Class 12th
Get insights from 11.8k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.5 The lowest tuning frequency = 7.5 MHz = 7.5 Hz
The highest tuning frequency = 12 MHz = 12 Hz
Speed of light, c = 3 m/s
The wavelength for lowest tuning frequency, = = = 40 m
The wavelength for highest tuning frequency, = = = 25 m
The wavelength of the band is 40m to 25 m
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.4 The electromagnetic wave travels in a vacuum along the z- direction. The electric field (E) and the magnetic field (H) are in the x-y plane. They are mutually perpendicular.
Frequency of the wave, = 30 MHz = 30 /s
Speed of light in vacuum, c = 3 m/s
Wavelength of a wave is given as
= = 10 m
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.3 The speed of light (3 m/s) in a vacuum is the same for all wavelengths. It is independent of the wavelength in the vacuum.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.28 (a) Let us consider a Gaussian surface that is lying wholly within a conductor and enclosing the cavity. The electric field intensity E inside the charged conductor is zero.
Let q be the charge inside the conductor and the permittivity of free space.
According to Gauss's law, Flux, = E.ds =
Here, E = 0, hence = 0, so q = 0 (as
Therefore, the charge inside the conductor is zero. The entire charge Q appears on the outer surface of the conductor.
(b) The outer surface of the conductor A has a charge amount Q. Another conductor B, having charge +q is kept inside conductor A and it is insulated from A. Hence, a cha
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.2 Radius of each circular plate, R = 6.0 cm = 0.06 m
Capacitance of parallel capacitor, C = 100 pF = 100 F
Supply voltage, V = 230 V
Angular frequency, = 300 rad/s
rms value of the conduction current, I = , where
Hence, I = V = 230 100 = 6.9 A = 6.9
Yes, the conduction current is equal to the displacement current.
Magnetic field is given as, B = , where
= Free space permeability = 4 N
= Maximum value of current =
r = distance between two plates on the axis = 3.0 cm = 0.03 m
then, B = 6.9 = 1.626&
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.1 Radius of the each circular plate, r = 12 cm = 0.12
Distance between the plates, d = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Charging current, I = 0.15 A
Permittivity of free space, = 8.85
Capacitance between two plates is given by the relation,
C = , where A = Area of each plate = =
C = = 8.007
F
Charge on each plate, q = CV, where V = potential difference across plates
Differentiating both sides w.r.t. t, we get
= C
But = I, therefore
= = 1.87 V/s
1.87 V/s
The displacement current across the plates is the same as the conduction current. Hence the displacement current is 0.15 A
Kirchhoff's first rule is
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.27 Dipole moment of the system, p = q = Cm
Rate of increase of electric field per unit length, = N
Force experienced by the system is given by the relation, F = qE = q
= (q =p = = N
The force is N in the negative z-direction i.e. opposite to the direction of electric field. Hence, the angle between electric field and dipole moment is 180
.
Torque ( ) is given by the relation, = pE = 0
Therefore, the torque experienced by the system is zero.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ans.1.26
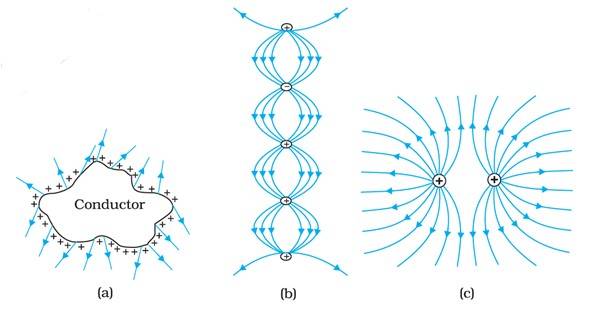
(a) The field lines showed in (a) do not represent electrostatic field lines because field lines must be normal to the surface of the conductor.
(b) The field lines shown in (b) do not represent electrostatic field lines because field lines can not emerge from a negative charge and cannot terminate at a positive charge.
(c) The field lines shown in (c) represent electrostatic field line. This is because the field lines emerge from the positive charge and repel each other.
(d) The field lines shown in (d) do not represent electrostatic field lines because the field lines should not intersect each other.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.25 Excess electrons on an oil drop, n = 12
Electric field intensity, E = 2.55
Density of oil, 1.26 g / = 1.26 g/
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/
Charge of an electron, e = 1.60C
Let the radius of the oil drop be r
Force (F) due to electric field (E) is equal to the weight of the oil drop (W)
F = W
Eq = mg
Ene =
= =
r = 9.815 m = 9.815 mm
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.24 The given conditions are explained in the adjacent diagram
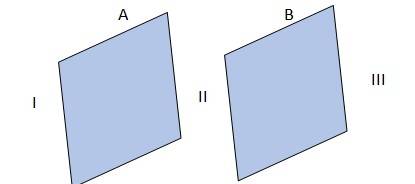
Where A and B represent two large, thin metal plates, parallel and close to each other. The outer surface of A is shown as I, outer surface of B is shown as II and the surface in between A and B is shown as III.
Charge density of plate A, = 17.0 C/
Charge density of plate B, = 17.0
C/
(a) & (b) In the region, I and III, electric field E is zero, because charge is not enclosed by the respective plates.
(c) Electric field, E in the region II is given by
E =
, where
= Permittivity of free space = 8.854
E = N/C = 1.92 N/C
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers