Class 12th
Get insights from 11.8k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The lower members of alcohols are completely miscible [highly soluble] with water but the solubility decreases with increase in the molecular weight. The lower members of the alcohol group have the capability to form intermolecular hydrogen bonding with water molecules as alcohols are polar molecules in nature.
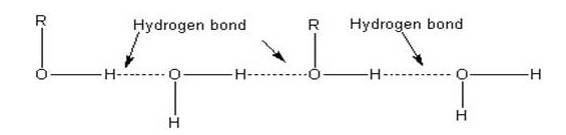
Alkyl groups are hydrophobic [prevents formation of hydrogen bonds with water] in nature. In lower alcohols, the alkyl group is small and the –OH group of alcohol is effective in making hydrogen bonds with water.
But with the increase in the size of alkyl group, the hydrophobic [water hating] nature of alkyl group dominates over
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.2
Basically drugs can be classified in a number of ways. For example classification on basis of their chemical structure, classification on the basis of their action etc.
In the above statement, the classification is based on the pharmacological effect of drugs on the human body.
Antacids refer to those class of drugs which relieve the acidity by either reacting with the excess acid in the stomach [eg – magnesium hydroxide] or by preventing the secretion of an excess of acids by the stomach cells [eg – ranitidine].
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given:
Level of contamination = 15 ppm [by mass]
To find: Mass Percentage and Molality
Formula:
Molality = Number of moles of solute / Mass of solvent in kg
Mass Percentage of Solute = Mass of solute / Mass of solution X 100
Solution:
Calculation of Mass Percentage:
15 ppm means 15 parts of Chloroform in 106 parts of drinking water
⇒ Mass Percentage = Mass of choloroform / Total mass X 100
= 15 / 106 X 100
= 1.5 * 10-3
Calculation of Molality:
⇒ Molecular Mass of Chloroform, CHCl3 = [12] + [1] + [35.5 * 3]
= 119.5 g
⇒ Number of Moles of Chloroform = [15 / 119.5]
= 0.1255 moles
Molality = Number of moles of solute / Mass of solvent in
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given:
Mass of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) = 222.6 g
Mass of water = 200 g
Density, d = 1.072 g/ml
To find: Molality and Molarity of solution
Formula:
Molality = Number of moles of solute/ Mass of solvent in kg
Molarity, Mo = number of moles of solute/ volume of solution in litres
Density, d = Mass (M) / volume (V)
Calculation of Molality:
⇒ Molecular Mass of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) = [12 * 2] + [6 * 1] + [16 * 2]
= 24 + 6 + 32
= 62 g
⇒ Number of moles of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) = [222.6/62]
= 3.59 moles
⇒ Mass of water = 200 g
⇒ Molality = numebr of moles of solute/ Mass of solvent in kg
= 3.59 / 200 X 1000
= 17.95 m
Calculation of Molarity:
⇒ T
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.1
Sleeping pills belong to tranquilizers class of drugs. Sleeping pills induce artificial sleep in people suffering from insomnia by depressing the activities of the central nervous system [brain and spinal cord].
When such drugs are taken for a prolonged time, such drugs can become addictive and the person can become addicted to such drugs and the aftereffects of such drugs are drowsiness, hallucinations, slow heart rate etc. and in extreme cases, the person can enter a state of coma and death can also take place.
Therefore it is highly recommended that sleeping pills should be administered to people suffering from insomnia but
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given:
Molarity of HCl, = 0.1 M
Mass of Mixture = 1g
To find: Volume of HCl to react completely with mixture
Formula:
Molarity, Mo = number of moles of solute/ Volume of solution in litres
Solution:
Calculation of Amount of each component in mixture:
⇒ Let the amount of Na2CO3 be X g
⇒ And Let amount of NaHCO3 be [1-X] g
⇒ Molecular Weight of Na2CO3 = [23 * 2] + [12] + [3 * 16]
= 106 g
⇒ Molecular Weight of NaHCO3 = [23] + [1] + [12] + [3 * 16]
= 84 g
⇒ Number of moles of NaHCO3 = 1-x / 84
⇒ Number of moles of Na2CO3 = x / 106
Now it is given in the question that the mixture is equimolar, so
⇒ Number moles of Na2CO3 = Number of moles
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given:
Concentration of Nitric Acid, HNO3 = 68%
Density of solution, d = 1.504 g/ml
To find: Molarity, Mo
Formula:
Density, d = Mass (M) / volume (V)
Molarity, Mo = Number of moles of solute/ Volume of solution in litres
Solution:
68% of Nitric acid by mass in aqueous solution means that 68g [68 * 100]/100] of Nitric acid present in 100g of solution.
⇒ Molecular mass of Nitric Acid, HNO3 = [1 * 1] + [1 * 14] + [16 * 3]
= 63g
⇒ Number of moles of Nitric Acid = [68/63]
= 1.079 moles
⇒ Given Density, d = 1.504 g/ml
⇒ Volume, v = [100/1.504]
= 66.489 ml
⇒ Molarity, Mo = [1.079/66.489] * 1000
= 16.23 M
Therefore the molarity of the sample is
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
As the name signifies, a solid solution is one in which solvent is solid.So considering this aspect absorption of hydrogen over platinum or palladium is an example of such solution. Platinum or palladium is used as a catalyst in hydrogenation processes.
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more than two substances on molecular level whose composition can vary within certain limits.
The part or component of the mixture present in a lesser amount is called
the SOLUTE and the one present in larger amount is called the SOLVENT. For eg- small amount of salt [solute] dissolved in water [solvent].
There are nine types of solutions formed. They are:
Sr.No. |
State of solute |
State of solvent |
Examples |
1 |
GAS |
GAS |
Air |
2 |
GAS |
LIQUID |
Oxygen in water, carbonated water |
3 |
SOLID |
GAS |
Smoke particles in air, dust particles in air |
4 |
LIQUID |
GAS |
Mist |
5 |
LIQUID |
LIQUID |
Alcohol in water |
6 |
LIQUID |
SOLID |
Mercury in silver |
7 |
GAS |
SOLID |
Adsorption of hydrogen over palladium or platinum |
8 |
SOLID |
LIQUID |
Sugar in water |
9 |
SOLID |
SOLID |
Carbon in Iron(steel), Alloy |
Out of these nine types solution, solid in liquid, liquid in liquid & gas in liquid are very common. When the components of the solution are mixed, the resulting solution may exist in any of the three possible states of matter that is solid, liquid or gaseous. They are: (1) Gaseous solution: In such solutions solvent is Since the solvent is gas,the solute can be solid, liquid or gas. For example, a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen gas is a gaseous solution. (2) Liquid solution: In such type of solutions liquid acts as the solvent. The solute in these solutions may be gas, liquid, or solid. (3) Solid solutions: As the name suggests, in such solutions solid acts as the solvent. The solute in these solutions may be a gas, liquid or solid. For example, a solution of copper in gold is a solid solution. |
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
