Environmental chemistry
Get insights from 152 questions on Environmental chemistry, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Environmental chemistry
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
Depletion of ozone layer creates some sort of holes in the blanket of ozone which surrounds us, this is known as ozone hole.
The consequences are:
- With the depletion of ozone layer, more UV radiation filters into troposphere. UV radiations lead to ageing of skin, cataract, sunburn, skin cancer, killing of many phytoplanktons, damage to fish productivity etc.
- It has also been reported that plant proteins get easily affected by UV radiations which leads to the harmful mutation of cells.
- It also increases evaporation of surface water through the stomata of the leaves and decreases the moisture content of the soil.
4. Increa
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
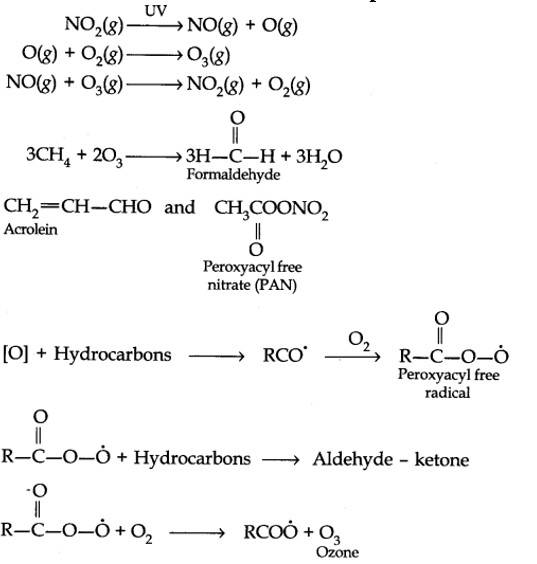
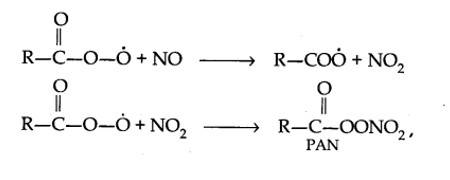
Harmful effects of photochemical smog: Photochemical smog causes serious health problems. Both ozone and PAN (peroxyacetyl nitrate) act as powerful eye irritants. Ozone and nitric oxide irritate the nose and throat and their high concentration causes headache, chest pain, dryness of the throat, cough and difficulty in breathing. Photochemical smog leads to cracking of rubber and extensive damage to plant life. It also causes corrosion of metals, stones, building materials, rubber and painted surfaces.
Control:
- Control of primary precursors of photochemical smog, such as NO2 and hydrocarbons, the secondary precursors such as ozone and PAN
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
The word smog is a combination of smoke and fog. It is a type of air pollution that occurs in many cities throughout the world. Classical smog occurs in a cool, humid climate. It is also called reducing smog. Whereas photochemical smog (photo means light) occurs in warm and dry sunny climates. It has a high concentration of oxidising agents and therefore, it is also called oxidising smog.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is mainly due to the large number of industries and power plants in the nearby areas. Acid rain has vapours of sulphuric acid dissolved in it. When it comes in contact with various statues or monuments, the acid reacts chemically with marble (calcium carbonate).
CaCO3 + H2SO4 à CaSO4 + H2O + CO2
As a result, the monument is being slowly disfigured, and the marble is getting discoloured and lustreless.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
CO2 is mainly responsible for the greenhouse effect. Other greenhouse gases are methane, nitrous oxide, water vapours, CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) and Ozone.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
Carbon monoxide binds to haemoglobin to form carboxyhaemoglobin, which is about 300 times more stable than the oxygen-haemoglobin complex. In blood, when the concentration of carboxyhaemoglobin reaches about 3–4 per cent, the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood is greatly reduced. This oxygen deficiency results into headache, weak eyesight, nervousness and cardiovascular disorder. This is the reason why people are advised not to smoke. In pregnant women who have the habit of smoking the increased CO level in blood may induce premature birth, spontaneous abortions and deformed babies. On the other hand, CO2 does not combine with ha
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
Tropospheric pollution occurs due to the presence of undesirable solid or gaseous particles in the air. The following are the major gaseous and particulate pollutants present in the troposphere:
1. Gaseous air pollutants: These are oxides of sulphur, nitrogen and carbon, hydrogen sulphide, hydrocarbons, ozone and other oxidants.
2. Particulate pollutants: These are dust, mist, fumes, smoke, smog etc.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
Environmental chemistry is a branch of environmental studies. Environmental studies deal with the sum of all social, economical, biological, physical and chemical interrelations with our surroundings. Environmental chemistry deals with the study of the origin, transport, reactions, effects and fates of chemical species in the environment
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers