45 X 96487 / 108X 1.5
t = 864 seconds.
The time of current flow, t = 864 seconds, the mass of Cu is 0.426 g and mass of Zn is 0.436 g
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Quantity of electricity passed = 5 A * (20 * 60 sec)
= 6000 C ⇒ Equation 1
The electrode reaction is written as,
Ni2+ + 2e → Ni
Thus, the quantity of electricity required = 2F
= 2*96487 C
= 192974 C
? 192974 C of electricity deposits 1 mole of Ni, which is 58.7 g ⇒ Equation 2
Thus, equating equations 1 and 2, we get
192974 C of electricity deposits = 58.7 g
6000 C of electricity will deposit = 58.7 X 6000 / 192974
= 1.825g of Ni
The mass of Ni deposited at the cathode is 1.825g of Ni
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) The electrode reaction for 1 mole of H2O is given as,
H2O → H2 + 1/2O2
i.e., O2- →1/2 O2 + 2e -
∴ The quantity of electricity required = 2F
= 2*96487 C
= 192974 C
The quantity of electricity required in coulomb for the oxidation of 1 mol of H2O to O2 is 192974 C
(ii) The electrode reaction for 1 mole of FeO is
FeO + 1/2 O2 → 1/2 Fe2O3
i.e., Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e -
∴ The quantity of electricity required = 1F
= 1*96487 C
= 96487 C
The quantity of electricity required in coulomb for the oxidation of 1 mol of FeO to Fe2O3 is 96487 C
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.14
Glycogen is a polysaccharide-type of carbohydrate. In animals, carbohydrates are stored as glycogen.
But starch is a carbohydrate which consists of two components –amylase (15 -20 %) and amylopectin (80 – 85%). However, glycogen is also like amylopectin but branching will take place after every 5 to 6 glucose unit. Also, glycogen is highly branched.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Ca2+ + 2e- → Ca
⇒ Here, 1 mole of Ca, i.e., 40g of Ca requires = 2 F electricity (F if Faraday)
∴ 20g of Ca requires = 20X2/40
= 1 F of electricity
Electricity in terms of Faraday required to produce 20.0 g of Ca from molten CaCl2 is 1 F of electricity.
(ii) Al3+ + 3e- → Al
⇒ 1 mole of Al, i.e., 27g of Al requires = 3 F electricity (F if Faraday)
∴ 40.0 g of Al will require = 3/27 X 40
= 4.44 F of electricity
Electricity in terms of Faraday required to produce 40.0 g of Al from molten Al2O3 is 4.44 F of electricit
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.13
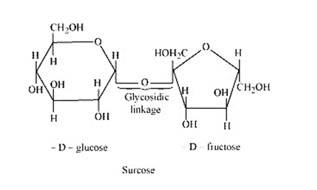
The condensation of the hydroxyl group of two monosaccharides to form a link between them is called glycosidic linkage. In other words, it refers to linkage developed between two different monosaccharide units through an oxygen atom by the loss of a water molecule. For example, in a sucrose molecule, two monosaccharide units, α-glucose and β–fructose, are joined together by a glycosidic linkage.

New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The electrode reaction is given as,
Al3+ (aq) + 3e- → Al (s)
∴ The quantity of charge required for the reduction of 1 mol of Al3+ = 3F
= 3*96487 C
= 289461 C
The electrode reaction is given as,
Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- → Cu (s)
∴ The quantity of charge required for the reduction of 1 mol of Cu2+ = 2F
= 2*96487 C
= 192974 C
The electrode reaction is given as, MnO4→ Mn2+
i.e., Mn7+ + 5e - → Mn2+
∴ The quantity of charge required for the reduction of 1 mol of Mn7+ = 5F
= 5*96487 C
= 482435 C
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.12
i. Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, galactose, and fructose are
Monosaccharides are the simplest units of carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler compounds.
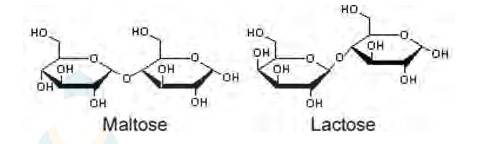
ii. Maltose and lactose are
A disaccharide is a carbohydrate that is formed when two monosaccharides are joined together and a molecule of water is removed from the structure. Lactose is a disaccharide formed from the combination of galactose and glucose.

New question posted
8 months agoTaking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
