Gravitation
Get insights from 91 questions on Gravitation, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Gravitation
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c
Explanation- a geostationary satellite is having same sense of rotation as that of earth i.e west east direction.
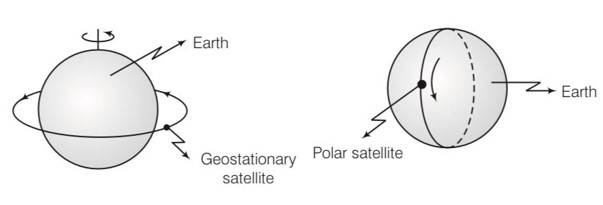
A polar satellite goes around earth's pole in north south direction.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a,c,d
Explanation- F1=-F2=- n
r12=r1-r2
acceleration due to gravity ,g = F/mass=
as g is constant hence constant of proportionality will not be constant in kepler's third law.
Hence kepler's law will not be valid.
For negative n, g=
=
Mo>m1 or m2 so objects lighter than water will sink
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-c, d
Explanation- Gravitation force F= where M is mass of sun and m is mass of earth.
When G decrease force will also decrease so according to this it will not in the fixed circular orbits around the sun. as when radius increases the force will decreases and soon earth leave the solar system.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c, d
Explanation-due to the huge amount of charges on the sun and the earth electrostatics force of attraction will be large. Gravitational force is also attractive in nature have both forces will be added and obeys kepler's law also.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c, d
Explanation- G'=10G
Consider the diagram
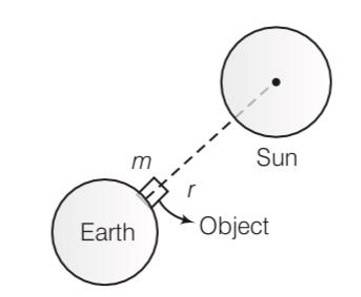
Force on the objects due to the earth =
= (10g)m= 10mg
Force on the objects due to the sun F=
As r>>R so F will be very small
So effect of sun will be neglected
Now g'=10g
Hence weight of person =10mg
So gravity pull on the person will increase, due to it walking on ground would be more difficult
Critical velocity Vc is proportional to g
So Vc
V'>g
Vc'>Vc hence rain will fall faster. To overcome the increased gravitational force of the earth the aeroplane will have to travel much faster.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c
Explanation- as we know F=
V= orbital speed=
Time period of revolution of planet T = =
T2 ……….1
Hence orbit will be elliptical.
F= =g'm
It is clear from equation 1 that its path is parabola.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-a, c, d
Explanation- acceleration due to gravity at altitude g'=
At depth d, g'=g (1-d/R)
In both cases value of g decreases
But in case of latitude the value of g increases when we increase
also we conclude from the formula that it is independent upon mass.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-c
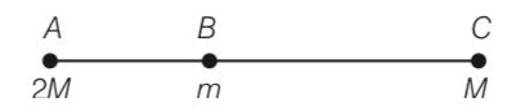
Explanation- force on B due to A = FBA=
force on B due to C = FBC=
BC = 2AB
FBC=
So it move towards BA
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-d
Explanation- gravitational mass of proton is equivalent to its inertial mass and independent of presence neighbouring heavy objects.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-d
Explanation- asteroids are also being acted upon by central gravitational forces, hence they are moving in circular orbits like planets and obey Kepler's law.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers